Abstract
It is controversial whether there is a different risk of recurrence between two histological subtypes in craniopharyngioma (CP) patients. Some reported that adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma (ACP) had a higher risk of recurrence than papillary craniopharyngioma (PCP), but others reported that there is no significant difference between them. So, we conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis to determine the association between the histological subtype of CP and the rate of recurrence. A comprehensive literature search was undertaken in PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science for all English articles published up to November 2020. Recurrence data stratified by ACP and PCP were extracted from studies meeting inclusion criteria. A pooled analysis of the association between the histological subtype of craniopharyngioma and rates of recurrence was performed. Thirteen articles containing 974 patients were included. When stratified by two pathological subtypes, the total recurrence rate of ACP was 26.0% and PCP was 14.1%, which showed ACP associated with a higher risk of tumor recurrence than PCP (odds ratio [OR] = 2.12, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.36, 3.30, P = 0.00). This is the first meta-analysis focusing on histological subtypes of CP. PCP associates with a lower risk of recurrence than ACP, indicating that ACP could act as one of recurrence risk factors for CP patients. Nevertheless, large sample size and well-designed multicenter studies in which the other clinical variables are controlled to determine the histological subtype of CP as an independent recurrence risk factor are needed.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the submitted article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Adamson TE, Wiestler OD, Kleihues P, Yaşargil MG (1990) Correlation of clinical and pathological features in surgically treated craniopharyngiomas. J Neurosurg 73:12–17. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1990.73.1.0012
Bal E, Oge K, Berker M (2016) Endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal surgery, a reliable method for treating primary and recurrent/residual craniopharyngiomas: nine years of experience. World Neurosurg 94:375–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.07.004
Balshem H, Helfand M, Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Vist GE, Falck-Ytter Y, Meerpohl J, Norris S, Guyatt GH (2011) GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol 64:401–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.07.015
Barbosa AP, Varela A, Carvalho D, Cerejo A, Pereira J, Castro L, Vinha E, Monteiro M, Cruz J, Vaz R, Medina JL (2002) Craniopharyngiomas. Clinicopathological aspects in different age groups (Craniofaringeomas. Aspectos clinicopatologicos em diferentes grupos etairios.). Acta Med Port 15:123–129
Bishokarma S, Shrestha S, Ranabhat K, Koirala S, Shrestha D, Panth R, Gongal ND (2018) Outcome of surgical resection of craniopharyngioma: single center 12 years’ experience. Kathmandu Univ Med J 16:328–332
Bunin GR, Surawicz TS, Witman PA, Preston-Martin S, Davis F, Bruner JM (1998) The descriptive epidemiology of craniopharyngioma. J Neurosurg 89:547–551. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1998.89.4.0547
Burghaus S, Hölsken A, Buchfelder M, Fahlbusch R, Riederer BM, Hans V, Blümcke I, Buslei R (2010) A tumor-specific cellular environment at the brain invasion border of adamantinomatous craniopharyngiomas. Virchows Arch 456:287–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-009-0873-0
Capatina C, Vintila M, Gherlan I, Dumitraşcu A, Caragheorgheopol A, Procopiuc C, Ciubotaru V, Poiana C (2018) Craniopharyngioma - clinical and therapeutic outcome data in a mixed cohort of adult and paediatric cases. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar) 14:549–555. https://doi.org/10.4183/aeb.2018.549
Cavallo L, Frank G, Cappabianca P, Solari D, Mazzatenta D, Villa A, Zoli M, D’Enza A, Esposito F, Pasquini E (2014) The endoscopic endonasal approach for the management of craniopharyngiomas: a series of 103 patients. J Neurosurg 121:100–113. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.3.Jns131521
Cheng J, Shao Q, Pan Z, You J (2016) Analysis and long-term follow-up of the surgical treatment of children with craniopharyngioma. J Craniofac Surg 27(8):e763–e766
Clark AJ, Cage TA, Aranda D, Parsa AT, Sun PP, Auguste KI, Gupta N (2013) A systematic review of the results of surgery and radiotherapy on tumor control for pediatric craniopharyngioma. Childs Nerv Syst 29:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1926-2
Coury J, Davis B, Koumas C, Manzano G, Dehdashti A (2020) Histopathological and molecular predictors of growth patterns and recurrence in craniopharyngiomas: a systematic review. Neurosurg Rev 43:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-018-0978-5
Crotty TB, Scheithauer BW, Young WF Jr, Davis DH, Shaw EG, Miller GM, Burger PC (1995) Papillary craniopharyngioma: a clinicopathological study of 48 cases. J Neurosurg 83:206–214. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1995.83.2.0206
Dandurand C, Sepehry AA, Asadi Lari MH, Akagami R, Gooderham P (2018) Adult craniopharyngioma: case series, systematic review, and meta-analysis. Neurosurgery 83:631–641. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyx570
de Divitiis E, Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Esposito F, de Divitiis O, Messina A (2007) Extended endoscopic transsphenoidal approach for extrasellar craniopharyngiomas. Neurosurgery 61(5 Suppl 2):219–227. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000303220.55393.73 (discussion 228)
Dho Y, Kim Y, Se Y, Han D, Kim J, Park C, Wang K, Kim D (2018) Endoscopic endonasal approach for craniopharyngioma: the importance of the relationship between pituitary stalk and tumor. J Neurosurg 129:611–619. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.4.Jns162143
Duff J, Meyer FB, Ilstrup DM, Laws ER Jr, Schleck CD, Scheithauer BW (2000) Long-term outcomes for surgically resected craniopharyngiomas. Neurosurgery 46(2):291–302. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200002000-00007 (discussion 302-295)
Duff JM, Meyer FB, Ilstrup DM, Laws ER, Schleck CD, Scheithauer BW (2000) Long-term outcomes for surgically resected craniopharyngiomas. Neurosurgery 46:291–302. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200002000-00007
Duo D, Gasverde S, Benech F, Zenga F, Giordana MT (2003) MIB-1 immunoreactivity in craniopharyngiomas: a clinico-pathological analysis. Clin Neuropathol 22:229–234
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
El Beltagy MA, Attia M, Refaat A, Taha H, Awad M, Zaghloul MS, Abdelaziz AM (2017) Different strategies in management of childhood craniopharyngiomas-experience of 114 case. Childs Nerv Syst 33:1836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3557-0
Eldevik OP, Blaivas M, Gabrielsen TO, Hald JK, Chandler WF (1996) Craniopharyngioma: radiologic and histologic findings and recurrence. Am J Neuroradiol 17:1427–1439
Eldevik OP, Blaivas M, Gabrielsen TO, Hald JK, Chandler WF (1996) Craniopharyngioma: radiologic and histologic findings and recurrence. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17:1427–1439
Fahlbusch R, Honegger J, Paulus W, Huk W, Buchfelder M (1999) Surgical treatment of craniopharyngiomas: experience with 168 patients. J Neurosurg 90:237–250. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1999.90.2.0237
Feng Y, Ni M, Wang Y-G, Zhong L-Y (2019) Comparison of neuroendocrine dysfunction in patients with adamantinomatous and papillary craniopharyngiomas. Exp Ther Med 17:51–56. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.6953
Fischer EG, Welch K, Shillito J Jr, Winston KR, Tarbell NJ (1990) Craniopharyngiomas in children. Long-term effects of conservative surgical procedures combined with radiation therapy. J Neurosurg 73:534–540. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1990.73.4.0534
JA Forbes, EG Ordóñez-Rubiano, HC Tomasiewicz, MA Banu, I Younus, GA Dobri, CD Phillips, A Kacker, B Cisse, VK Anand, TH Schwartz 2018 Endonasal endoscopic transsphenoidal resection of intrinsic third ventricular craniopharyngioma: surgical results. J Neurosurg:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.5.Jns18198
Gardner P, Kassam A, Snyderman C, Carrau R, Mintz A, Grahovac S, Stefko S (2008) Outcomes following endoscopic, expanded endonasal resection of suprasellar craniopharyngiomas: a case series. J Neurosurg 109:6–16. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns/2008/109/7/0006
Garnett MR, Puget S, Grill J, Sainte-Rose C (2007) Craniopharyngioma. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1750-1172-2-18
Guadagno E, de Divitiis O, Solari D, Borrelli G, Bracale UM, Di Somma A, Cappabianca P, Caro DBD, M, (2017) Can recurrences be predicted in craniopharyngiomas? β-Catenin coexisting with stem cells markers and p-ATM in a clinicopathologic study of 45cases. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36:95. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0562-9
Gupta DK, Gupta A, Mahapatra AK, Sharma BS, Vaishya S, Sarkar C, Suri V, Suri A, Kale SS, Singh M (2012) A single centre study of 860 cases of craniopharyngiomas over 5 decades: radical or conservative surgical management. Childs Nerv Syst 28:1609. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1849-y
Gupta DK, Ojha BK, Sarkar C, Mahapatra AK, Mehta VS (2006) Recurrence in craniopharyngiomas: analysis of clinical and histological features. J Clin Neurosci 13:438–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2005.05.013
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses Bmj 327:557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Iglesias P, Nocete I, Moure Rodríguez MD, Venegas-Moreno E, Ares J, Biagetti B, Rodríguez Berrocal V, Guerrero-Pérez F, Vicente A, Villar-Taibo R, Cordido F, Paja M, Glerean M, González Rivera N, Dios Fuentes E, Blanco C, Alvaréz-Escolá C, Martín T, Webb SM, Bernabéu I, Villabona C, Soto-Moreno A, Gaztambide S, Díez JJ (2020) Craniopharyngioma in the elderly: a multicenter and nation-wide study in Spain. Neuroendocrinology. https://doi.org/10.1159/000512161
Iuzzolino P (2001) Craniopharyngioma - histopathology. Rivista. Medica 7:11–13
Jamshidi AO, Beer-Furlan A, Prevedello DM, Sahyouni R, Elzoghby MA, Safain MG, Carrau RL, Jane JA, Laws ER (2018) A modern series of subdiaphragmatic craniopharyngiomas. J Neurosurg 131:526–531. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.4.Jns172330
Jane JA Jr, Laws ER (2006) Craniopharyngioma Pituitary 9:323–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-006-0413-8
Karavitaki N, Brufani C, Warner JT, Adams CB, Richards P, Ansorge O, Shine B, Turner HE, Wass JA (2005) Craniopharyngiomas in children and adults: systematic analysis of 121 cases with long-term follow-up. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 62:397–409. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2005.02231.x
Karavitaki N, Cudlip S, Adams CB, Wass JA (2006) Craniopharyngiomas. Endocr Rev 27:371–397. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2006-0002
Li Z, Xu J, Huang S, You C (2015) Aberrant membranous expression of β-catenin predicts poor prognosis in patients with craniopharyngioma. Ann Diagn Pathol 19:403–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2015.10.002
Lilia Tena-Suck M, Moreno-Reyes I, Rembao D, Vega R, Moreno-Jimenez S, de Jesus C-L, Fernandez-Plata R, Martinez-Briseno D, Salinas-Lara C (2009) Clinical pathological study of craniopharyngioma. Fifteen years at the National Institute of Neurology and Neurosurgery “Manuel Velasco Suarez.” Gac Med Mex 145:361–368
Liu J, Sevak I, Carmel P, Eloy J (2016) Microscopic versus endoscopic approaches for craniopharyngiomas: choosing the optimal surgical corridor for maximizing extent of resection and complication avoidance using a personalized, tailored approach. Neurosurg Focus 41:E5. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.9.Focus16284
Lopes MBS (2012) Craniopharyngioma and other cystic lesions of the sellar region: histopathological distinctions and clinical outcomes. Endocr Pathol 23:68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-011-9187-2
Lopez-Serna R, Gómez-Amador JL, Barges-Coll J, Nathal-Vera E, Revuelta-Gutiérrez R, Alonso-Vanegas M, Ramos-Peek M, Portocarrero-Ortiz L (2012) Treatment of craniopharyngioma in adults: systematic analysis of a 25-year experience. Arch Med Res 43:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2012.06.009
A Lukas, H Benjamin, AH Robert, E-K Marwan, M Luigi, R Andreas, SW Rolf, C Emanuel 2018 A ten-year follow-up study of treatment outcome of craniopharyngiomas. Swiss Med Wkly 148. https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2017.14521
Mahapatra AK, Gupta DK, Gupta A, Sarkar C, Suri A, Suri V, Kale S, Sharma BS (2013) Recurrence factors in craniopharyngiomas: study of clinicomorphologic and histopathologic factors. Childs Nerv Syst 29:1737. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2261-y
Maira G, Anile C, Rossi GF, Colosimo C (1995) Surgical treatment of craniopharyngiomas: an evaluation of the transsphenoidal and pterional approaches. Neurosurgery 36:715–724. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-199504000-00012
Miller DC (1994) Pathology of craniopharyngiomas: clinical import of pathological findings. Pediatr Neurosurg 21(Suppl 1):11–17. https://doi.org/10.1159/000120855
Minamida Y, Mikami T, Hashi K, Houkin K (2005) Surgical management of the recurrence and regrowth of craniopharyngiomas. J Neurosurg 103:224–232. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2005.103.2.0224
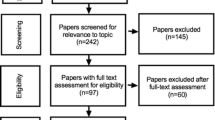
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151(264–269):w264. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
Mortini P, Losa M, Pozzobon G, Barzaghi R, Riva M, Acerno S, Angius D, Weber G, Chiumello G, Giovanelli M (2011) Neurosurgical treatment of craniopharyngioma in adults and children: early and long-term results in a large case series. J Neurosurg 114:1350–1359. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.11.Jns10670
Muller HL, Merchant TE, Warmuth-Metz M, Martinez-Barbera JP, Puget S (2019) Craniopharyngioma Nat Rev Dis Primers 5:75. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0125-9
Nielsen EH, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Poulsgaard L, Kristensen LO, Astrup J, Jørgensen JO, Bjerre P, Andersen M, Andersen C, Jørgensen J, Lindholm J, Laurberg P (2011) Incidence of craniopharyngioma in Denmark (n = 189) and estimated world incidence of craniopharyngioma in children and adults. J Neurooncol 104:755–763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0540-6
Nishioka H, Nagata Y, Fukuhara N, Yamaguchi-Okada M, Yamada S (2018) Endoscopic endonasal surgery for subdiaphragmatic type craniopharyngiomas. Neurol Med Chir 58:260–265. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.oa.2018-0028
J Pan, S-T Qi, Y-J Deng, Y-Q Ding, L Peng, X-Q Li 2002 Expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen in craniopharyngioma and tumor recurrence. Di 1 jun yi da xue xue bao = Academic journal of the first medical college of PLA 22:363–365
Pan J, Qi S, Liu Y, Lu Y, Peng J, Zhang X, Xu Y, Huang G-l, Fan J (2016) Growth patterns of craniopharyngiomas: clinical analysis of 226 patients. J Pediatr Neurosurg 17:418–433. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.7.Peds14449
Park H, Dho Y, Kim J, Kim J, Park C, Kim Y (2020) Recurrence rate and prognostic factors for the adult craniopharyngiomas in long-term follow-up. World Neurosurg 133:e211–e217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.08.209
Park HJ, Dho YS, Kim JH, Kim JW, Park CK, Kim YH (2020) Recurrence rate and prognostic factors for the adult craniopharyngiomas in long-term follow-up. World Neurosurg 133:e211–e217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.08.209
Paulus W, Honegger J, Keyvani K, Fahlbusch R (1999) Xanthogranuloma of the sellar region: a clinicopathological entity different from adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma. Acta Neuropathol 97:377–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004010051001
Paulus W, Stöckel C, Krauss J, Sörensen N, Roggendorf W (1997) Odontogenic classification of craniopharyngiomas: a clinicopathological study of 54 cases. Histopathology 30:172–176. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2559.1997.d01-584.x
Pekmezci M, Louie J, Gupta N, Bloomer MM, Tihan T (2010) Clinicopathological characteristics of adamantinomatous and papillary craniopharyngiomas: University of California, San Francisco experience 1985–2005. Neurosurgery 67:1341–1349. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e3181f2b583
Petito CK, DeGirolami U, Earle KM (1976) Craniopharyngiomas: a clinical and pathological review. Cancer 37:1944–1952. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(197604)37:4
Polom K, Marano L, Marrelli D, De Luca R, Roviello G, Savelli V, Tan P, Roviello F (2018) Meta-analysis of microsatellite instability in relation to clinicopathological characteristics and overall survival in gastric cancer. Br J Surg 105:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.10663
Prieto R, Pascual J (2018) Can tissue biomarkers reliably predict the biological behavior of craniopharyngiomas? A comprehensive overview. Pituitary 21:431–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-018-0890-6
Prieto R, Pascual JM, Rosdolsky M, Castro-Dufourny I, Carrasco R, Strauss S, Barrios L (2016) Craniopharyngioma adherence: a comprehensive topographical categorization and outcome-related risk stratification model based on the methodical examination of 500 tumors. Neurosurg Focus 41:E13. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.9.Focus16304
Prieto R, Pascual JM, Subhi-Issa I, Jorquera M, Yus M, Martinez R (2013) Predictive factors for craniopharyngioma recurrence: a systematic review and illustrative case report of a rapid recurrence. World Neurosurg 79:733–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2012.07.033
Qi S, Huang G, Pan J, Li J, Zhang X, Fang L, Liu B, Meng W, Zhang Y, Liu X (2010) Involvement of osteopontin as a core protein in craniopharyngioma calcification formation. J Neurooncol 98:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0053-8
Richardson WS, Wilson MC, Nishikawa J, Hayward RS (1995) The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP J Club 123:A12-13
Stang A (2010) Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol 25:603–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
Szeifert GT, Sipos L, Horvath M, Sarker MH, Major O, Salomvary B, Czirjak S, Balint K, Slowik F, Kolonics L, Pasztor E (1993) Pathological characteristics of surgically removed craniopharyngiomas: analysis of 131 cases. Acta Neurochir 124:139–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01401137
Tang B, Xiao L, Xie S, Huang G, Wang Z, Zhou D, Zeng E, Hong T (2018) Extended endoscopic endonasal approach for recurrent or residual symptomatic craniopharyngiomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 168:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2018.02.002
Tang B, Xie S, Huang G, Wang Z, Yang L, Yang X, Xu S, Zeng E, Hong T (2020) Clinical features and operative technique of transinfundibular craniopharyngioma. J Neurosurg 133:119–128. https://doi.org/10.3171/2019.3.JNS181953
Tang B, Xie S, Xiao L, Huang G, Wang Z, Yang L, Yang X, Xu S, Chen Y, Ji Y, Zeng E, Hong T (2018) A novel endoscopic classification for craniopharyngioma based on its origin. Sci Rep 8:10215. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28282-4
Tavangar SM, Larijani B, Mahta A, Hosseini SM, Mehrazine M, Bandarian F (2004) Craniopharyngioma: a clinicopathological study of 141 cases. Endocr Pathol 15:339–344. https://doi.org/10.1385/ep:15:4:339
Tena-Suck ML, Salinas-Lara C, Arce-Arellano RI, Rembao-Bojórquez D, Morales-Espinosa D, Sotelo J, Arrieta O (2006) Clinico-pathological and immunohistochemical characteristics associated to recurrence/regrowth of craniopharyngiomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 108:661–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2006.01.007
Torres LFB, Reis JS, Netto MRM, Delle LAB, Sluminsky BG, Faoro LN, Antoniuk A, Ramina R (1999) Craniopharyngiomas: clinical, epidemiological and pathological findings of 25 cases. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 57:255–260. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0004-282x1999000200014
Van Effenterre R, Boch AL (2002) Craniopharyngioma in adults and children: a study of 122 surgical cases. J Neurosurg 97:3–11. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2002.97.1.0003
Weiner HL, Wisoff JH, Rosenberg ME, Kupersmith MJ, Cohen H, Zagzag D, Shiminski-Maher T, Flamm ES, Epstein FJ, Miller DC, Sweet WH, Laws ER Jr, Cirie IS (1994) Craniopharyngiomas: a clinicopathological analysis of factors predictive of recurrence and functional outcome. Neurosurgery 35:1001–1011
Xu J, You C, Zhou L, Li Q, Zhou P, Chen N (2010) The cell-cycle kinetics of craniopharyngioma and its clinical significance. J Neurooncol 98:71–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0047-6
Xu J, Zhang S, You C, Wang X, Zhou Q (2006) Microvascular density and vascular endothelial growth factor have little correlation with prognosis of craniopharyngioma. Surg Neurol 66:30–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2006.05.047
Yalçin N, Akbulut M, Çagli S, Bir F, Demirtaş E (2009) Prognostic significance of the Ki-67 labeling index and p53 protein expression for patient with craniopharyngioma. J Neurol Sci 26:286–291
Yamada S, Fukuhara N, Oyama K, Takeshita A, Takeuchi Y, Ito J, Inoshita N (2010) Surgical outcome in 90 patients with craniopharyngioma: an evaluation of transsphenoidal surgery. World Neurosurg 74:320–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2010.06.014
Yang I, Sughrue ME, Rutkowski MJ, Kaur R, Ivan ME, Aranda D, Barani IJ, Parsa AT (2010) Craniopharyngioma: a comparison of tumor control with various treatment strategies. Neurosurg Focus 28:E5. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.1.Focus09307
Yang L, Xie S, Fang C, Zeng E, Tang B, Hong T (2019) Preservation of hypothalamic function with endoscopic endonasal resection of hypothalamus-invaded craniopharyngiomas. World Neurosurg 132:e841–e851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.07.225
Zacharia BE, Bruce SS, Goldstein H, Malone HR, Neugut AI, Bruce JN (2012) Incidence, treatment and survival of patients with craniopharyngioma in the surveillance, epidemiology and end results program. Neuro Oncol 14:1070–1078. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nos142
Zdravkovski P, Ilievski B, Janevska V, Jovanovik R, Cvetkovski P, Mirchevski V, Rendevski V, Aliji V, Zdravkovska M, Petrusevska G (2018) Craniopharyngiomas: 20-year-period evaluation study. Virchows Arch 473:s27–s28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-018-2422-1
Zhang YQ, Ma ZY, Wu ZB, Luo SQ, Wang ZC (2008) Radical resection of 202 pediatric craniopharyngiomas with special reference to the surgical approaches and hypothalamic protection. Pediatr Neurosurg 44:435–443. https://doi.org/10.1159/000172965
Zoicas F, Schofl C (2012) Craniopharyngioma in adults Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 3:46. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2012.00046
Zuccaro G (2005) Radical resection of craniopharyngioma. Childs Nerv Syst 21:679–690. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-005-1201-x
Zucchini S, Fantini J, Mazzatenta D, Pozzobon G, Partenope C, Pedicelli S, Ubertini G, Parpagnoli M, Genitori L, Menardi R, Driul D, Matarazzo P, Tuli G, Guzzetti C, Iughetti L, Aversa T, Di Mase R, Rutigliano I, Iezzi ML, Cherubini V, Grandone A, Cassio A (2019) Management and treatment outcome of childhoodonset craniopharyngioma (CP) in Italy: multicentre collection of 117 cases. Horm Res Paediatr 91:329. https://doi.org/10.1159/000501868
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, through grant 82060246.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: Tao Hong.
Collection and assembly of data: Han Ding, Le Yang, You Yuan Bao, Lin Zhou, and Chen Xing Yang.
Data analysis and interpretation: Jie Wu, Xiao Wu, and You Qing Yang.
Manuscript writing: Jie Wu.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Due to the nature of the present study (literature review), no ethical approval was needed.
Consent to participate
Due to the nature of the present study (literature review), no consent to participate was needed.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Wu, X., Yang, Y.Q. et al. Association of histological subtype with risk of recurrence in craniopharyngioma patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev 45, 139–150 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01563-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-021-01563-9