Abstract
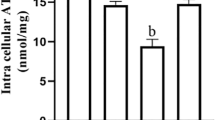
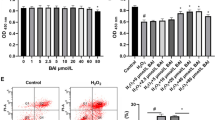
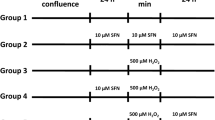
This study investigates the protective effect of small peptides from Periplaneta americana (SPPA) on hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)–induced apoptosis of ovarian granular cells. H2O2 was applied to human ovarian granular cells (KGN cell strains). Cell viability was tested by cell counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Cell apoptosis was tested by flow cytometry, and a cell apoptosis model was established. The model cells were treated with SPPA, and the cell survival rate was monitored using the CCK-8 method. The oxidative stress state of cells was examined using SOD, ROS, MDA, and NO kits. The protein expression levels of SIRT1, p53, and the apoptosis-related gene Caspase3 were measured using Western Blot methodology. Relative to the control group, cell viability declined significantly after the H2O2 treatment only (P < 0.01), while the apoptosis rate increased significantly (P < 0.01). The activity of SOD was weakened significantly (P < 0.01), while the cell levels of ROS, MDA, and NO increased dramatically (P < 0.01). Cell viability dramatically recovered (P < 0.01), and the SOD activity is hugely increased (P < 0.01) after SPPA treatment. In contrast, contents of ROS, MDA, and NO decreased sharply (P < 0.01), and significant dose-response relationships are characterized. Moreover, the H2O2 treatment group showed significantly downregulated expression of SIRT1 (P < 0.01) but significantly upregulated expressions of p53 and Caspase3 (P < 0.01) compared to the control group. Following the SPPA treatment of apoptosis cells, expression of SIRT1 increased significantly, while expressions of p53 and Caspase3 declined significantly (P < 0.01). This study suggests that SPPA inhibits H2O2-induced human KGN cell apoptosis through antioxidation, and the SIRT1/p53 signal pathway mediates the antioxidation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal A, Gupta S, Sharma RK (2005) Role of oxidative stress in female reproduction. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 3:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7827-3-28
Blander G, Guarente L (2004) The Sir2 family of protein deacetylases. Annu Rev Biochem 73:417–435. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.073651
Chen C, Zhou M, Ge Y, Wang X (2020) SIRT1 and aging related signaling pathways. Mech Ageing Dev 187:111215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2020.111215
Daitoku H, Hatta M, Matsuzaki H, Aratani S, Ohshima T, Miyagishi M, Nakajima T, Fukamizu A (2004) Silent information regulator 2 potentiates Foxo1-mediated transcription through its deacetylase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(27):10042–10047. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0400593101
Gao L, Xiao J (2018) A study on the role of p53 gene in the regulation of mice aging. Genomic Appl Biol 37(06):2663–2667. https://doi.org/10.13417/j.gab.037.002663
Goud AP, Goud PT, Diamond MP, Gonik B, Abu-Soud HM (2007) Reactive oxygen species and oocyte aging: role of superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and hypochlorous acid. Free Radic Biol Med 44(7):1295–1304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.11.014
Hack CT, Buck T, Bagnjuk K, Eubler K, Kunz L, Mayr D, Mayerhofer A (2019) A role for H2O2 and TRPM2 in the induction of cell death: studies in KGN Cells. Antioxidants (Basel) 8(11):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8110518
Ito M, Miyado K, Nakagawa K, Muraki M, Imai M, Yamakawa N, Qin J, Hosoi Y, Saito H, Takahashi Y (2010) Age-associated changes in the subcellular localization of phosphorylated p38 MAPK in human granulosa cells. Mol Hum Reprod 16(12):928–937. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/gaq076
Li L, Shen M, Ning C, Guan Z, Jiang Yi WW, Liu H (2016) Induction of granulosa cell autophagy and effects in apoptosis by hydrogen peroxide in porcine ovaries. J Nanjing Agri Univ 39(05):814–818. https://doi.org/10.7685/jnau.201601001
Li W, Yan Y, Yin X, Qin Y, Liu J (2017) Relationship of ovarian granulosa cells apoptosis and reactive oxygen species with outcome of IVF-ET in patients with different ages. Chin J Birth Health Hered 25(3):109–111. https://doi.org/10.13404/j.cnki.cjbhh.2017.03.048
Liang M, Yao G, Yin M, Lü M, Tian H, Liu L, Lian J, Huang X, Sun F (2013) Transcriptional cooperation between p53 and NF-ĸB p65 regulates microRNA-224 transcription in mouse ovarian granulosa cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 370(1-2):119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2013.02.014
Liu ZQ, Shen M, Wu WJ, Li BJ, Weng QN, Li M, Liu HL (2014) Expression of PUMA in follicular granulosa cells regulated by FoxO1 activation during oxidative stress. Reprod Sci 22(6):696–705. https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719114556483
Massin N, Méduri G, Bachelot A, Misrahi M, Kuttenn F, Touraine P (2008) Evaluation of different markers of the ovarian reserve in patients presenting with premature ovarian failure. Mol Cell Endocrinol 282(1-2):95–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2007.11.017
Molavi M, Razi M, Malekinejad H, Amniattalab A, Rezaie H (2014) Vitamin E improved cypermethrin-induced damages in the ovary of rats; evidence for angiogenesis and p53 involvement. Pestic Biochem Physiol 110:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.02.004
Qi J, Wang F, Yang P, Wang X, Xu R, Chen J, Yuan Y, Lu Z, Duan J (2018) Mitochondrial fission is required for angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis mediated by a Sirt1-p53 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 9:176. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00176
Sobinoff AP, Pye V, Nixon B, Roman SD, McLaughlin EA (2012) Jumping the gun: smoking constituent BaP causes premature primordial follicle activation and impairs oocyte fusibility through oxidative stress. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 260(1):70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2012.01.028
Sui S, Ge Y, Xu Q, Su J (2017) Influence of Periplaneta americana extract on antioxidant stress in rats. Sichuan J Zool 36(02):198–202. https://doi.org/10.11984/j.issn.1000-7083.20160279
Tiwari M, Prasad S, Tripathi A, Pandey AN, Ali I, Singh AK, Shrivastav TG, Chaube SK (2015) Apoptosis in mammalian oocytes: a review. Apoptosis 20(8):1019–1025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1136-y
Wang B, Gong Z, Song J, Xia T, Ma R (2020) Research progress on SIRT1 improving ovarian reservation by inhibiting oocyte senescence. J Int Reprod Health/Fam Plan 39:45–48,58
Wathes DC, Abayasekara DR, Aitken RJ (2007) Polyunsaturated fatty acids in male and female reproduction. Biol Reprod 77(2):190–201. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.107.060558
Weng Q, Liu Z, Li B, Liu K, Wu W, Liu H (2016) Oxidative stress induces mouse follicular granulosa cells apoptosis via JNK/FoxO1 pathway. PLoS One 11(12):e0167869. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0167869
Xi H, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Feng X (2019) Advances in research on the pathogenesis of premature ovarian failure. J Liaoning Coll Tradit Chin Med 21(12):103–106. https://doi.org/10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2019.12.026
Xiang L, Yao G, Li R, Zhang J, Huang Y (2015) Review of the establishing methods of premature ovarian failure’s animal model. Chin Pharm J 50(5):386–389. https://doi.org/10.11669/cpj.2015.05.002
Zeng C, Liao Q, Hu Y, Shen Y, Geng F, Chen L (2019) The role of Periplaneta americana (Blattodea: Blattidae) in modern versus traditional Chinese medicine. J Med Entomol 56(6):1522–1526. https://doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjz081
Zhang C, He Z, Jiao C, Liu G (2010) In vitro antioxidant activity analysis of anticancer active components of Periplaneta americana. Lishizhen Med Mat Res 21(09):2249–2250. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2010.09.058
Zhou Q, Li Z, Liu J, Lin Q, Wang C, Jiang X (2009) Effect of Periplaneta americana meal on immunity and antioxidation of broliers. J Fujian Agri Fore Univ (Natu Sci Edit) 38(02):175–180. https://doi.org/10.13323/j.cnki.j.fafu(nat.sci.).2009.02.018
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31760719 to Shiyan Sui) and the Fund program of Scientific Research, Ministry of Education, Yunnan Province (2021Y414 to Qin Wang).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shiyan Sui and Qin Wang conceived the project. Rong Fu and Qin Wang performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript, respectively. Caihua Kong and Kena Liu offered technical support. Shiyan Sui and Caihua Kong participated in revising the manuscript. Huaxin Si and other authors assisted with the experiments. All authors approved the manuscript. No conflict of interest is associated with this work.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 50.6 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Fu, R., Kong, C. et al. The protective effect of small peptides from Periplaneta americana on hydrogen peroxide–induced apoptosis of granular cells. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 57, 610–619 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-021-00586-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-021-00586-2