Abstract
This paper proposes a new framework for epileptic seizure detection using non-invasive scalp electroencephalogram (sEEG) signals. The major innovation of the current study is using the Riemannian geometry for transforming the covariance matrices estimated from the EEG channels into a feature vector. The spatial covariance matrices are considered as features in order to extract the spatial information of the sEEG signals without applying any spatial filtering. Since these matrices are symmetric and positive definite (SPD), they belong to a special manifold called the Riemannian manifold. Furthermore, a kernel based on Riemannian geometry is proposed. This kernel maps the SPD matrices onto the Riemannian tangent space. The SPD matrices, obtained from all channels of the segmented sEEG signals, have high dimensions and extra information. For these reasons, the sequential forward feature selection method is applied to select the best features and reduce the computational burden in the classification step. The selected features are fed into a support vector machine (SVM) with an RBF kernel to classify the feature vectors into seizure and non-seizure classes. The performance of the proposed method is evaluated using two long-term scalp EEG (CHB-MIT benchmark and private) databases. Experimental results on all 23 subjects of the CHB-MIT database reveal an accuracy of 99.87%, a sensitivity of 99.91%, and a specificity of 99.82%. In addition, the introduced algorithm is tested on the private sEEG signals recorded from 20 patients, having 1380 seizures. The proposed approach achieves an accuracy, a sensitivity, and a specificity of 98.14%, 98.16%, and 98.12%, respectively. The experimental results on both sEEG databases demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method for automated epileptic seizure detection, especially for the private database which has noisier signals in comparison to the CHB-MIT database.

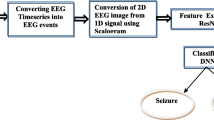
Block diagram of the proposed epileptic seizure detection algorithm






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya UR, Sree SV, Swapna G, Martis RJ, Suri JS (2013) Automated EEG analysis of epilepsy: a review. Knowl-Based Syst 45:147–165
Song J-L, Li Q, Pan M, Zhang B, Westover MB, Zhang R (2020) Seizure tracking of epileptic eegs using a model-driven approach. J Neural Eng 17(1):016024
Vidyaratne LS, Iftekharuddin KM (2017) Real-time epileptic seizure detection using EEG. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehab Eng 25(11):2146–2156
Islam MK, Rastegarnia A, Yang Z (2015) A wavelet-based artifact reduction from scalp EEG for epileptic seizure detection. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 20(5):1321–1332
Aldana YR, Hunyadi B, Reyes EJM, Rodríguez VR, Van Huffel S (2018) Nonconvulsive epileptic seizure detection in scalp EEG using multiway data analysis. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 23(2):660–671
Sadatnejad K, Rahmati M, Rostami R, Kazemi R, Ghidary SS, Müller A, Alimardani F (2019) Eeg representation using multi-instance framework on the manifold of symmetric positive definite matrices. J Neural Eng 16(3):036016
Misulis KE (2013) Atlas of eeg, seizure semiology, and management. Oxford University Press
Yuan Y, Xun G, Jia K, Zhang A (2018) A multi-view deep learning framework for EEG seizure detection. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 23(1):83–94
Zabihi M, Kiranyaz S, Jantti V, Lipping T, Gabbouj M (2019) Patient-specific seizure detection using nonlinear dynamics and nullclines. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics
Li Y, Wang X-D, Luo M-L, Li K, Yang X-F, Guo Q (2017) Epileptic seizure classification of EEGs using time–frequency analysis based multiscale radial basis functions. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 22(2):386–397
Zavar M, Rahati S, Akbarzadeh-T M-R, Ghasemifard H (2011) Evolutionary model selection in a wavelet-based support vector machine for automated seizure detection. Expert Syst Appl 38 (9):10751–10758
Khan YU, Rafiuddin N, Farooq O (2012) Automated seizure detection in scalp EEG using multiple wavelet scales. In: 2012 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Computing and Control (ISPCC). IEEE, pp 1–5
Xiang J, Li C, Li H, Cao R, Wang B, Han X, Chen J (2015) The detection of epileptic seizure signals based on fuzzy entropy. J Neurosci Methods 243:18–25
Ivanov A, Riccardi G (2012) Kolmogorov-smirnov test for feature selection in emotion recognition from speech. In: Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2012 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, pp 5125–5128
Zandi AS, Javidan M, Dumont GA, Tafreshi R (2010) Automated real-time epileptic seizure detection in scalp EEG recordings using an algorithm based on wavelet packet transform. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(7):1639–1651
Shoeb AH (2009) Application of machine learning to epileptic seizure onset detection and treatment. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Barachant A, Bonnet S, Congedo M, Jutten C (2013) Classification of covariance matrices using a riemannian-based kernel for bci applications. Neurocomputing 112:172–178
Kaleem M, Gurve D, Guergachi A, Krishnan S (2018) Patient-specific seizure detection in long-term eeg using signal-derived empirical mode decomposition (emd)-based dictionary approach. J Neural Eng 15(5):056004
Wang Y, Qi Y, Wang Y, Lei Z, Zheng X, Pan G (2016) Delving into α-stable distribution in noise suppression for seizure detection from scalp eeg. J Neural Eng 13(5):056009
Yuan S, Zhou W, Wu Q, Zhang Y (2016) Epileptic seizure detection with log-euclidean gaussian kernel-based sparse representation. Int J Neural Syst 26(03):1650011
Bolagh SNG, Clifford G, et al. (2017) Subject selection on a riemannian manifold for unsupervised cross-subject seizure detection. arXiv:1712.00465
Bakhshali MA, Khademi M, Ebrahimi-Moghadam A, Moghimi S (2020) Eeg signal classification of imagined speech based on riemannian distance of correntropy spectral density. Biomed Signal Process Control 59:101899
Goldberger AL, Amaral Luis AN, Glass L, Hausdorff JM, Ivanov PC, Mark RG, Mietus JE, Moody GB, Peng C-K, Stanley HE (2000) Physiobank, physiotoolkit, and physionet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101(23):e215–e220
Fingelkurts AA, Fingelkurts AA, Kaplan AY (2006) Interictal eeg as a physiological adaptation. part i. composition of brain oscillations in interictal eeg. Clin Neurophysiol 117(1):208–222
Tuzel O, Porikli F, Meer P (2008) Pedestrian detection via classification on riemannian manifolds. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell (10):1713–1727
Barachant A, Bonnet S, Congedo M, Jutten C (2012) Multiclass brain–computer interface classification by riemannian geometry. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59(4):920–928
Zarei A, Asl BM (2020) Automatic classification of apnea and normal subjects using new features extracted from HRV and ECG-derived respiration signals. Biomed Signal Process Control 59:101927
Zarei A, Asl BM (2018) Automatic detection of obstructive sleep apnea using wavelet transform and entropy-based features from single-lead ECG signal. IEEE J Biomed Health Inf 23(3):1011–1021
Gu X, Guo J, Xiao L, Ming T, Li C (2019) A feature selection algorithm based on equal interval division and minimal-redundancy–maximal-relevance. Neural Process Lett:1–27
Kaya GT, Kaya H (2014) Optimization of svm parameters using high dimensional model representation and its application to hyperspectral images. In: Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), 2014 22nd. IEEE, pp 642–645
Wang D, Miao D, Blohm G (2013) A new method for EEG-based concealed information test. IEEE Trans Inf Forensic Secur 8(3):520–527
De Sá JPM (2007) Applied statistics using spss, statistica, matlab and r. Springer Science & Business Media
Hunyadi B, Signoretto M, Van Paesschen W, Suykens JAK, Van Huffel S, De Vos M (2012) Incorporating structural information from the multichannel eeg improves patient-specific seizure detection. Clin Neurophysiol 123(12):2352–2361
Chen L-L, Zhang J, Zou J-Z, Zhao C-J, Wang G-S (2014) A framework on wavelet-based nonlinear features and extreme learning machine for epileptic seizure detection. Biomed Signal Process Control 10:1–10
Kiranyaz S, Ince T, Zabihi M, Ince D (2014) Automated patient-specific classification of long-term electroencephalography. J Biomed Inf 49:16–31
Fürbass F, Ossenblok P, Hartmann M, Perko H, Skupch AM, Lindinger G, Elezi L, Pataraia E, Colon AJ, Baumgartner C, et al. (2015) Prospective multi-center study of an automatic online seizure detection system for epilepsy monitoring units. Clin Neurophysiol 126(6):1124–1131
Fergus P, Hignett D, Hussain A, Al-Jumeily D, Abdel-Aziz K (2015) Automatic epileptic seizure detection using scalp EEG and advanced artificial intelligence techniques. Biomed Research International 2015
Samiee K, Kiranyaz S, Gabbouj M, Saramäki T (2015) Long-term epileptic EEG classification via 2d mapping and textural features. Expert Syst Appl 42(20):7175–7185
Zabihi M, Kiranyaz S, Rad AB, Katsaggelos A K, Gabbouj M, Ince T (2016) Analysis of high-dimensional phase space via poincaré section for patient-specific seizure detection. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehab Eng 24(3):386–398
Zarei A, Asl B M (2021) Automatic seizure detection using orthogonal matching pursuit, discrete wavelet transform, and entropy based features of EEG signals. Comput Biol Med 131:104250
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shariat, A., Zarei, A., Karvigh, S.A. et al. Automatic detection of epileptic seizures using Riemannian geometry from scalp EEG recordings. Med Biol Eng Comput 59, 1431–1445 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-021-02385-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-021-02385-z