Abstract
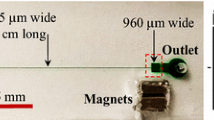
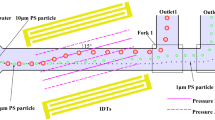
Separation of microparticles is of great importance in diagnostic, chemical, and biological analysis, as well as food processing and environmental assessments. In the present work, a novel microfluidic device is designed to focus microparticles based on inertial and magnetophoretic impacts. Three permanent magnets are mounted in the vicinity of the microchannel to separate the diamagnetic particles suspended in a ferrofluid by applying a negative magnetophoretic force. Polystyrene particles with three sizes of 5, 10, and 15 µm are separated from each other using the proposed device with 100% separation efficiency. The results show that high purity of particle collection can be achieved using Halbach array of magnets at Reynolds numbers of 100 and 110. The influence of inlet flow velocity, magnets’ configuration, and their distance from the microchannel is investigated and the optimal situations are determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Sajeesh and A. K. Sen, Microfluid Nanofluidics, 17, 1 (2014).
M. Bayareh, Chem. Eng. Process., 153, 107984 (2020).
Y.-Y. Chiu, C.-K. Huang and Y.-W. Lu, Biomicroflluidics, 10, 011906 (2016).
T. S. Tran, B. D. Ho, J. P. Beech and J. O. Tegenfeldt, Lab on a Chip, 17, 3592 (2017).
M. Yamada, M. Nakashima and M. Seki, Anal. Chem., 76(18), 5465 (2004).
S. S. Kuntaegowdanahalli, A. A. S. Bhagat, G. Kumar and I. Papautsky, Lab on a Chip, 9, 2973 (2009).
I. Doh and Y.-H. Cho, Sens. Actuators A, 121, 59 (2005).
D. Baresch, J.-L. Thomas and R. Marchiano, Phys. Rev. Lett., 116, 024301 (2016).
A. Abdulla, W. Liu, A. Gholamipour-Shirazi, J. Sun and X. Ding, Anal. Chem., 90, 4397 (2018).
Y. Zhou, Z. Ma and Y. Ai, Microsyst. Nanoeng., 4, 1 (2018).
D. Di Carlo, D. Irimia, R. G. Tompkins and M. Toner, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 104, 18892 (2007).
S. Dutz, M. E. Hayden, A. Schaap, B. Stoeber and U.O. Hafeli, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 324, 3791 (2012).
A. Russom, A. K. Gupta, S. Nagrath, D. Di Carlo, J. F. Edd and M. Toner, New J. Phys., 11, 075025 (2009).
J. M. Martel and M. Toner, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng., 16, 371 (2014).
A. A. S. Bhagat, S. S. Kuntaegowdanahalli and I. Papautsky, Lab on a Chip, 8, 1906 (2008).
A. Al-Halhouli, W. Al-Fagheri, B. Alhamarneh, L. Hecht and A. Dietzel, Micromachines, 9, 171 (2018).
J. Sun, M. Li, C. Liu, Y. Zhang, D. Liu, W. Liu, G. Hu and X. Jiang, Lab on a Chip, 12, 3952 (2012).
P. Yeh, Z. Dai, M. Bergeron, Z. Zhang, M. Lin and X. Cao, Sens. Actuators B Chem., 252, 606 (2017).
A. S. Rzhevskiy, S. R. Bazaz, L. Ding, A. Kapitannikova, N. Sayyadi, D. Campbell, B. Walsh, D. Gillatt, M. Ebrahimi Warkiani and A. V. Zvyagin, Cancers, 12, 81 (2020).
A. Munaz, M. J. Shiddiky and N.-T. Nguyen, Biomicroflluidics, 12, 031501 (2018).
A. Munaz, M. J. Shiddiky and N.-T. Nguyen, Sens. Actuators B Chem., 275, 459 (2018).
T. Zhu, R. Cheng, S. A. Lee, E. Rajaraman, M. A. Eiteman, T. D. Querec, E. R. Unger and L. Mao, Microflluidic Nanofluidics, 13, 645 (2012).
J. Zhang, S. Yan, D. Yuan, Q. Zhao, S.H. Tan, N.-T Nguyen and W. Li, Lab on a Chip, 16, 3947 (2016).
W. Zhao, R. Cheng, S. H. Lim, J. R. Miller, W. Zhang, W. Tang, J. Xie and L. Mao, Lab Chip, 17, 2243 (2017).
J. Wu, Y. Cui, S. Xuan and X. Gong, Microfluidic Nanofluidics, 22, 103 (2018).
M. Xue, A. Xiang, Y. Guo, L. Wang, W. Wang, G. Ji and Z. Lu, RSC Adv., 9, 38496 (2019).
S. Ookawara, D. Street and K. Ogawa, Chem. Eng. Sci., 61, 3714 (2006).
X. Han, Y. Feng, Q. Cao and L. Li, Microfluidic Nanofluidics, 18, 1209 (2015).
M. E. Warkiani, A. K. P. Tay, G. Guan and J. Han, Sci. Rep., 5, 11018 (2015).
J. M. Martel and M. Toner, Phys. Fluids, 24, 032001 (2012).
D. Y. Kim and J. M. Kim, Korean J. Chem. Eng., 36, 837 (2019).
A. Thanormsridetchai, D. Ketpun, W. Srituravanich, P. Piyaviriyakul, A. Sailasuta, W. Jeamsaksiri, W. Sripumkhai and A. Pimpin, J. Mech. Sci. Technol., 31, 5397 (2017).
A. Özbey, M. Karimzadehkhouei, S. Akgonul, D. Gozuacik and A. Kosar, Sci. Rep., 6, 38809 (2016).
A. Shiriny and M. Bayareh, Meccanica, 55, 1903 (2020).
J. Vanderlinde, Classical electromagnetic theory, Springer, Netherland (2006).
S.-E. K. Fateen and M. Magdy, Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 95, 69 (2015).
R. Cheng, T. Zhu and L. Mao, Microfluidic Nanofluidics, 16, 1143 (2014).
Y. Zhou, D. T. Kumar, A. Kale, J. DuBose, Y. Song, J. Wang, D. Li and X. Xuan, Biomicrofluidics, 9, 044102 (2015).
Q. Chen, D. Li, J. Lin, M. Wang and X. Xuan, Anal. Chem., 89, 6915 (2017).
A. Shiriny and M. Bayareh, Chem. Eng. Sci., 229, 116102 (2021).
H. W. Hou, M. Ebrahimi Warkiani, B. L. Khoo, Z. R. Li, R. A. Soo, D. S.-W. Tan, W. T. Lim, J. Han, A. A. S. Bhagat and C. T. Lim, Sci. Rep., 3, 1259 (2013).
Y. He, L. Luo and S. Huang, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B, 33, 1950047 (2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiriny, A., Bayareh, M. & Nadooshan, A.A. Combination of inertial focusing and magnetoporetic separation in a novel microdevice. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 38, 1686–1702 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-021-0795-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-021-0795-3