Abstract
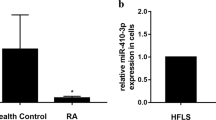
Our previous studies have identified miR-483-3p to be highly expressed in synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arhtirits (RA); however, its effects on inflammation of RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) have remained unclear. The expression of miR-483-3p and cytokines in RA FLSs was detected using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent was conducted to determine interleukin (IL)-33 production from RA FLSs. Western blotting was employed to quantify the levels of p-ERK and total ERK. Overexpressed miR-483-3p significantly increased the mRNA and protein expression of IL-33, but not of IL-27 or IL-34, in RA FLSs, whereas miR-483-3p suppression showed the opposite effects. Furthermore, miR-483-3p upregulation activated the ERK signaling pathway. The ERK signaling inhibitor PD98059 partly reversed the elevation of IL-33 levels mediated by miR-483-3p overexpression. Our results reveal that miR-483-3p promotes IL-33 expression by regulating the ERK signaling pathway in RA FLSs. Thus, miR-483-3p may be a potential effective target for RA treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sparks, J.A. 2019. Rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of Internal Medicine 170 (1): ITC1–ITC16. https://doi.org/10.7326/AITC201901010.
Smolen, J.S., D. Aletaha, and I.B. McInnes. 2016. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 388 (10055): 2023–2038. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30173-8.
Safiri, S., A.A. Kolahi, D. Hoy, E. Smith, D. Bettampadi, M.A. Mansournia, A. Almasi-Hashiani, A. Ashrafi-Asgarabad, M. Moradi-Lakeh, M. Qorbani, G. Collins, A.D. Woolf, L. March, and M. Cross. 2019. Global, regional and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis 1990-2017: a systematic analysis of the global burden of disease study 2017. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 78 (11): 1463–1471. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215920.
Goll, G.L., and T.K. Kvien. 2020. What next after biologic therapy fails in rheumatoid arthritis? The New England Journal of Medicine 383 (16): 1588–1589. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMe2026142.
Garcia-Carbonell, R., A.S. Divakaruni, A. Lodi, I. Vicente-Suarez, A. Saha, H. Cheroutre, G.R. Boss, S. Tiziani, A.N. Murphy, and M. Guma. 2016. Critical role of glucose metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis & Rhematology 68 (7): 1614–1626. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39608.
Bottini, N., and G.S. Firestein. 2013. Duality of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: passive responders and imprinted aggressors. Nature Reviews Rheumatology 9 (1): 24–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2012.190.
Chu, C.Q. 2020. Fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. The New England Journal of Medicine 383 (17): 1679–1681. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcibr2024718.
Xiao, C., and K. Rajewsky. 2009. MicroRNA control in the immune system: basic principles. Cell 136 (1): 26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.12.027.
Chen, J., M. Liu, X. Luo, L. Peng, Z. Zhao, C. He, and Y. He. 2020. Exosomal miRNA-486-5p derived from rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes induces osteoblast differentiation through the Tob1/BMP/Smad pathway. Biomaterials Science 8 (12): 3430–3442. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9bm01761e.
Najm, A., F.M. Masson, P. Preuss, S. Georges, B. Ory, T. Quillard, S. Sood, C.S. Goodyear, D.J. Veale, U. Fearon, B. le Goff, and F. Blanchard. 2020. MicroRNA-17-5p reduces inflammation and bone erosions in mice with collagen-induced arthritis and directly targets the JAK/STAT pathway in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis & Rhematology 72 (12): 2030–2039. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.41441.
Wang, Y., L. Hou, X. Yuan, N. Xu, S. Zhao, L. Yang, and N. Zhang. 2020. miR-483-3p promotes cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting IGF-1. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 130: 110519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110519.
Wang, Y., N. Xu, S. Zhao, T. Jiao, W. Fu, L. Yang, and N. Zhang. 2019. miR-410-3p Suppresses cytokine release from fibroblast-like synoviocytes by regulating nf-kappab signaling in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation 42 (1): 331–341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0896-2.
Lim, H.J., S.G. Bak, H.J. Lim, S.W. Lee, S. Lee, S.K. Ku, S.I. Park, S.J. Lee, and M.C. Rho. 2020. Acyclic triterpenoid isolated from Alpinia katsumadai alleviates formalin-induced chronic mouse paw inflammation by inhibiting the phosphorylation of ERK and NF-kappaB. Molecules 25 (15). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25153345.
Buch, M.H., S. Eyre, and D. McGonagle. 2021. Persistent inflammatory and non-inflammatory mechanisms in refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Reviews Rheumatology 17 (1): 17–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-020-00541-7.
Takeuchi, Y., K. Hirota, and S. Sakaguchi. 2019. Synovial tissue inflammation mediated by autoimmune t cells. Frontiers in Immunology 10: 1989. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01989.
Tsai, M.H., M.C. Chi, J.F. Hsu, I.T. Lee, K.M. Lin, M.L. Fang, M.H. Lee, C.W. Lee, and J.F. Liu. 2020. Urban particulate matter enhances ROS/IL-6/COX-II production by inhibiting microrna-137 in synovial fibroblast of rheumatoid arthritis. Cells 9 (6). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061378.
Yang, S., S. Jiang, Y. Wang, S. Tu, Z. Wang, and Z. Chen. 2016. Interleukin 34 upregulation contributes to the increment of microRNA 21 expression through stat3 activation associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of Rheumatology 43 (7): 1312–1319. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.151253.
Figueiredo Neto, M., and M.L. Figueiredo. 2017. Combination of interleukin-27 and microRNA for enhancing expression of anti-inflammatory and proosteogenic genes. Arthritis 2017: 6365857–6365813. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6365857.
Riviere, E., J. Sellam, J. Pascaud, P. Ravaud, J.E. Gottenberg, and X. Mariette. 2018. Serum IL-33 level is associated with auto-antibodies but not with clinical response to biologic agents in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy 20 (1): 122. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1628-6.
Talabot-Ayer, D., T. McKee, P. Gindre, S. Bas, D.L. Baeten, C. Gabay, and G. Palmer. 2012. Distinct serum and synovial fluid interleukin (IL)-33 levels in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and osteoarthritis. Joint, Bone, Spine 79 (1): 32–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.02.011.
Kunisch, E., S. Chakilam, M. Gandesiri, and R.W. Kinne. 2012. IL-33 regulates TNF-alpha dependent effects in synovial fibroblasts. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 29 (4): 530–540. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2012.883.
Murdaca, G., M. Greco, A. Tonacci, S. Negrini, M. Borro, F. Puppo, and S. Gangemi. 2019. IL-33/IL-31 Axis in immune-mediated and allergic diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20 (23). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235856.
Sellam, J., E. Riviere, A. Courties, P.O. Rouzaire, B. Tolusso, E.M. Vital, P. Emery, et al. 2016. Serum IL-33, a new marker predicting response to rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy 18 (1): 294. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-016-1190-z.
Wu, S., Y. Jiang, Y. Teng, X. Liu, L. Zhou, and W. Li. 2020. Interleukin-33 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology
Lv, Y.P., Y.S. Teng, F.Y. Mao, L.S. Peng, J.Y. Zhang, P. Cheng, Y.G. Liu, H. Kong, T.T. Wang, X.L. Wu, C.J. Hao, W. Chen, S.M. Yang, Y.L. Zhao, B. Han, Q. Ma, Q.M. Zou, and Y. Zhuang. 2018. Helicobacter pylori-induced IL-33 modulates mast cell responses, benefits bacterial growth, and contributes to gastritis. Cell Death & Disease 9 (5): 457. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0493-1.
Liu, F., X.X. Feng, S.L. Zhu, H.Y. Huang, Y.D. Chen, Y.F. Pan, R.R. June, S.G. Zheng, and J.L. Huang. 2018. Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway mediates proliferation and migration of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. Frontiers in Immunology 9: 2847. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02847.
Huang, C.C., C.H. Chiou, S.C. Liu, S.L. Hu, C.M. Su, C.H. Tsai, and C.H. Tang. 2019. Melatonin attenuates TNF-alpha and IL-1beta expression in synovial fibroblasts and diminishes cartilage degradation: implications for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Pineal Research 66 (3): e12560. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12560.
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Faculty Post-doctoral Research Startup Fund of China Medical University (No.M0470 to Yuejiao Wang) and the 345 Talent Project of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University (No.M0686 to Yuejiao Wang).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YW: conception and design of the research; KZ: acquisition of data and drafting the manuscript; KZ, TJ, and SZ: analysis and interpretation of data; DW: statistical analysis; WF and YW: revision of manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors contributed to data analysis, drafting and revising the article, gave final approval of the version to be published, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
This study was performed according to the recommendations of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University (2019PS637K).
Consent for Publication
Not Applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, K., Fu, W., Zhao, S. et al. miR-483-3p Promotes IL-33 Production from Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes by Regulating ERK Signaling in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflammation 44, 2302–2308 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01503-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01503-1