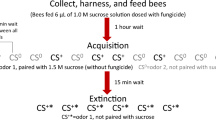
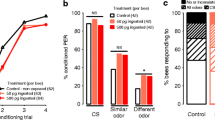
Abstract
Learning and memory are important biological processes that allow for optimized honey bee behavior. Factors negatively affecting bee cognition are important contributors to declines in pollination and food security. Agrochemical use, including herbicides, is one of the primary stressors linked to bee decline. Predicted agricultural expansion and associated increased use of glyphosate combined with scarcity of honey bees further highlights the need to understand the relationship between glyphosate and honey bee cognition and health. Here we investigated the effect of field-realistic doses of glyphosate on honey bee olfactory learning and memory. We used the conditioning of the Proboscis Extension Reflex (PER) to evaluate olfactory absolute conditioning. We found no differences in olfactory PER performance between glyphosate-exposed and control bees. We also did not find differences in olfactory memory retrieval at 15 min or 24 h after conditioning between exposed and non-exposed bees. However, we found that sublethal doses of glyphosate impaired memory retention; bees exposed to sublethal doses of glyphosate showed a decay trajectory of learned information, while in non-exposed bees the trajectory had a positive increment with time. This trend in memory retention was significantly different between bees exposed to 1500 ng and controls. Implications for insect conservation: Field-realistic doses of glyphosate had negative effect on memory dynamics in the honey bee. These results suggest glyphosate affects time-dependent neural mechanisms underlying information processing. This negative effect contributes to declines in pollination function and food security. We highlight the need to critically evaluate the cost-benefit analysis of indiscriminate glyphosate use.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson CI, Aquino IS, Silva MC, Price JM (1997) Learning in the Africanized honey bee: Apis mellifera L. Physiol Behav 62:657–674
Abramson CI, Squire J, Sheridan A, Mulder PG (2004) The effect of insecticides considered harmless to honey bees (Apis mellifera): proboscis conditioning studies by using the insect growth regulators tebufenozide and diflubenzuron. Environ Entomol 33:378–388. https://doi.org/10.1603/0046-225X-33.2.378
Abramson CI, Singleton JB, Wilson MK, Wanderley PA, Ramalho FS, Michaluk LM (2006) The effect of an organic pesticide on mortality and learning in Africanized honey bees (Apis mellifera L.) in Brasil. Am J Environ Sci 2:37–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002449900548
Aizen MA, Harder LD (2009) The global stock of domesticated honey bees is growing slower than agricultural demand for pollination. Curr Biol 19:915–918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.03.071
Aizen MA, Garibaldi LA, Cunningham SA, Klein AM (2009) How much does agriculture depend on pollinators? Lessons from long-term trends in crop production. Ann Bot 103:1579–1588. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcp076
Amaya-Márquez M (2019) Olfactory learning in the stingless bee Melipona eburnean Friese (Apidae:Meliponini). Insects 10:412. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10110412
Ángel-Coca C, Nates-Parra G, Ospina-Torres R, Melo Ortiz CD, Amaya-Márquez M (2011) Biología floral y reproductiva de la gulupa (pasiflora edulis Sims f. edulis). Caldasia 33:413–431
Balbuena MS, Tison L, Hahn ML, Greggers U, Menzel R, Farina WM (2015) Effects of sublethal doses of glyphosate on honey bee navigation. J Exp Biol 218:2799–2805. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.117291
Bascompte J, Jordano P (2007) Plant-Animal mutualistic networks: the architecture of biodiversity. Ann Rev Ecol Evol Syst 38:567–593. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.38.091206.095818
Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw 67:1–48. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v067.i01
Becher MA, Osborne JL, Thorbek P, Kenedy PJ, Grimm V (2013) Towards a system approach for understanding honey bee decline: a stocktaking and synthesis of existing models. J Appl Ecol 50:868–886. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.12112
BIOLOGÍA FLORAL Y REPRODUCTIVA DE LA GULUPA PASSIFLORA EDULIS SIMS F. EDULIS (scielo.org.co)
Bitterman ME, Menzel R, Fietz A, Schäfer S (1983) Classical conditioning of proboscis extension in honeybees (Apis mellifera). J Comp Psych 97:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1037/0735-7036.97.2.107
Blaauw BR, Isaacs R (2014) Flower plantings increase wild bee abundance and the pollination services provided to a pollination-dependent crop. J Appl Ecol 51:890–898. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.12257
Blot N, Veillat L, Rouzé R, Delatte H (2019) Glyphosate, but not its metabolite AMPA, alters the honeybee gut microbiota. PLOS ONE 14(4):e0215466. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0215466
Boily M, Sarrasin B, DeBlois C, Aras P, Chagnon M (2013) Acetylcholinesterase in honey bees (Apis mellifera) exposed to neonicotinoids, atrazine and glyphosate: laboratory and field experiments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:5603–5614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1568-2
Breeze TD, Bailey AP, Balcombe KG, Potts SG (2011) Pollination services in the UK: how important are honeybees? Agric Ecosyst Environ 142:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.03.020
Collison E, Hird H, Cresswell J, Tyler C (2016) Interactive effects of pesticide exposure and pathogen infection on bee health—a critical analysis. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc 91:1006–1019
Currie RW, Pernal SF, Guzmán-Novoa E (2010) Honey bee colony losses in Canada. J Apic Res 49:104–106. https://doi.org/10.3896/IBRA.1.49.1.18
Decourtye A, Pham-Delègue MH (2020) The proboscis extension response: assessing the sublethal effects of pesticides on the honey bee. In: Devillers J, Pham-Delegue MH (eds) Honey Bees: estimating the environmental impact of chemicals. Taylor &Francis Inc, New York, pp 72–88
Domjan M (2003) Principios de aprendizaje y conducta, 5th edn. Thomson-Paraninfo, Madrid
Dukas R (1998) Evolutionary ecology of learning. In: Dukas R (ed) Cognitive ecology: the evolutionary ecology of information processing and decision making. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 129–174
Eisenhardt D (2006) Learning and memory formation in the honeybee (Apis mellifera) and its dependency on the cAMP-protein kinase A pathway. Anim Biol 56:259–278. https://doi.org/10.1163/157075606777304249
Erber J, Masuhr T, Menzel R (1980) Localization of short-term memory in the brain of the bee, Apis mellifera. Physiol Entomol 5:343–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3032.1980.tb00244.x
Faraway JJ (2016) Extending the linear model with R: generalized linear, mixed effects and nonparametric regression models, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Farina WM, Balbuena MS, Herbert LT, Mengoni Goñalons C (2019) Effects of the herbicide glyphosate on honey bee sensory and cognitive abilities: individual impairments with implications for the hive. Insects 10:354. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10100354
Fewell JH, Winston ML (1996) Regulation of nectar collection in relation to honey storage levels by honey bees, Apis mellifera. Behav Ecol 7:286–291. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/7.3.286
Fox J (2003) Effect displays in R for generalised linear models. J Stat Softw 8:1–27
Fox J, Weisberg S (2019) An {R} companion to applied regression, 3rd edn. Sage, Thousand Oaks
Frost EH, Shutler D, Hillier NK (2012) The proboscis extension reflex to evaluate learning and memory in honey bees (Apis mellifera): some caveats. Naturwissenschaften 99:677–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114012-0955-8
Garibaldi et al (2013) Wild pollinators enhance fruit set of crops regardless of honey bee abundance. Science 339:1608–1611
Garibaldi LA et al (2016) Mutually beneficial pollinator diversity and crop yieldoutcomes in small and large farms. Science 351:388–391
Giesy JP, Dobson S, Solomon KR (2000) Ecotoxicological risk assessment for Roundup® Herbicide. In: Ware GW (ed) Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 35–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-1156-3_2
Gill RA (1991) The value of honey bee pollination to society. Apiacta 26:97–105
Gill RJ, Baldock KCR, Brown MJF, Creswell JE, Dicks LV, Fountain MT, Garratt MPD, Gough LA, Heard MS, Holland JM, Ollerton J, Stone GN, Tang CQ, Vanbergen AJ, Vogler AP, Woodward G, Arce AN, Boatman ND, Brand-Hardy R, Breeze TD, Green M, Hartfield CM, O’Connor RS, Osborne JL, Phillips J, Sutton PB, Potts SG (2016) Protecting an ecosystem service: approaches to understanding and mitigating threats to wild insect pollinators. Adv Ecol Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.aecr.2015.10.007
Gill JPK, Sethi N, Mohan A, Datta S, Girdhar M (2017) Glyphosate toxicity for animals. Environ Chem Lett 16:401–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-017-0689-0
Giurfa M (2007) Behavioral and neural analysis of associative learning in the honey bee: a taste from the magic well. J Comp Physiol A 193:801–824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-007-0235-9
Giurfa M, Sandoz JC (2012) Invertebrate learning and memory: fifty years of olfactory conditioning of the proboscis extension response in honey bees. Learn Mem 19:54–66. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.024711.111
Godfray HCJ et al (2015) A restatement of recent advances in the natural science evidence base concerning neonicotinoid insecticides and insect pollinators. Proc R Soc Lond B 282:20151821
Godfray HCJ, Blacquière T, Field LM, Hails RS, Petrokofsky G, Potts SG, Raine NE, Vanbergen AJ, McLean AR (2014) A restatement of the natural science evidence base concerning neonicotinoid insecticides and insect pollinators. Proc R Soc B 281:20140558. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2014.0558
Goldsborough LG, Brown DJ (1988) Effect of glyphosate (Roundup® formulation) on periphytic algal photosynthesis. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 41:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01705439
Gould JL (1984) Natural history of honey bee learning. In: Marler P, Terrace HS (eds) The biology of learning. Springer, New York, pp 149–180
Goulson D, Nicholls E, Botias C, Rotheray EL (2015) Bee declines driven by combined stress from parasites, pesticides, and lack of flowers. Science 347:1255957. Doi:https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1255957
Grüter C, Farina WM (2007) Nectar distribution and its relation to food quality in honey bee (Apis mellifera) colonies. Insectes Soc 54:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00040-007-0915-z
Hagler JR, Mueller S, Teuber LR, Machtley SA, Deynze A (2011) Foraging range of honey bees, Apis mellifera, in Alfalfa seed production fields. J Insect Sci 11:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1673/031.011.14401
Hammer M, Menzel R (1995) Learning and memory in the honey bee. J Neurosci 15:1617–1630. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.15-03-01617.1995
Helmer SH, Kerbaol A, Aras P, Jumarie C, Boily M (2015) Effects of realistic doses of atrazine, metolachlor, and glyphosate on lipid peroxidation and diet-derived antioxidants in caged honey bees (Apis mellifera). Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:8010–8021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2879-7
Herbert LH, Vazquez DE, Arenas A, Farina WM (2014) Effects of field-realistic doses of glyphosate on honey bee appetitive behaviour. J Exp Biol 217:3457–3464. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.109520
IPBES, Imperatriz-Fonseca VL, Ngo HT (eds) (2016) The assessment report of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services on pollinators, pollination and food production. Potts SG. Secretariat of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, Bonn
Kearns C, Inouye D, Waser NM (1998) Endangered mutualisms: the conservation of plant-pollinator interactions. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 29:83–112. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.29.1.83
Kevan PG, Menzel R (2012) The plight of pollination and the interface of neurobiology, ecology and food security. Environmentalist 32:300–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-012-9394-5
Kirchner WH (1999) 17. Mad-Bee-Disease? Subletale Effekte von Imidacloprid (Gaucho®) auf das Verhalten von Honigbienen. Apidologie 30:421–422
Klatt BK, Holzschuh A, Westphal C, Clough Y, Smit I, Pawelzik E, Tscharntke T (2013) Bee pollination improves crop quality, shelf life and commercial value. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 281:20132440. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2013.2440
Klein S, Cabirol A, Daevaud JM, Barron AB, Lihoreau M (2017) Why bees are so vulnerable to environmental stressors. Trends Ecol Evol 33:268–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2016.12.009
Kolpin DW, Thurman EM, Lee EA, Meyer MT, Furlong ET, Glassmeyer ST (2006) Urban contributions of glyphosate and its degradate AMPA to streams in the United States. Sci Total Environ 354:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.01.028
Kujawa M (1996) Glyphosate. Environmental Health Criteria 159, 177 Seiten, 3 Abbildungen und 25 Tabellen. World Health Organization, Geneva 1994. Preis: 27,—Sw.fr. Food / Nahrung 40(3):166–166. https://doi.org/10.1002/food.19960400341
Maggi M, Antúnez K, Invernizzi C, Aldea P, Vargas M, Negri P, Brasesco C, De Jong D, Message D, Teixeira EW, Principal J, Barrios C, Rufinengo S, Rodriguez Da Silva R, Eguaras M (2016) Honey bee health in South America. Apidologie 47:835–854
Matsumoto Y, Menzel R, Sandoz J-C, Giurfa M (2012) Revisiting olfactory classical conditioning of the proboscis extension response in honey bees: a step toward standardized procedures. J Neurosci Meth 211:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neumeth.2012.08.018
Memmott J (1999) The structure of plant-pollinator food web. Ecol Lett 2:276–280. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1461-0248.1999.00087.x
Mengoni Goñalons C, Farina WM (2018) Impaired associative learning after chronic exposure to pesticides in young adult honey bees. J Exp Biol 221:jeb176644. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.176644
Menzel R (1990) Learning, memory, and “cognition” in honey bees. In: Kesner RP, Olten DS (eds) Neurobiology of comparative cognition. Erlbaum Inc, New Jersey
Menzel R (1999) Memory dynamics in the honey bee. J Comp Physiol A 185:323–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003590050392
Menzel R (2001a) Behavioral and neural mechanisms of learning and memory as determinants of flower constancy. In: Chittka L, Thomson JD (eds) Cognitive ecology of pollination: animal behavior and floral evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 21–40
Menzel R (2001b) Searching for the memory trace in a mini-brain, the honey bee. Learn Mem 8:53–62
Menzel R (2012) The honey bee as a model for understanding the basis of cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:758–768. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3357
Menzel R, Mülller U (1996) Learning and memory in honey bees: from behavior to neural substrate. Ann Rev Neurosci 19:379–404. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ne.19.030196.002115
Menzel R, Greggers U, Hammer M (1993) Functional organization of appetitive learning and memory in a generalist pollinator, the honey bee. In: Papaj DR, Lewis AC (eds) Insect learning. Chapman & Hall, Inc, London, pp 79–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-2814-2_4
Michener CD (2007) The bees of the world, 2nd edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Moore D, Siegfried D, Wilson R, Rankin MA (1989) The influence of time of day on the foraging behavior of the honeybee Apis mellifera. J Biol Rhythms 4:305–325
Motta EVS, Raymann K, Moran NA (2018) Glyphosate perturbs the gut microbiota of honey bees. PNAS 115:10305. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1803880115
Müller U (2000) Prolonged activation of cAMP dependent protein kinase during conditioning induces long-term memory in honey bees. Neuron 27:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00017-9
Müller U (2012) The molecular signalling processes underlying olfactory learning and memory formation in honey bees. Apidologie 43:322–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13592-011-0115-8
Mwebaze P, Marris GC, Budge GE, Brown M, Potts SG, Breeze TD, Macleod A (2010) Quantifying the value of ecosystem services: a case study of honey bee pollination in UK. In: 12th Annual BIOECON conference from the Wealth of Nations to the Wealth of Nature: rethinking economic growth 27–28 September, Venice, Italy
Neumann P, Carreck NL (2010) Honey bee colony losses. J Apic Res 49:1–6. https://doi.org/10.3896/IBRA.1.49.1.01
Ollerton J, Winfree R, Tarrant S (2011) How many flowering plants are pollinated by animals? Oikos 120:321–326. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0706.2010.18644.x
Osborne JL, Clark SJ, Morris RJ, Williams IH, Riley JR, Smith AD, Reynolds DR, Edwards AS (1999) A landscape-scale study of bumble bee foraging range and constancy, using harmonic radar. J Appl Ecol 36:519–533. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2664.1999.00428.x
O’Toole C, Raw a (1991) Bees of the world. Blandford Publishing, an imprint of Cassell plc, London
Pavlov IP (1927) Conditioned reflexes: an investigation of the physiological activity of the cerebral cortex (Anrep GV translation). Oxford University Press, London
Pettis JS, Delaplane KS (2010) Coordinated responses to honey bee decline in the USA. Apidologie 41:256–263. https://doi.org/10.1051/apido/2010013
Pisa LW et al (2015) Effects of neonicotinoids and fipronil on non-target invertebrates. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2:68–102. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3471-x
Ponisio LC et al (2015) Diversification practices reduce organic to conventional yield gap. Proc R Soc B 282:20141396
Potts SG, Biesmeijer JC, Kremen C, Neumann P, Schweiger O, Kunin WE (2010) Global pollinator declines: trends, impacts and drivers. Trends Ecol Evol 25:345–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2010.01.007
Potts SG, Imperatriz-Fonseca V, Ngo HT, Aizen MA, Biesmeijer JC, Breeze TD, Dicks LV, Garibaldi LA, Hill R, Settele J, Vanbergen AJ (2016) Safeguarding pollinators and their values to human well-being. Nature 540:220–229. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20588
Pywell RF et al (2015) Wildlife-friendly farming increases crop yield. evidence forecological intensification. Proc R Soc B 282:20151740
R Core Team (2019) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Rader et al (2016) Non-bee insects are important contributors to global crop pollination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:146–151
Redhead JW, Dreier S, Bourke AFG, Heard MS, Jordan WC, Sumner S, Wang J, Carvell C (2016) Effects of habitat composition and landscape structure on worker foraging distances of five bumble bee species. Ecol Appl 26:726–739
Rueppel ML, Brightwell BB, Schaefer J, Marvel JT (1977) Metabolism and degradation of glyphosate in soil and water. J Agric Food Chem 25:517–528. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf60211a018
Sammons RD, Gaines TA (2014) Glyphosate resistance: state of knowledge. Pest Manag Sci 70:1367–1377. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.3743
Siviter H, Koricheva J, Brown MJF, Leadbeater E (2018) Quantifying the impact of pesticides on learning and memory in bees. J Appl Ecol 55:2812–2821. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.13193
Smith BH, Burden CM (2014) A proboscis extension response protocol for investigating behavioral plasticity in insects: application to basic, biomedical, and agricultural research. J Vis Exp JoVE 91:e51057. https://doi.org/10.3791/51057
Smith KM, Loh EH, Rostal MK, Zambrana-Torrelio CM, Mendiola L, Daszak P (2013) Pathogens, pests, and economics: drivers of honey bee colony declines and loose. Ecohealth 10:434–445
Southwick EE, Southwick L (1992) Estimating the economic value of honey bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae) as agricultural pollinators in the United States. J Econ Entom 85:621–633. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/85.3.621
Stokstad E (2007) The case of the empty hives. Science 316:970–972. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.316.5827.9
Takano HK, Mendes RR, Scoz LB, Lopez Ovejero RF, Constantin J, Gaines TA, Westra P, Dayan FE, Oliveira RS Jr (2019) Proline-106 EPSPS mutation imparting glyphosate resistance in goosegrass (Eleusine indica) emerges in South America. Weed Sci 67:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1017/wsc.2018.71
Takeda K (1961) Classical conditioned response in the honey bee. J Insect Physiol 3:168–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1910(61)90060-9
Thompson JN (2006) Mutualistic webs of species. Science 312:372–373. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1126904
Thompson HM, Levine SL, Doering J, Norman S, Manson P, Sutton P, von Mérey G (2014) Evaluating exposure and potential effects on honey bee brood (Apis mellifera) development using glyphosate as an example. Integr Environ Assess Manag 10:463–470. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.1529
van der Sluijs JP, Amaral-Rogers V, Belzunces LP, van Lexmond MFIJB, Bonmatin JM, Chagnon M, Downs CA, Furlan L, Gibbons DW, Giorio C, Girolami V, Goulson D, Kreutzweiser DP, Krupke C, Liess M, Long E, McField M, Mineau P, Mitchell EAD, Morrissey CA, Noome DA, Pisa L, Settele J, Simon-Delso N, Stark JD, Tapparo A, Van Dyck H, Van Praagh J, Whitehorn PR, Wiemers M (2015) Conclusions of the Worldwide Integrated Assessment on the risks of neonicotinoids and fipronil to biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:148–154
Vanbergen AJ, the Insect Pollinators Initiative (2013) Threats to an ecosystem service: pressures on pollinators. Front Ecol Environ 11:251–259. https://doi.org/10.1890/120126
vanEngelsdorp D, Hayes J, Underwood RM, Pettis JS (2010) A survey of honey bee colony losses in the United States, fall 2008 to spring 2009. J Apic Res 49:7–14. https://doi.org/10.3896/IBRA.1.49.1.03
Villar ME, Marchal P, Viola H, Giurfa M (2020) Redefining single-trial memories in the honeybee. Cell Rep 30:2603–2613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01086
von Frisch K (1967) The dance language and orientation of bees. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Zachepilo TG, Davydova AA, Vaido AI, Lopatina NG (2018) Role of the GluR2 subunit of AMPA receptors in associative learning in the honey bee Apis mellifera L. J Evol Biochem Phys 54:449–456. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093018060042
Zgurzynski MI, Lushington GH (2019) Glyphosate impact on Apis mellifera navigation: a combined behavioral and chemioinformatics study. EC Pharmacol Toxicol 7:806–824
Zhang WJ, Jiang FB, Ou JF (2011) Global pesticide consumption and pollution: with China as a focus. Proc Int Acad Ecol Environ Sci 1:125–144
Zuur A, Ieno EN, Walker N, Saveliev AA, Smith GM (2009) Mixed effects models and extensions in ecology with R. Springer, Berlin
Acknowledgements
To the Instituto de Ciencias Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Colombia for supporting the development of the Cognitive Ecology Laboratory, and Colciencias for funding this research. To Rodulfo Ospina for support with the use of the LABUN’s Apiary. To the anonym reviewers whose observations and generous suggestions greatly help to improve the quality of the manuscript.
Funding
Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Colciencias granted to JH a Young Researcher Funding (Code number: M301PR03F17), Hermes code: 38989. Grant IV-FGD003 (DIeI, Universidad del Rosario to AJR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández, J., Riveros, A.J. & Amaya-Márquez, M. Sublethal doses of glyphosate impair olfactory memory retention, but not learning in the honey bee (Apis mellifera scutellata). J Insect Conserv 25, 683–694 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10841-021-00335-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10841-021-00335-6