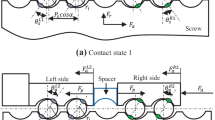
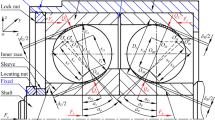
Abstract
The sliding-rolling mixed motion behavior degrades the ball screw’s precision at different levels. Based on the sliding-rolling mixed motion between ball and screw/nut raceway, the ball screw’s precision loss considering different given axial loading and rotational speed working conditions was investigated. Since creep and lubrication relate to sliding and rolling motion wear, the creep and lubrication characteristics are analyzed under different working conditions. Besides, the precision loss was calculated considering the sole influence of sliding behavior between ball and screw and compared with the results from other current models. Finally, research on precision loss owing to the sliding-rolling mixed motion behavior was realized under given working conditions, and suitable wear tests were carried out. The analytical results of precision loss are in good agreement with the experimental test conclusions, which is conducive to better predicting the law of precision loss in stable wear period.
摘要
滑-滚混合运动行为在不同程度上会退化滚珠丝杠副的精度。基于滚珠与丝杠/螺母滚道之间的 滑-滚混合运动分析, 研究了滚珠丝杠副在不同轴向负载及旋转速度工况下的精度损失。由于滑动、滚 动磨损与蠕滑、润滑紧密相关, 研究了不同运行工况下蠕滑及润滑特性。此外, 当探究滚珠与滚道之 间的滑动运动行为对精度损失的影响时, 计算了滚珠丝杠副的精度损失并对比了其他模型。最后, 在 给定运行工况下, 研究了滑-滚混合运动下的精度损失, 设计相关实验, 对精度衰退模型进行验证。精 度损失的分析结果与试验测试具有很好的吻合性, 表明该模型能够很好地预测处于稳定磨损时期内的 精度损失。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
YANG Y, ZHANG W M, ZHU Q X, JIANG Q S. Dynamic characteristic optimization of ball screw feed drive in machine tool based on modal extraction of state space model [J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 55524–55542. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2909550.
LIN M C, RAVANI B, VELINSKY S A. Kinematics of the ball screw mechanism [J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 1994, 116(3): 849–855. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2919459.
WEI C C, LIN J F. Kinematic analysis of the ball screw mechanism considering variable contact angles and elastic deformations [J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2003, 125(4): 717–733. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1623761.
LIN M C, VELINSKY S A, RAVANI B. Design of the ball screw mechanism for optimal efficiency [J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 1994, 116(3): 856–861. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2919460.
LIU H, ZHANG J, ZHAO W. An intelligent non-collocated control strategy for ball-screw feed drives with dynamic variations [J]. Engineering, 2017, 3(5): 641–647. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENG.2017.04.007.
WEI C, LAI R. Kinematical analyses and transmission efficiency of a preloaded ball screw operating at high rotational speeds [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2011, 46(7): 880–898. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2011.02.009.
WEI C C, LIN J F, HORNG J. Analysis of a ball screw with a preload and lubrication [J]. Tribology International, 2009, 42: 11–19. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2008.12.013.
CHEN Yong-jiang, TANG Wen-cheng. Dynamic contact stiffness analysis of a double-nut ball screw based on quasi-static method [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2014, 73(3): 76–90. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2013.10.008.
ZHAO J, LIN M, SONG X, GUO Q Z. Investigation of load distribution and deformations for ball screws with the effects of turning torque and geometric errors [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2019, 141: 95–116. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2019.07.006.
ZHEN N, AN Q. Analysis of stress and fatigue life of ball screw with considering the dimension errors of balls [J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2018, 137: 68–76. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2017.12.038.
LIN B, OKWUDIRE C E, WOU J S. Low order static load distribution model for ball screw mechanisms including effects of lateral deformation and geometric errors [J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2018, 140(2): 022301. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4038071.
KANG X M, WANG L. Experimental analysis of axial load internal circulation ball screw pair of friction torque and the impact [J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, (401-403): 139–145. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.401-403.139.
XU N, TANG W, CHEN Y, BAO D, GUO Y. Modeling analysis and experimental study for the friction of a ball screw [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2015, 87: 57–69. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2014.12.019.
ZHOU C, FENG H, CHEN Z, OU Y. Correlation between preload and no-load drag torque of ball screws [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2016, 102: 35–40. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2015.11.010.
WEI C C, LIOU W L, LAI R S. Wear analysis of the offset type preloaded ball-screw operating at high speed [J]. Wear, 2012, 292: 111–123. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2012.05.024.
KAMALZADEH A, GORDON D J, ERKORKMAZ K. Robust compensation of elastic deformations in ball screw drives [J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2010, 50(6): 559–574. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2010.03.001.
GNANAMOORTHY R, GOVINDARAIAN N, MUTOH Y. Effect of slid-roll ratio on the contact fatigue behavior of sintered and hardened steels [J]. Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2004, 4(2): 78–83. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/15477020419082.
GOVINDARAJAN N, GNANAMOORTHY R. Rolling/sliding contact fatigue life prediction of sintered and hardened steels [J]. Wear, 2007, 262(1, 2): 70–78. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2006.03.053.
ARCHARD J F. Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces [J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1953, 24(8): 981–988. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1721448.
ZHOU C, OU Y, FENG H, CHE Z. Investigation of the precision loss for ball screw based on the modified Archard theory [J]. Industrial Lubrication and Tribology, 2017, 69(2): 166–173. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-12-2015-0204.
LIU Jia-lan, CHI Ma, WANG Shi-long. Precision loss modeling method of ball screw pair [J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 135: 106397. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.106397.
CHENG Q, QI BB, LIU Z F, ZHANG C X, XUE D Y. An accuracy degradation analysis of ball screw mechanism considering time-varying motion and loading working conditions [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2019, 134: 1–23. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2018.12.024.
ZHOU C G, ZHOU H X, FENG H T. Experimental analysis of the wear coefficient of double-nut ball screws [J]. Wear, 2020, 446: 203201. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2020.203201.
LIU K, LIU H, LI T, WANG Y, SUN M, WU Y. Prediction of comprehensive thermal error of a preloaded ball screw on a gantry milling machine [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 2017, 140(2): 021004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4037236.
NGUYEN T L, RO S K, PARK J W. Study of ball screw system preload monitoring during operation based on the motor current and screw-nut vibration [J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2019, 131: 18–32. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.05.036.
CHENG Q, ZHAO H W, ZHAO Y S, SUN B W, GU P H. Machining accuracy reliability analysis of multi-axis machine tool based on Monte Carlo simulation [J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2018, 29(1): 191–209. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-015-1101-1.
CAI L G, ZHANG Z L, CHENG Q, LIU Z F, GU P H. An approach to optimize the machining accuracy retainability of multi-axis NC machine tool based on robust design [J]. Precision Engineering, 2016, 43: 370–386. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precisioneng.2015.09.001.
CHENG Q, FENG Q N, LIU Z F, GU P H, ZHANG G J. Sensitivity analysis of machining accuracy of multi-axis machine tool based on POE screw theory and Morris method [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 84(9-12): 2301–2318. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7791-x.
CHENG Q, ZHAO H W, ZHANG G G, GU P H, CAI L G. An analytical approach for crucial geometric errors identification of multi-axis machine tool based on global sensitivity analysis [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2014(75): 107–121. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-6133-8.
ZHANG Z L, CAI L G, CHENG Q, LIU Z F, GU P H. A geometric error budget method to improve machining accuracy reliability of multi-axis machine tools [J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2019, 30(2): 495–519. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-016-1260-8.
FAN J W, TAO H H, WU C J, PAN R, TANG Y H, LI Z S. Kinematic errors prediction for multi-axis machine tools’ guideways based on tolerance [J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 98(5-8): 1131–1144. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2335-9.
RODRÍGUEZ-TEMBLEQUE L, ABASCAL R, ALIABADI M H. A boundary element formulation for wear modeling on 3D contact and rolling-contact problems [J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2010, 47(18, 19): 2600–2612. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2010.05.021.
KALKER J J, JOHNSON K L. Three-dimensional elastic bodies in rolling contact [J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1993, 60(1): 34–45. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-7889-9.
HOU K P, ZHU D, WEN S Z. An inverse solution to the point contact EHL problem under heavy load [J]. ASME Journal of Tribology, 1987, 109(3): 432–436. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3261466.
HAMROCK B J, DOWSON D. Isothermal elastohydrodynamic lubrication of point contacts: Part 3-Fully flooded results [J]. Journal of Lubrication Technology, Trans ASME, 1977, 99(2): 264–276. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3453074.
DING H, KAHRAMAN A. Interactions between nonlinear spur gear dynamics and surface wear [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2007, 307(3-5): 662–679. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2007.06.030.
MARKHO P H. Highly accurate formulas for rapid calculation of the key geometrical parameters of elliptic Hertzian contacts [J]. ASME Journal of Tribology, 1988, 109(4): 640–647. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3261525.
LAUN H M. Pressure dependent viscosity and dissipative heating in capillary rheometry of polymer melts [J]. Rheologica Acta, 2003, 42(4): 295–308. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-002-0291-6.
SHIMIZU S, SHIMODA H, SHARMA C S. Re-evaluation of basic dynamic load rating and life formula for a ball screw [J]. Tribology Transactions, 2007, 50(1): 88–95. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10402000601105599.
MEI X, TSUTSUMI M, TAO T, SUN N. Study on the load distribution of ball screws with errors [J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2003, 38(11): 1257–1269. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0094-114X(03)00070-3.
VERL A, FREY S, HEINZE T. Double nut ball screw with improved operating characteristics[J]. CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 2014, 63(1): 361–364. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2014.03.128.
CHEN K, ZU L, WANG L. Prediction of preload attenuation of ball screw based on support vector machine [J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 10(9): 1687814018799161. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1687814018799161.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item
Project(51975012) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(Z1511000003150138) supported by the Beijing Nova Program, China; Project(Z191100001119010) supported by the Shanghai Sailing Program, China; Project(2018ZX04033001-003) supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project, China
Contributors
QI Bao-bao provided the data curation, methodology and writing-original draft. CHENG Qiang provided the funding acquisition and methodology. LI Shun-lei replied to reviewers’ comments and revised the final version. LIU Zhifeng conducted the formal analysis and funding acquisition. YANG Cong-bin provided the software.
Conflict of interest
QI Bao-bao, CHENG Qiang, LI Shun-lei, LIU Zhi-feng and YANG Cong-bin declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Bb., Cheng, Q., Li, Sl. et al. Precision loss of ball screw mechanism under sliding-rolling mixed motion behavior. J. Cent. South Univ. 28, 1357–1376 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4537-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-020-4537-1