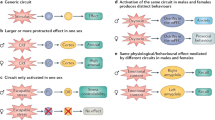
Abstract
Rationale
Anxiety, a negative state of high arousal and vigilance, is especially prevalent in women, making identification of underlying mechanisms critical for developing effective therapies. With the challenge of disentangling biological and social factors in humans, animal tests can provide valuable insights, although such tests, developed in males, have unclear validity for females.
Objective
To better understand patterns of sex differences across multiple measures within two classical rodent anxiety tests.
Methods
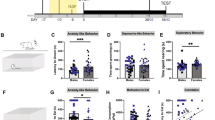
We examined female and male adult Wistar rats (n = 15–18/group) that were single-housed in the novelty suppression of feeding test (NSFT) that involves food under a bright light in food-restricted animals, and light–dark test (LDT), which reflects innate aversion to bright light. To further validate these tests in females, we also examined the impact of 1 mg/kg diazepam.
Results
NSFT measures of the most direct interaction with food, latency to grab food and food consumed, indicated increased anxiety-like behavior in females versus males, with diazepam altering these behaviors in females but not males. Most other measures showed more similar effects of diazepam across the sexes, with some evidence of reduced anxiety-like behavior in LDT for females. Principal component analyses indicated limited relationships across behavioral factors, underscoring previous suggestions of the importance of assessing multiple measures to maximize information and ethological relevance.
Conclusions
Combining our findings and previous studies, we speculate that increased anxiety-like behavior in females manifests especially when there is a specific, life-relevant condition (e.g., food in the NSFT). Our findings also validate NSFT and LDT use in females.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramov U, Raud S, Koks S, Innos J, Kurrikoff K, Matsui T, Vasar E (2004) Targeted mutation of CCK(2) receptor gene antagonises behavioural changes induced by social isolation in female, but not in male mice. Behav Brain Res 155:1–11
Acevedo MB, Nizhnikov ME, Molina JC, Pautassi RM (2014) Relationship between ethanol-induced activity and anxiolysis in the open field, elevated plus maze, light-dark box, and ethanol intake in adolescent rats. Behav Brain Res 265:203–215
Albonetti ME, Farabollini F (1995) Effects of single restraint on the defensive behavior of male and female rats. Physiol Behav 57:431–437
Albrechet-Souza L, Schratz CL, Gilpin NW (2020) Sex differences in traumatic stress reactivity in rats with and without a history of alcohol drinking. Biol Sex Differ 11:27–38
Altemus M, Sarvaiya N, Neill EC (2014) Sex differences in anxiety and depression clinical perspectives. Front Neuroendocrinol 35:320–330
Amodeo LR, Wills DN, Sanchez-Alavez M, Nguyen W, Conti B, Ehlers CL (2018) Intermittent voluntary ethanol consumption combined with ethanol vapor exposure during adolescence increases drinking and alters other behaviors in adulthood in female and male rats. Alcohol 73:57–66
Bangasser DA, Wicks B (2017) Sex-specific mechanisms for responding to stress. J Neurosci Res 95:75–82
Baratta MV, Leslie NR, Fallon IP, Dolzani SD, Chun LE, Tamalunas AM, Watkins LR, Maier SF (2018) Behavioural and neural sequelae of stressor exposure are not modulated by controllability in females. Eur J Neurosci 47:959–967
Becker JB, Chartoff E (2019) Sex differences in neural mechanisms mediating reward and addiction. Neuropsychopharm 44:166–183
Belviranli M, Atalik KE, Okudan N, Gokbel H (2012) Age and sex affect spatial and emotional behaviors in rats: the role of repeated elevated plus maze test. Neuroscience 227:1–9
Blasco-Serra A, Gonzalez-Soler EM, Cervera-Ferri A, Teruel-Marti V, Valverde-Navarro AA (2017) A standardization of the novelty-suppressed feeding test protocol in rats. Neurosci Lett 658:73–78
Bodnoff SR, Suranyi-Cadotte B, Quirion R, Meaney MJ (1989) A comparison of the effects of diazepam versus several typical and atypical anti-depressant drugs in an animal model of anxiety. Psychopharm 97:277–279
Bourin M, Hascoet M (2003) The mouse light/dark box test. Eur J Pharmacol 463:55–65
Chaouloff F, Durand M, Mormede P (1997) Anxiety- and activity-related effects of diazepam and chlordiazepoxide in the rat light/dark and dark/light tests. Behav Brain Res 85:27–35
Chisholm D, Sweeny K, Sheehan P, Rasmussen B, Smit F, Cuijpers P, Saxena S (2016) Scaling-up treatment of depression and anxiety: a global return on investment analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 3:415–424
Dalla C, Antoniou K, Drossopoulou G, Xagoraris M, Kokras N, Sfikakis A, Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z (2005) Chronic mild stress impact: are females more vulnerable? Neuroscience 135:703–714
De Jesus-Burgos MI, Gonzalez-Garcia S, Cruz-Santa Y, Perez-Acevedo NL (2016) Amygdalar activation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors produces anti- and pro-conflict effects depending upon animal sex in a sexually dimorphic conditioned conflict-based anxiety model. Behav Brain Res 302:200–212
Donner NC, Lowry CA (2013) Sex differences in anxiety and emotional behavior. Pflugers Arch 465:601–626
Du Preez A, Law T, Onorato D, Lim YM, Eiben P, Musaelyan K, Egeland M, Hye A, Zunszain PA, Thuret S, Pariante CM, Fernandes C (2020) The type of stress matters: repeated injection and permanent social isolation stress in male mice have a differential effect on anxiety- and depressive-like behaviours, and associated biological alterations. Transl Psychiatry 10:325–242
Fernandes C, Gonzalez MI, Wilson CA, File SE (1999) Factor analysis shows that female rat behaviour is characterized primarily by activity, male rats are driven by sex and anxiety. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 64:731–738
Fleming W, Jones Q, Chandra U, Saini A, Walker D, Francis R, Ocampo G, Kuhn C (2019) Withdrawal from brief repeated alcohol treatment in adolescent and adult male and female rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 43:204–211
Gobinath AR, Wong S, Chow C, Lieblich SE, Barr AM, Galea LAM (2018) Maternal exercise increases but concurrent maternal fluoxetine prevents the increase in hippocampal neurogenesis of adult offspring. Psychoneuroendo 91:186–197
Gonzalez LE, File SE (1997) A five minute experience in the elevated plus-maze alters the state of the benzodiazepine receptor in the dorsal raphe nucleus. J Neurosci 17:1505–1511
Griebel G, Perrault G, Sanger DJ (1997) CCK receptor antagonists in animal models of anxiety: comparison between exploration tests, conflict procedures and a model based on defensive behaviours. Behav Pharmacol 8:549–560
Heinrich LM, Gullone E (2006) The clinical significance of loneliness: a literature review. Clin Psychol Rev 26:695–718
Henricks AM, Berger AL, Lugo JM, Baxter-Potter LN, Bieniasz KV, Petrie G, Sticht MA, Hill MN, McLaughlin RJ (2017) Sex- and hormone-dependent alterations in alcohol withdrawal-induced anxiety and corticolimbic endocannabinoid signaling. Neuropharm 124:121–133
Homberg JR, Olivier JD, Blom T, Arentsen T, van Brunschot C, Schipper P, Korte-Bouws G, van Luijtelaar G, Reneman L (2011) Fluoxetine exerts age-dependent effects on behavior and amygdala neuroplasticity in the rat. PLoS One 6:e16646–e16656
Hughes RN (2011) Adult anxiety-related behavior of rats following consumption during late adolescence of alcohol alone and in combination with caffeine. Alcohol 45:365–372
Jaric I, Rocks D, Cham H, Herchek A, Kundakovic M (2019) Sex and estrous cycle effects on anxiety- and depression-related phenotypes in a two-hit developmental stress model. Front Mol Neurosci 12:74–89
Johnston AL, File SE (1991) Sex differences in animal tests of anxiety. Physiol Behav 49:245–250
Keeley RJ, Bye C, Trow J, McDonald RJ (2015) Strain and sex differences in brain and behaviour of adult rats: learning and memory, anxiety and volumetric estimates. Behav Brain Res 288:118–131
Kokras N, Dioli C, Paravatou R, Sotiropoulos MG, Delis F, Antoniou K, Calogeropoulou T, Charalampopoulos I, Gravanis A, Dalla C (2020) Psychoactive properties of BNN27, a novel neurosteroid derivate, in male and female rats. Psychopharm 237:2435–2449
Kosobud AE, Wetherill L, Plawecki MH, Kareken DA, Liang T, Nurnberger JL, Windisch K, Xuei X, Edenberg HJ, Foroud TM, O’Connor SJ (2015) Adaptation of subjective responses to alcohol is affected by an interaction of GABRA2 genotype and recent drinking. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 39:1148–1157
Le Moene O, Ramirez-Renteria ML, Agmo A (2020) Male and female immediate fear reaction to white noise in a semi-natural environment: a detailed behavioural analysis of the role of sex and oestrogen receptors. J Neuroendocrinol 32:e12902–e12921
Lopez-Aumatell R, Martinez-Membrives E, Vicens-Costa E, Canete T, Blazquez G, Mont-Cardona C, Johannesson M, Flint J, Tobena A, Fernandez-Teruel A (2011) Effects of environmental and physiological covariates on sex differences in unconditioned and conditioned anxiety and fear in a large sample of genetically heterogeneous (N/Nih-HS) rats. Behav Brain Funct 7:48–63
Martin AL, Brown RE (2010) The lonely mouse: verification of a separation-induced model of depression in female mice. Behav Brain Res 207:196–207
Mead H, Andres E, Katch H, Siegel B, Regenstein M (2010) Gender differences in psychosocial issues affecting low-income, underserved patients’ ability to manage cardiovascular disease. Womens Health Issues 20:308–315
Miragaia AS, de Oliveira Wertheimer GS, Consoli AC, Cabbia R, Longo BM, Girardi CEN, Suchecki D (2018) Maternal deprivation increases anxiety- and depressive-like behaviors in an age-dependent fashion and reduces neuropeptide Y expression in the amygdala and hippocampus of male and female young adult rats. Front Behav Neurosci 12:159–176
Oh JE, Zupan B, Gross S, Toth M (2009) Paradoxical anxiogenic response of juvenile mice to fluoxetine. Neuropsychopharm 34:2197–2207
Olivier JD, Van Der Hart MG, Van Swelm RP, Dederen PJ, Homberg JR, Cremers T, Deen PM, Cuppen E, Cools AR, Ellenbroek BA (2008) A study in male and female 5-HT transporter knockout rats: an animal model for anxiety and depression disorders. Neuroscience 152:573–584
Olvera-Hernandez S, Fernandez-Guasti A (2011) Sex differences in the burying behavior test in middle-aged rats: effects of diazepam. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 99:532–539
Ou C, Dringenberg HC, Soutar CN (2019) Is hippocampal theta frequency related to individual and sex differences in anxiety-like behaviour? An analysis in male and female Long-Evans rats. Behav Brain Res 364:366–373
Palanza P, Gioiosa L, Parmigiani S (2001) Social stress in mice: gender differences and effects of estrous cycle and social dominance. Physiol Behav 73:411–420
Palanza P, Parmigiani S (2017) How does sex matter? Behavior, stress and animal models of neurobehavioral disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 76:134–143
Pereira JK, Vieira RJ, Konishi CT, Ribeiro RA, Frussa-Filho R (1999) The phenomenon of “one-trial tolerance” to the anxiolytic effect of chlordiazepoxide in the elevated plus-maze is abolished by the introduction of a motivational conflict situation. Life Sci 65:PL101–7.
Pisu MG, Garau A, Boero G, Biggio F, Pibiri V, Dore R, Locci V, Paci E, Porcu P, Serra M (2016) Sex differences in the outcome of juvenile social isolation on HPA axis function in rats. Neuroscience 320:172–182
Pittman DW, McGinnis MR, Richardson LM, Miller EJ, Alimohamed ML, Baird JP (2012) Multiple processes underlie benzodiazepine-mediated increases in the consumption of accepted and avoided stimuli. Chem Senses 37:431–444
Pomrenze MB, Millan EZ, Hopf FW, Keiflin R, Maiya R, Blasio A, Dadgar J, Kharazia V, De Guglielmo G, Crawford E, Janak PH, George O, Rice KC, Messing RO (2015) A transgenic rat for investigating the anatomy and function of corticotrophin releasing factor circuits. Front Neurosci 9:487–501
Ramaker MJ, Dulawa SC (2017) Identifying fast-onset antidepressants using rodent models. Mol Psychiatry 22:656–665
Ramos A (2008) Animal models of anxiety: do I need multiple tests? Trends Pharmacol Sci 29:493–498
Roman E, Arborelius L (2009) Male but not female Wistar rats show increased anxiety-like behaviour in response to bright light in the defensive withdrawal test. Behav Brain Res 202:303–307
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S, Weisstaub N, Lee J, Duman R, Arancio O, Belzung C, Hen R (2003) Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 301:805–809
Scholl JL, Afzal A, Fox LC, Watt MJ, Forster GL (2019) Sex differences in anxiety-like behaviors in rats. Physiol Behav 211:112670–112678
Shephard RA, Broadhurst PL (1982) Effects of diazepam and picrotoxin on hyponeophagia in rats. Neuropharm 21:771–773
Shepherd JK, Flores T, Rodgers RJ, Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC (1992) The anxiety/defense test battery: influence of gender and ritanserin treatment on antipredator defensive behavior. Physiol Behav 51:277–285
Sheynin J, Beck KD, Pang KC, Servatius RJ, Shikari S, Ostovich J, Myers CE (2014) Behaviourally inhibited temperament and female sex, two vulnerability factors for anxiety disorders, facilitate conditioned avoidance (also) in humans. Behav Processes 103:228–235
Slavich GM, Sacher J (2019) Stress, sex hormones, inflammation, and major depressive disorder: Extending Social Signal Transduction Theory of Depression to account for sex differences in mood disorders. Psychopharm 236:3063–3079
Vicente MA, Zangrossi H Jr (2014) Involvement of 5-HT2C and 5-HT1A receptors of the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala in the anxiolytic effect of chronic antidepressant treatment. Neuropharm 79:127–135
Wegner SA, Hu B, De Oliveira Sergio T, Darevsky D, Kwok CC, Lei K, Hopf FW (2019) A novel NMDA receptor-based intervention to suppress compulsion-like alcohol drinking. Neuropharm 157:107681–107688
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Molly Sazer-Hopf for assistance with Fig. 1.
Funding
Work was supported by National Institutes of Health (R01 AA024109 to FWH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Oliveira Sergio, T., Wetherill, L., Kwok, C. et al. Sex differences in specific aspects of two animal tests of anxiety-like behavior. Psychopharmacology 238, 2775–2787 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05893-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05893-w