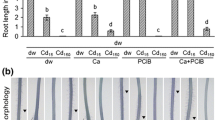
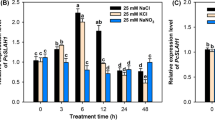
Abstract
It is known that rice roots take up cadmium (Cd) via the symplastic route mediated by membrane-bound mineral transporters. Here we provide evidence that apoplastic bypass flow is another Cd uptake route in rice. High concentrations of Cd rendered apoplastic bypass flow rate increased in rice seedlings. These concentrations of Cd compromised membrane integrity in the root meristem and transition zone. Polyethleneglycol and proline inhibited the Cd-induced apoplastic bypass flow and Cd transfer to the shoots. Loss-of-function mutant of the Cd uptake transporter, nramp5, showed Cd transport to the shoot comparable to the wild type. At a low Cd concentration, increased apoplastic bypass flow rate by NaCl stress resulted in an elevation of Cd transport to shoots both in the wildtype and nramp5. These observations indicate that apoplastic bypass flow in roots carries Cd transport leading to xylem loading of Cd in addition to the symplastic pathway mediated by mineral transporters under stressed conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertin G, Averbeck D (2006) Cadmium: Cellular effects, modifications of biomolecules, modulation of DNA repair and genotoxic consequences (a review). Biochimie 88:1549–1559
Brundrett MC, Enstone DE, Peterson CA (1988) A berberine-aniline blue fluorescent staining procedure for suberin, lignin, and callose in plant tissue. Protoplasma 146:133–142
Clemens S, Aarts MGM, Thomie S, Verbruggen N (2013) Plant science: the key to preventing slow cadmium poisoning. Trends Plant Sci 18:92–99
DalCorso G, Farinati S, Maistri S, Furini A (2008) How plants cope with cadmium: Staking all on metabolism and gene expression. J Integr Plant Biol 50:1268–1280
Faiyue B, Vijayalakshmi C, Nawaz S, Nagato Y, Taketa S, Ichii M, Al-Azzawi MJ, Flowers TJ (2010a) Studies on sodium bypass flow in lateral rootless mutants lrt1 and lrt2, and crown rootless mutant crl1 of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Environ 33:687–701
Faiyue B, Al-Azzawi MJ, Flowers TJ (2010b) The role of lateral roots in bypass flow in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Environ 33:702–716
Flam-Shepherd R, Huynh WQ, Coskun D, Hamam AM, Britto DT, Kronzucker HJ (2018) Membrane fluxes, bypass flows, and sodium stress in rice: the influence of silicon. J Exp Bot 69:1679–1692
Flowers TJ, Yeo AR (1995) Breeding for salinity resistance in crop plants: where next? Australian J Plant Physiol 22:875–884
Fritz M, Ehwald R (2013) Radial transport of salt and water in roots of the common reed (Phragmites australis Trin. ex Steudel). Plant Cell Environ 36:1860–1870
Garcia A, Rizzo CA, Ud-Din J, Bartos SL, Senadhira D, Flowers TJ, Yeo AR (1997) Sodium and potassium transport to the xylem are inherited independently in rice, and the mechanism of sodium: potassium selectivity differs between rice and wheat. Plant Cell Environ 20:1167–1174
Greger M, Johansson M (1992) Cadmium effects on leaf transpiration of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris). Physiol Plant 86:465–473
Hirayama T, Lei GJ, Yamaji N, Nakagawa N, Ma JF (2018) The putative peptide gene FEP1 regulates iron deficiency response in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 59:1739–1752
Ishimaru Y, Suzuki M, Tsukamoto T, Suzuki K, Nakazono M, Kobayashi T, Wada Y, Watanabe S, Matsuhashi S, Takahashi M, Nakanishi H, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2006) Rice plants take up iron as an Fe3+-phytosiderophore and as Fe2+. Plant J 45:335–346
Krishnamurthy P, Ranathunge K, Franke R, Prakash HS, Screiber L, Mathew MK (2009) The role of root apoplastic transport barriers in salt tolerance of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Planta 230:119–134
Krishnamurthy P, Ranathunge K, Nayak S, Schreiber L, Mathew MK (2011) Root apoplastic barriers block Na+ transport to shoots in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Exp Bot 62:4215–4228
Li J, Zhu S, Song X, Shen Y, Chen H, Yu J, Yi K, Liu Y, Karplus VJ, Wu P, Deng XW (2006) A rice glutamate receptor-like gene is critical for the division and survival of individual cells in the root apical meristem. Plant Cell 18:340–349
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:951–981
Nakanishi H, Ogawa I, Ishimaru U, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2006) Iron deficiency enhances cadmium uptake and translocation mediated by the Fe2+ transporters OsIRT1 and OsIRT2 in rice. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 52:464–469
Nawrot T, Plusquin M, Hogevorst J, Roels HA, Celis H, Thijs L, Vangronsveld J, Van Hecke E, Staessen JA (2006) Environmental exposure to cadmium and risk of cancer: a prospective population-based study. Lancet Oncol 7:119–126
Ochiai K, Matoh T (2002) Characterization of the Na+ delivery from roots to shoots in rice under saline stress: excessive salt enhances apoplastic transport in rice plants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 43:371–337
Pedas P, Ytting CK, Fuglsang AT, Jahn TP, Schjoerring JK, Husted S (2008) Manganese efficiency in barley: Identification and characterization of the metal ion transporter HIRT1. Plant Physiol 148:455–466
Prasad MNV (1995) Cadmium toxicity and tolerance in vascular plants. Envir Exp Bot 35:525–545
Qi X, Tam NF, WC L, Ye Z (2020) The role of root apoplastic barriers in cadmium translocation and accumulation in cultivars of rice (Oryza sativa L.) with different Cd-accumulating characteristics. Environ Pollut 254:1147736
Ranathunge K, Steudle E, Laritte R (2005) Blockage of apoplastic bypass-flow of water in rice roots by insoluble salt precipitates analogous to a Pfeffer cell. Plant Cell Environ 28:121–133
Sasaki A, Yamaji N, Yokosho K, Ma JF (2012) Nramp5 is a major transporter responsible for manganese and cadmium uptake in rice. Plant Cell 24:2155–2167
Shah K, Dubey RS (1997) Effect of cadmium on proline accumulation and ribonuclease activity in rice seedlings: role of proline as a possible enxyme protectant. Biol Plant 40:121–130
Sharma SS, Dietz KJ (2006) The significance of amino acid and amino acid-derived molecules in plant responses and adaptation to heavy metal stress. J Exp Bot 57:711–726
Sobahan MA, Arias CR, Okuma E, Shimoishi Y, Nakamura Y, Hirai Y, Mori IC, Murata Y (2009) Exogenous proline and glycinebetaine suppress apoplastic flow to reduce Na+ uptake in rice seedlings. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:2037–2042
Ueno D, Kono I, Yokosho K, Ando T, Yano M, Ma JF (2009) A major quantitative trait locus controlling cadmium translocation in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol 182:644–653
Ueno D, Yamaji N, Kono I, Huang CF, Ando T, Yano M, Ma JF (2010) Gene limiting cadmium accumulation in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:16500–16505
UNEP (United Nations Environmental Programme) (2008) Draft final review of scientific information on cadmium. http://www.chem.unep.ch/Pb_and_Cd/SR/Draft_final_reviews/Cd_Review/Final_UNEP_Cadmium_review_Nov_2008.pdf. Accessed 30 Sept 2018
Van der Vliet L, Peterson C, Hale B (2007) Cd accumulation in roots and shoots of durum wheat: the roles of transpiration rate and apoplastic bypass. J Exp Bot 58:2939–2947
Yadav R, Flowers TJ, Yeo AR (1996) The involvement of the transpirational bypass flow in sodium uptake by high- and low-sodium-transporting lines of rice developed through intravarietal selection. Plant Cell Environ 19:329–336
Yan GC, Fan XP, Tan L, Yin C, Li TQ, Liang YC (2021) Root silicon deposition and its resultant reduction of sodium bypass flow is modulated by OsLsi1 and OsLsi2 in rice. Plant Physiol Biochem 158:219–227
Yeo AR, Yeo ME, Flowers TJ (1987) The contribution of an apoplastic pathway to sodium uptake by rice roots in saline condition. J Exp Bot 38:1141–1153
Yeo AR, Flowers SA, Rao G, Welfare K, Senanayake N, Flowers TJ (1999) Silicon reduces sodium uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.) in saline conditions and this is accounted for by a reduction in the transpirational bypass flow. Plant Cell Environ 22:559–565
Zhang J, Li C, Wu C, Xiong L, Chen G, Zhang Q, Wang S (2006) RMD: a rice mutant database for functional analysis of the rice genome. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D745–D748
Acknowledgements
ICP analysis and histochemical analysis were helped by Ms. Sanae Rikiishi and Ms. Chiemi Hasegawa (Institute of Plant Science and Resource, Okayama University). The authors thank Dr. Jian Feng Ma and Rice Mutant Database for providing the mutant seeds. This study was funded by The Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI (17078006 to Y.M. and I.C.M).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mori, I.C., Arias-Barreiro, C.R., Ooi, L. et al. Cadmium uptake via apoplastic bypass flow in Oryza sativa. J Plant Res 134, 1139–1148 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-021-01319-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-021-01319-y