Abstract
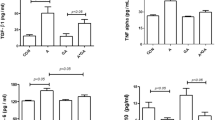
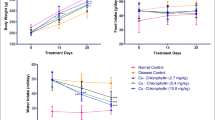
This study aimed to evaluate the protective effects of camel milk (CM) and allopurinol in an adenine-induced acute renal failure (ARF) model in rats. Rats received adenine oral gavage and were treated with either CM (33 mL/kg) or allopurinol (50 mg/kg) for ten consecutive days. Urine and blood samples were collected on the 1st, 5th, and 10th days of the experiment. Renal tissues were collected for oxidative stress and histopathological change analysis. Adenine induced ARF as indicated by a significant decrease in glomerular filtration rate, heavy proteinuria, hyperuricemia, and histological alterations. Serum concentrations of urea, uric acid, serum osmolarity, and urine output were significantly increased, while urine osmolarity was significantly decreased in the adenine-treated rats. Furthermore, in the adenine group, catalase and superoxide dismutase activities and total thiol content were significantly lower, and MDA concentration was significantly higher than the control group. Treatment with CM and allopurinol improved renal function, attenuated structural lesions, and ameliorated oxidative stress in renal tissues. The results indicated that CM and, more effectively, allopurinol were able to protect against adenine-induced kidney injury, possibly by lowering uric acid. Therefore, as a valuable nutrition, CM could be useful in the protection of the kidney against adenine-induced ARF.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abbas S, Ashraf H, Nazir A, Sarfraz L (2013) Physico-chemical analysis and composition of camel milk. Int Res 2:85–98
Abrhaley A, Leta S (2018) Medicinal value of camel milk and meat. J Appl Anim Res 46:552–558. https://doi.org/10.1080/09712119.2017.1357562
Aebi H (1984) [13] Catalase in vitro. In: Methods in enzymology, vol 105. Academic Press, pp 121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Afifi ME (2010) Effect of camel’s milk on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in Swiss Albino mice. Am J Biochem Biotechnol 6:147. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajbbsp.2010.141.147
Al-Asmari AK, Abbasmanthiri R, Al-Elewi AM, Al-Omani S, Al-Asmary S, Al-Asmari SA (2014) Camel milk beneficial effects on treating gentamicin induced alterations in rats. J Toxicol 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/917608
Al-Hashem F (2009) Camel’s milk protects against aluminum chloride-induced normocytic normocromic anemia, lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress in erythrocytes of white albino rats. Am J Biochem Biotechnol 5:127–136. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajbbsp.2009.127.136
Al-Humaid A, Mousa H, El-Mergawi R, Abdel-Salam A (2010) Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of dates and dates-camel-milk mixtures as a protective meal against lipid peroxidation in rats. Am J Food Technol 5:22–30. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajft.2010.22.30
Ali BH et al (2013) Effect of gum arabic on oxidative stress and inflammation in adenine–induced chronic renal failure in rats. PLoS One 8:e55242. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055242
Ali BH et al (2010) Effects of Gum Arabic in rats with adenine-induced chronic renal failure. Exp Biol Med 235:373–382
Augustin AJ, Böker T, Blumenröder SH, Lutz J, Spitznas M (1994) Free radical scavenging and antioxidant activity of allopurinol and oxypurinol in experimental lens-induced uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 35:3897–3904
Bao YW, Yuan Y, Chen JH, Lin WQ (2018) Kidney disease models: tools to identify mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Zool Res 39:72–86. https://doi.org/10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2017.055
Chang XY, Cui L, Wang XZ, Zhang L, Zhu D, Zhou XR, Hao LR (2017) Quercetin attenuates vascular calcification through suppressed oxidative stress in adenine-induced chronic renal failure rats. Biomed Res Int 2017:5716204. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5716204
Diwan V, Mistry A, Gobe G, Brown L (2013) Adenine-induced chronic kidney and cardiovascular damage in rats. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 68:197–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vascn.2013.05.006
Dziuba B, Dziuba M (2014) Milk proteins-derived bioactive peptides in dairy products: molecular, biological and methodological aspects. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment 13:5–25. https://doi.org/10.17306/j.afs.2014.1.1
Evenepoel P (2004) Acute toxic renal failure. Best Pract Res Clin 18:37–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpa.2003.09.007
Goicoechea M et al (2010) Effect of allopurinol in chronic kidney disease progression and cardiovascular risk. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:1388–1393. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.01580210
Gómez A (2007) Acute Renal failure in the transretinoic syndrome. Nefrología (English Edition) 27:184–190
Hailu Y, Hansen EB, Seifu E, Eshetu M, Ipsen R, Kappeler S (2016) Functional and technological properties of camel milk proteins: a review. J Dairy Res 83:422–429. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022029916000686
Hosseinian S et al (2018) Nigella sativa extract is a potent therapeutic agent for renal inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress in a rat model of unilateral ureteral obstruction. Phytother Res 32:2290–2298. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6169
Kinugasa Y et al (2003) Allopurinol improves cardiac dysfunction after ischemia-reperfusion via reduction of oxidative stress in isolated perfused rat hearts. Circ J 67:781–787. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.67.781
Korish AA, Abdel Gader AG, Korashy HM, Al-Drees AM, Alhaider AA, Arafah MM (2015) Camel milk attenuates the biochemical and morphological features of diabetic nephropathy: Inhibition of Smad1 and collagen type IV synthesis. Chem Biol Interact 229:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2015.01.013
Kumar A, Singh G, Kumar BVS, Meur SK (2011) Modulation of antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in erythrocyte by dietary supplementation during heat stress in buffaloes. Livest Sci 138:299–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.livsci.2010.12.021
Lieberthal W, Nigam SK (2000) Acute renal failure. II Experimental Models of Acute Renal Failure: Imperfect but Indispensable. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 278:F1-f12. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.2000.278.1.F1
Morishita Y, Ohnishi A, Watanabe M, Ishibashi K, Kusano E (2011) Establishment of acute kidney injury mouse model by 0.75% adenine ingestion. Ren Fail 33:1013–1018. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2011.618906
Navarro I, Poveda R, Torras J, Castelao AM, Grinyó JM (2007) Acute renal failure associated to renin–angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors: its burden in a nephrology department. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:413–414. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfm612
Perazella MA (1999) Crystal-Induced Acute Renal Failure. Am J Med 106:459–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9343(99)00041-8
Salami M et al (2011) Biological activity of camel milk casein following enzymatic digestion. J Dairy Res 78:471–478. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022029911000628
Salwa MQ, Lina AF (2010) Antigenotoxic and anticytotoxic effect of camel milk in mice treated with cisplatin Saudi. J Biol Sci 17:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2010.02.010
Samadi-Noshahr Z, Hadjzadeh MAR, Moradi-Marjaneh R, Khajavi-Rad A (2021) The hepatoprotective effects of fennel seeds extract and trans-Anethole in streptozotocin-induced liver injury in rats. Food Sci Nutr 9:1121–1131. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.2090
Santos IFD, Sheriff S, Amlal S, Ahmed RPH, Thakar CV, Amlal H (2019) Adenine acts in the kidney as a signaling factor and causes salt- and water-losing nephropathy: early mechanism of adenine-induced renal injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 316:F743–F757. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00142.2018
Schrier RW, Wang W (2004) Acute renal failure and sepsis. N Engl J Med 351:159–169. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra032401
Sikka SC (1996) Oxidative stress and role of antioxidants in normal and abnormal sperm function. Front Biosci 1:e78-86. https://doi.org/10.2741/a146
Simsek M, Opperman RCM, Mulder CJJ, Lambalk CB, de Boer NKH (2018) The teratogenicity of allopurinol: a comprehensive review of animal and human studies. Reprod Toxicol 81:180–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2018.08.012
Singh AP, Junemann A, Muthuraman A, Jaggi AS, Singh N, Grover K, Dhawan R (2012) Animal models of acute renal failure. Pharmacol Rep 64:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1734-1140(12)70728-4
Sreedharan R, Devarajan P, Van Why SK (2009) Pathogenesis of acute renal failure. In: Avner E, Harmon W, Niaudet P, Yoshikawa N (eds) Pediatric nephrology: sixth completely revised, Updated and Enlarged Edition. Springer, Berlin, pp 1579–1602
Star RA (1998) Treatment of acute renal failure. Kidney Int 54:1817–1831. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.1998.00210.x
Wan L, Bagshaw SM, Langenberg C, Saotome T, May C, Bellomo R (2008) Pathophysiology of septic acute kidney injury: what do we really know? Crit Care Med 36:S198-203. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e318168ccd5
Yokozawa T, Zheng PD, Oura H, Koizumi F (1986) Animal model of adenine-induced chronic renal failure in rats. Nephron 44:230–234. https://doi.org/10.1159/000183992
Zhang D, Liu H, Luo P, Li Y (2018) production inhibition and excretion promotion of urate by fucoidan from laminaria japonica in adenine-induced hyperuricemic mice. Mar Drugs. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16120472
Zhu W, Pang M, Dong L, Huang X, Wang S, Zhou L (2012) Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of iridoid glycosides from Paederia scandens (LOUR.) MERRILL (Rubiaceae) on uric acid nephropathy rats. Life Sci 91:369–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2012.08.013
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Research Council of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences for their financial support.
Funding
The research leading to these results received funding from Research Council of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences under Grant Agreement No.: 971797.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA contributed to acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data for the work. ZSN contributed to conception, writing—original draft and acquisition of the work. SH contributed to conception, acquisition and supervision of the work. HS contributed to investigation of the work. MN contributed to conception of the work. AKR contributed to conception and design, supervision, funding acquisition, interpretation of data of the work and revising it critically for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. All persons designated as authors qualify for authorship, and all those who qualify for authorship are listed.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical Approval
All the experimental procedure were approved by the ethical committee of the Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (Approval Code: IR.MUMS.MEDICAL.REC.1398.210).
Additional information
Co-first author: Zahra Samadi-Noshahr.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allahyari, M., Samadi-Noshahr, Z., Hosseinian, S. et al. Camel Milk and Allopurinol Attenuated Adenine-induced Acute Renal Failure in Rats. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 45, 1539–1548 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-021-01155-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-021-01155-8