Abstract
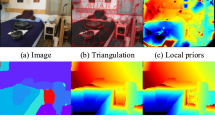
In multi-view stereo, unreliable matching in low-textured regions has a negative impact on the completeness of reconstructed models. Since the photometric consistency of low-textured regions is not discriminative under a local window, non-local information provided by the Markov Random Field (MRF) model can alleviate the matching ambiguity but is limited in continuous space with high computational complexity. Owing to its sampling and propagation strategy, PatchMatch multi-view stereo methods have advantages in terms of optimizing the continuous labeling problem. In this paper, we propose a novel method to address this problem, namely the Coarse-Hypotheses Guided Non-Local PatchMatch Multi-View Stereo (CNLPA-MVS), which takes the advantages of both MRF-based non-local methods and PatchMatch multi-view stereo and compensates for their defects mutually. First, we combine dynamic programing (DP) and sequential propagation along scanlines in parallel to perform CNLPA-MVS, thereby obtaining the optimal depth and normal hypotheses. Second, we introduce coarse inference within a universal window provided by winner-takes-all to eliminate the stripe artifacts caused by DP and improve completeness. Third, we add a local consistency strategy based on the hypotheses of similar color pixels sharing approximate values into CNLPA-MVS for further improving completeness. CNLPA-MVS was validated on public benchmarks and achieved state-of-the-art performance with high completeness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xiao X, Xu C, Wang J, Xu M. Enhanced 3-D modeling for landmark image classification. IEEE Trans. Multim., 2012, 14(4): 1246-1258. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2012.2190384.
Forster C, Pizzoli M, Scaramuzza D. Air-ground localization and map augmentation using monocular dense reconstruction. In Proc. the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Sept. 2014, pp.3971-3978. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2013.6696924.
Hedman P, Alsisan S, Szeliski R, Kopf J. Casual 3D photography. ACM Trans. Graph., 2017, 36(6): Article No. 234. https://doi.org/10.1145/3130800.3130828.
Knapitsch A, Park J, Zhou Q Y, Koltun V. Tanks and temples: Benchmarking large-scale scene reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph., 2017, 36(4): Article No. 78. https://doi.org/10.1145/3072959.3073599.
Schöps T, Schönberger J L, Galliani S, Sattler T, Schindler K, Pollefeys M, Geiger A. A multi-view stereo benchmark with high resolution images and multicamera videos. In Proc. the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Jul. 2017, pp.2538-2547. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.272.
Strecha C, Von Hansen W, Van Gool L, Fua P, Thoennessen U. On benchmarking camera calibration and multiview stereo for high resolution imagery. In Proc. the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Jun. 2008. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2008.4587706.
Huang P, Matzen K, Kopf J, Ahuja N, Huang J. DeepMVS: Learning multi-view stereopsis. In Proc. the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Jun. 2018, pp.2821-2830. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00298.
Luo K, Guan T, Ju L, Huang H, Luo Y. P-MVSNet: Learning patch-wise matching confidence aggregation for multiview stereo. In Proc. the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, October 27–November 2, 2019, pp.10451-10460. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.01055.
Yao Y, Luo Z, Li S, Fang T, Quan L. MVSNet: Depth inference for unstructured multi-view stereo. In Proc. the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Sept. 2018, pp.785-801. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01237-3_47.
Campbell N D F, Vogiatzis G, Hernández C, Cipolla R. Using multiple hypotheses to improve depth maps for multi-view stereo. In Proc. the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision, Oct. 2008, pp.766-779. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-88682-2_58.
Woodford O J, Torr P H S, Reid I, Fitzgibbon A W. Global stereo reconstruction under second-order smoothness priors. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2009, 31(12): 2115-2128. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2009.131.
Schönberger J L, Zheng E, Frahm J, Pollefeys M. Pixelwise view selection for unstructured multi-view stereo. In Proc. the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Oct. 2016, pp.501-518. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46487-9_31.
Galliani S, Lasinger K, Schindler K. Massively parallel multiview stereopsis by surface normal diffusion. In Proc. the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Dec. 2015, pp.873-881. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.106.
Xu Q, Tao W. Multi-scale geometric consistency guided multi-view stereo. In Proc. the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Jun. 2019, pp. 5483-5492. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00563.
Bleyer M, Rhemann C, Rother C. PatchMatch stereo—Stereo matching with slanted support windows. In Proc. British Machine Vision Conference, August 29–September 2, 2011. https://doi.org/10.5244/C.25.14.
Besse F, Rother C, Fitzgibbon A W, Kautz J. PMBP: PatchMatch belief propagation for correspondence field estimation. Int. J. Comput. Vis., 2014, 110(1): 2-13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-013-0653-9.
Heise P, Klose S, Jensen B, Knoll A C. PM-Huber: PatchMatch with huber regularization for stereo matching. In Proc. the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Dec. 2013, pp.2360-2367. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2013.293.
Li L, Zhang S, Yu X, Zhang L. PMSC: PatchMatch-based superpixel cut for accurate stereo matching. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol., 2018, 28(3): 679-692. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2016.2628782.
Liao J, Fu Y, Yan Q, Xiao C. Pyramid multi-view stereo with local consistency. Comput. Graph. Forum, 2019, 38(7): 335-346. https://doi.org/10.1111/cgf.13841.
Zheng E, Dunn E, Jojic V, Frahm J. PatchMatch based joint view selection and depthmap estimation. In Proc. the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Jun. 2014, pp.1510-1517. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.196.
Furukawa Y, Ponce J. Accurate, dense, and robust multiview stereopsis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2010, 32(8): 1362-1376. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2009.161.
Locher A, Perdoch M, van Gool L. Progressive prioritized multiview stereo. In Proc. the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Jun. 2016, pp.3244-3252. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.353.
Vogiatzis G, Esteban C H, Torr P H S, Cipolla R. Multiview stereo via volumetric graph-cuts and occlusion robust photo-consistency. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2007, 29(12): 2241-2246. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2007.70712.
Ulusoy A O, Geiger A, Black M J. Towards probabilistic volumetric reconstruction using ray potentials. In Proc. the 2015 International Conference on 3D Vision, Oct. 2015, pp.10-18. https://doi.org/10.1109/3DV.2015.9.
Vu H H, Labatut P, Pons J P, Keriven R. High accuracy and visibility-consistent dense multiview stereo. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2012, 34(5): 889-901. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2011.172.
Seitz S M, Curless B, Diebel J, Scharstein D, Szeliski R. A comparison and evaluation of multi-view stereo reconstruction algorithms. In Proc. the 2006 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Jun. 2006, pp.519-528. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2006.19.
Furukawa Y, Hernandez C. Multi-View Stereo: A Tutorial. Now Publishers Inc., 2015. https://doi.org/10.1561/0600000052.
Barnes C, Shechtman E, Finkelstein A, Goldman D B. PatchMatch: A randomized correspondence algorithm for structural image editing. ACM Trans. Graph., 2009, 28(3): Article No. 24. https://doi.org/10.1145/1531326.1531330.
Barnes C, Zhang F, Lou L, Wu X, Hu S. PatchTable: Efficient patch queries for large datasets and applications. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2015, 34(4): Article No. 97. https://doi.org/10.1145/2766934.
Barnes C, Zhang F. A survey of the state-of-the-art in patch-based synthesis. Computational Visual Media, 2017, 3(1): 3-20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41095-016-0064-2.
Wei J, Resch B, Lensch H P A. Multi-view depth map estimation with cross-view consistency. In Proc. the 2014 British Machine Vision Conference, Sept. 2014. https://doi.org/10.5244/C.28.76.
Romanoni A, Matteucci M. TAPA-MVS: Textureless-aware PAtchMatch multi-view stereo. In Proc. the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Oct. 27–Nov. 2, 2019, pp.10412-10421. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.01051.
Xu Q, Tao W. Planar prior assisted PatchMatch multiview stereo. In Proc. the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Feb. 2020, pp.12516-12523. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6940.
Xu Z, Liu Y, Shi X, Wang Y, Zheng Y. MARMVS: Matching ambiguity reduced multiple view stereo for efficient large scale scene reconstruction. In Proc. the 2010 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Jun. 2020, pp.5980-5989. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00602.
Boykov Y, Veksler O, Zabih R. Fast approximate energy minimization via graph cuts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2001, 23(11): 1222-1239. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.969114.
Taniai T, Matsushita Y, Naemura T. Graph cut based continuous stereo matching using locally shared labels. In Proc. the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Jun. 2014, pp.1613-1620. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2014.209.
Ogawara K. Approximate belief propagation by hierarchical averaging of outgoing messages. In Proc. the 20th IEEE International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Aug. 2010, pp.1368-1372. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR.2010.338.
Yu T, Lin R, Super B J, Tang B. Efficient message representations for belief propagation. In Proc. the 11th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Oct. 2007. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2007.4408905.
Hallek M, Smach F, Atri M. Real-time stereo matching on CUDA using Fourier descriptors and dynamic programming. Computational Visual Media, 2019, 5(1): 59-71. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41095-019-0133-4.
Kolmogorov V, Zabih R. Computing visual correspondence with occlusions via graph cuts. In Proc. International Conference on Computer Vision, Jul. 2001, pp.508-515. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2001.937668.
Klaus A, Sormann M, Karner K F. Segment-based stereo matching using belief propagation and a self-adapting dissimilarity measure. In Proc. the 18th IEEE International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Aug. 2006, pp.15-18. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR.2006.1033.
Wang W, Hu L, Hu Z. Energy-based multi-view piecewise planar stereo. Sci. China Inf. Sci., 2017, 60(3): Article No. 32101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-015-0710-5.
Neal R M, Hinton G E. A view of the EM algorithm that justifies incremental, sparse, and other variants. In Learning in Graphical Models, Jordan M I (ed.), Springer, 1998, pp.355-368. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-5014-9_12.
Kopf J, Cohen M F, Lischinski D, Uyttendaele M. Joint bilateral upsampling. ACM Trans. Graph., 2007, 26(3): Article No. 96. https://doi.org/10.1145/1276377.1276497.
Li Y, Min D, Brown M S, Do M N, Lu J. SPM-BP: Sped-up PatchMatch belief propagation for continuous MRFs. In Proc. the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Dec. 2015, pp.4006-4014. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.456.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 900 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Luo, S., Wang, L. et al. CNLPA-MVS: Coarse-Hypotheses Guided Non-Local PatchMatch Multi-View Stereo. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 36, 572–587 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-021-1299-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11390-021-1299-7