Abstract
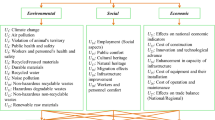
The selection of sustainable building materials has attracted much attention from society because it is essential for environment, economy, and human health. To meet the need of the building development, the identified criteria for optimal sustainable building materials are determined based on sustainability building standards and previous studies including economic, environmental, social, and technological aspects. To represent the qualitative preferred and non-preferred cognitions of the decision makers, linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers (LIFNs) are utilized to describe the evaluation information, which is a powerful and flexible tool. Then, new accuracy function and score function are defined to rank LIFNs more objectively. In addition, this paper employs a new linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy entropy to calculate the weights of criteria, and models based on the Shapley function with respect to 2-additive measure are constructed to reflect the correlations among elements in a set. Based on these results, a linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy Preference Ranking Organization Method for Enrichment Evaluation and prospect theory based hybrid method is proposed to assess the sustainable building materials. Finally, the effectiveness of the new method is testified by a case study for sustainable indoor flooring material selection, and comparative analysis is made.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeysundara U, Babel S, Gheewala S (2009) A matrix in life cycle perspective for selecting sustainable materials for buildings in Sri Lanka. Build Environ 44(5):997–1004
Akadiri PO, Olomolaiye PO (2012) Development of sustainable assessment criteria for building materials selection. Eng Constr Archit Manag 19(6):666–687
Akadiri PO, Olomolaiye PO, Chinyio EA (2013) Multi-criteria evaluation model for the selection of sustainable materials for building projects. Autom Constr 30:113–125
Awadh O (2017) Sustainability and green building rating systems: LEED, BREEAM, GSAS and Estidama critical analysis. J Build Eng 11:25–29
Behzadian M, Otaghsaea SK, Yazdani M, Ignatius J (2012) A state-of the-art survey of TOPSIS applications. Expert Syst Appl 39(17):13051–13069
Brans JP (1982) L’ingénièrie de la decision; Elaboration d’instruments d’aide à la décision. La méthode PROMETHEE. In: Nadeau R, Landry M (eds) L’aide a la decision: nature, instruments et Perspectives d’Avenir, pp 183–213
Brans JP, Vincke P, Mareschal B (1986) How to select and how to rank projects: the promethee method. Eur J Oper Res 24(2):228–238
Burillo PJ, Bustince H (1996) Entropy on intuitionistic fuzzy sets and on interval valued fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Set Syst 78(3):305–316
Chen Z, Liu P, Pei Z (2015) An approach to multiple attribute group decision making based on linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Int J Comput Int Syst 8(4):747–760
Chen Z, Martinez L, Chang J, Wang X, Xionge S, Chin K (2019) Sustainable building material selection: A QFD-and ELECTRE III-embedded hybrid MCGDM approach with consensus building. Eng Appl Artif Intel 85:783–807
Drejeris R, Kavolynas A (2014) Multi-criteria evaluation of building sustainability behavior. Procedia Soc Behav Sci 110:502–511
Falqi II, Ahmed M, Mallick J (2019) Siliceous concrete materials management for sustainability using fuzzy-TOPSIS approach. Appl Sci (basel) 9(17):3457–3471
Gervasio H, Silva LS (2012) A probabilistic decision-making approach for the sustainable assessment of infrastructures. Expert Syst Appl 39(8):7121–7131
Godfaurd J, Clements-Croome D, Jeronimidis G (2005) Sustainable building solutions: a review of lessons from the natural world. Build Environ 40(3):19–28
Govindan K, Shankar KM, Kannan D (2016) Sustainable material selection for construction industry: a hybrid multi criteria decision making approach. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 55:1274–1288
Grabisch M (1997) K-order additive discrete fuzzy measures and their representation. Fuzzy Set Syst 92(2):167–189
Guo L, Guo Y (2011) Study on building materials and indoor pollution. Procedia Eng 21:789–794
Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E (2000) Linguistic decision analysis: steps for solving decision problems under linguistic information. Fuzzy Sets Syst 115(1):67–82
Herrera F, Martinez L (2000) A 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model for computing with words. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 8(6):746–752
Huedo P, Mulet E, Lopezmesa B (2016) A model for the sustainable selection of building envelope assemblies. Environ Impact Asses 57:63–77
Kahneman D, Tversky A (1979) Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica 47(2):263–291
Khoshnava SM, Rostami R, Valipour A, Ismail M, Rahmat AR (2018) Rank of green building material criteria based on the three pillars of sustainability using the hybrid multi criteria decision making method. J Clean Prod 173:82–99
Li Z, Liu P, Qin X (2017) An extended VIKOR method for decision making problem with linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers based on some new operational laws and entropy. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 33(3):1919–1931
Liao H, Xu Z (2014) Multi-criteria decision making with intuitionistic fuzzy PROMETHEE. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 27(4):1703–1717
Lin J, Meng F, Chen R (2018) Preference attitude-based method for ranking intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and its application in renewable energy selection. Complexity 2018:1–14
Liu P, Liu J (2019) A multiple attribute group decision-making method based on the partitioned Bonferroni mean of linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Cogn Comput 12(1):49–70
Liu P, Shen M (2019) An extended C-TODIM method with linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 37(3):3615–3627
Liu P, Liu X, Ma G, Liang Z, Wang C, Alsaadi FE (2020) A multi-attribute group decision-making method based on linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers and Dempster–Shafer evidence theory. Int J Inf Tech Decis 19(2):499–524
Mahmoudkelaye S, Azari KT, Pourvaziri M, Asadian E (2018) Sustainable material selection for building enclosure through ANP method. Case Stud Const Mater 9:200–209
Meng F, Tang J (2013) Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy multiattribute group decision making based on cross entropy measure and Choquet integral. Int J Intell Syst 28(12):1172–1195
Meng F, Tang J, Fujita H (2019) Linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations and their application to multi-criteria decision making. Inf Fusion 46:77–90
Meng F, Xu Y, Wang N (2020) Correlation coefficients of dual hesitant fuzzy sets and their application in engineering management. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput 11(7):2943–2961
Murata T (2008) Sustainability assessment: criteria and processes. Futures 40(5):513–514
Ou Y, Yi L, Zou B, Pei Z (2018) The linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy set TOPSIS method for linguistic multi-criteria decision makings. Int J Comput Int Syst 11(1):120–132
Peng H, Wang J, Cheng P (2018) A linguistic intuitionistic multi-criteria decision-making method based on the frank heronian mean operator and its application in evaluating coal mine safety. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 9:1053–1068
Plessis C (2007) A strategic framework for sustainable construction in developing countries. Constr Manag Econ 25(1):67–76
Pulselli RM, Simoncini E, Pulselli FM, Bastianoni S (2007) Emergy analysis of building manufacturing, maintenance and use: Em-building indices to evaluate housing sustainability. Energy Build 39(5):620–628
Rashid K, Razzaq A, Ahmad M, Rashid T, Tariq S (2017) Experimental and analytical selection of sustainable recycled concrete with ceramic waste aggregate. Constr Build Mater 154:829–840
Reddy AS, Kumar PR, Raj PA (2019) Entropy-based fuzzy TOPSIS framework for selection of a sustainable building material. Int J Constr Manag 6:1–12
Ries R, Bilec M, Gokhan NM, Needy KL (2006) The economic benefits of green buildings: a comprehensive case study. Eng Econ 51(3):259–295
Rong Y, Liu Y, Pei Z (2020) Novel multiple attribute group decision-making methods based on linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy information. Mathematics 8(3):322–352
Roy J, Das S, Kar S, Pamučar D (2019) An extension of the CODAS approach using interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy set for sustainable material selection in construction projects with incomplete weight information. Symmetry (basel) 11(3):393–416
Tang J, Meng F (2019) Linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy Hamacher aggregation operators and their application to group decision making. Granul Comput 4:109–124
Tarantini M, Loprieno AD, Porta PL (2011) A life cycle approach to Green Public Procurement of building materials and elements: a case study on windows. Energy 36(5):2473–2482
Tian G, Zhang H, Feng Y, Peng Y, Jia H (2018) Green decoration materials selection under interior environment characteristics: a grey-correlation based hybrid MCDM method. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81(1):682–692
Tian X, Xu Z, Gu J (2019) Group decision-making models for venture capitalists: the PROMETHEE with hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. Technol Econ Dev Econ 25(5):743–773
Wang W, Zmeureanua R, Rivard H (2005) Applying multi-objective genetic algorithms in green building design optimization. Build Environ 40(11):1512–1525
Wang J, Wu J, Wang J, Zhang H, Chen X (2014) Interval-valued hesitant fuzzy linguistic sets and their applications in multi-criteria decision-making problems. Inf Sci 288:55–72
Xu Z (2004) Eowa and eowg operators for aggregating linguistic labels based on linguistic preference relations. Int J Uncertain Fuzzy 12(6):791–810
Yuan R, Meng F, Tang J (2019) Linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making based on aggregation operators. Int J Fuzzy Syst 21:407–420
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf Control 8(3):338–353
Zadeh LA (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning-I. Inf Sci 8:199–249
Zavadskas EK, Bausys R, Juodagalviene B, Garnyte-Sapranaviciene I (2017) Model for residential house element and material selection by neutrosophic MULTIMOORA method. Eng Appl Artif Intell 64:315–324
Zhang Q, Jiang S (2008) A note on information entropy measures for vague sets and its applications. Inf Sci 178(21):4184–4191
Zhang H, Peng H, Wang J, Wang J (2017) An extended outranking approach for multi-criteria decision-making problems with linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy numbers. Appl Soft Comput 59:462–474
Zuo J, Zhao Z (2014) Green building research-current status and future agenda: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 30:271–281
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully thank the Editor-in-Chief Professor Vincenzo Loia, the Associated Editor Professor Aniello Castiglione, and three anonymous referees for their valuable and constructive comments, which have much improved the paper. This work was supported by the Major Project for National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 72091515).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, F., Dong, B. Linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy PROMETHEE method based on similarity measure for the selection of sustainable building materials. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 13, 4415–4435 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03338-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-03338-y