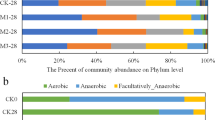
Abstract
China is the world's largest livestock and poultry breeding country, but also the largest use of veterinary antibiotics. When a large amount of chicken manure is applied to the soil, it will cause the number of antibiotic residues and resistant bacteria to increase, which will bring about the pollution of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in the soil, and then increase the risk of environmental pollution and human health. Field experiments were conducted to study the changes of soil tetracycline antibiotic residues, resistant bacteria and resistance genes treated with different types and dosage of chicken manure (no chicken manure, (CK), low fresh chicken manure treatment (300 kg·667 m−2), high fresh chicken manure treatment (600 kg·667 m−2), low decomposed chicken manure treatment (300 kg·667 m−2) and high decomposed chicken manure treatment (600 kg·667 m−2)). After one-year application of chicken manure, content of soil organic matter increased by 1.0%-3.2% compared with the control. The activity of soil catalase significantly increased by 84.3–91.5%, 81.9–102.9% in fresh and decomposed chicken manure treatments compared with the control, respectively. The amount of soil resistant bacteria under the same treatment was in the order of Anti-OTC > Anti-TC > Anti-CTC. After one-year application of chicken manure, the total tetracycline amount in the soil was increased by 168.5–217.9% compared with the control. The amount of antibiotic residue in soil treated with fresh chicken manure was 3.0–9.1% higher than that treated with decomposed chicken manure. The abundance of ARGs in the soil was in the order of that treated with high fresh chicken manure > low fresh chicken manure > high decomposed chicken manure > low decomposed chicken manure. The risk of tetracycline antibiotics to soil ecological environment may be greatly reduced after chicken manure decomposed.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Arau´jo, A. S. F., & Monteiro, R. T. R. (2006). Microbial biomass and activity in a Brazilian soil amended with untreated and composted textile sludge. Chemosphere, 64(10), 1043–1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.01.040
Brandt, K. K., Sjoholm, O. R., Krogh, K. A., Halling, S. B., & Nybroe, O. (2009). Increased pollution-induced bacterial community tolerance to sulfadiazine insoil hotspots amended with artificial root exudates. Environmental Science and Technology, 43(8), 2963–2968. https://doi.org/10.1021/es803546y
Brown, M. G., Mitchell, E. H., & Balkwill, D. L. (2008). Tet 42, a novel tetracycline resistance determinant isolated from deep terrestrial Subsurface Bacteria. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 52(12), 4518–4521. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00640-08
Chen, H. R., Rairat, T., Loh, S. H., Wu, Y. C., Vickroy, T. W., & Chou, C. C. (2017). Assessment of veterinary drugs in plants using pharmacokinetic approaches: The absorption, distribution and elimination of tetracycline and sulfamethoxazole in ephemeral vegetables. Plos one. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0183087
Chen, Q., An, X., Li, H., Su, J., Ma, Y., & Zhu, Y. G. (2016). Long-term field application of sewage sludge increases the abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in soil. Environment International, 92–93, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.03.026
Chen, Y. S., Zhang, H. B., Luo, Y. M., & Song, J. (2012). Occurrence and assessment of veterinary antibiotics in swine manures: A case study in East China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(6), 606–614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-011-4830-3
Gao, Y. F., & He, Z. D. (2010). Study on soils effect factors to fungi diversity in Hebei province. Chinese Agricultural Sciences Bulletin, 26(10), 177–181.
Guan, S. M. (1986). Soil enzymes and their research methods. Agriculture press.
Han, J. C., Zhang, C. G., Cheng, J., Wang, F., & Qiu, L. (2019). Effects of biogas residues containing antibiotics on soil enzyme activity and lettuce growth. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(6), 6116–6122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-4046-z
He, T., Wei, R. C., Zhang, L., Gong, L., Zhu, L., Gu, J., et al. (2021). Dissemination of the tet(X)-Variant Genes from Layer Farms to Manure-Receiving Soil and Corresponding Lettuce. Environmental Science and Technology, 55(3), 1604–1614. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c05042
Hong, P. Y., Yannarell, A. C., Dai, Q. H., Ekizoglu, M., & Mackie, R. I. (2013). Monitoring the Perturbation of Soil and Groundwater Microbial Communities Due to Pig Production Activities. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 79(8), 2620–2629. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03760-12n
Jacobsen, A. M., Halling-Sorensen, B., Ingerslev, F., & Hansen, S. H. (2004). Simultaneous extraction of tetracycline, macrolide and sulfonamide antibiotics from agricultural soils using pressurised liquid extraction, followed by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1038(1–2), 157–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2004.03.034
Li, B., Yang, Y., Ma, L., Ju, F., Guo, F., Tiedje, J. M., et al. (2015). Metagenomic and network analysis reveal wide distribution and co-occurrence of environmental antibiotic resistance genes. ISME Journal, 9(11), 2490–2502. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2015.59
Mullen, R. A., Hurst, J. J., Naas, K. M., Sassoubre, L. M., & Aga, D. S. (2019). Assessing uptake of antimicrobials by Zea mays L. and prevalence of antimicrobial resistance genes in manure-fertilized soil. Science of the Total Environment, 646, 409–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.199
Negreanu, Y., Pasternak, Z., & Jurkevitch, E. (2012). Impact of treated wastewater irrigation onantibiotic resistance in agricultural soils. Environmental Science and Technology, 46(9), 4800–4808. https://doi.org/10.1021/es204665b
Pils, J. R. V., & Laird, D. A. (2007). Sorption of tetracycline and chlortetracycline on K- and Ca-saturated soil clays, humic substances, and clay-humic complexes. Environmental Science and Technology, 41(6), 1928–1933. https://doi.org/10.1021/es062316y
Pu, Q., Zhao, L. X., Li, Y. T., & Su, J. Q. (2020). Manure fertilization increase antibiotic resistance in soils from typical greenhouse vegetable production bases China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 321, 122267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122267
Qi, R. M., Li, J., Lin, Z. A., Li, Z. J., Li, Y. T., Yang, X. D., et al. (2016). Temperature effects on soil organic carbon, soil labile organic carbon fractions, and soil enzyme activities under long-term fertilization regimes. Applied Soil Ecology, 102, 36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.02.004
Roberts, M. C. (2010). Update on acquired tetracycline resistance genes. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 245(2), 195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2005.02.034
Shen, L. (2013). Effect of chicken manure and tetracycline on soil enzyme activity and the number of microbial quantity. Shen’yang Agricultural University.
Tasho, R. P., & Cho, J. Y. (2016). Veterinary antibiotics in animal waste, its distribution in soil and uptake by plants: A review. Science of the Total Environment, 563, 366–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.140
Thompson, S. A., Maani, E. V., Lindell, A. H., King, C. J., & McArthur, J. V. (2007). Novel tetracycline resistance determinant isolated from an environmental strain of Serratia marcescens. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 73(7), 2199–2206. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02511-06
Tien, Y. C., Li, B., Zhang, T., Scott, A., Murray, R., Sabourin, L., et al. (2017). Impact of dairy manure pre-application treatment on manure composition, soil dynamics of antibiotic resistance genes, and abundance of antibiotic-resistance genes on vegetables at harvest. Science of the Total Environment, 581, 32–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.138
Van Boeckel, T. P., Brower, C., Gilbert, M., Grenfell, B. T., Levin, S. A., Robinson, T. P., et al. (2015). Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(18), 5649–5654. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1503141112
Wang, W. Z., Chi, S. L., Xu, W. H., & Zhang, C. L. (2018). Influence of long-term chicken manure application on the concentration of soil tetracycline antibiotics and resistant bacteria variations. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 16(2), 1143–1153. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1602_11431153
Xiong, W. G., Wang, M., Dai, J. J., Sun, Y. X., & Zeng, Z. L. (2018). Application of manure containing tetracyclines slowed down the dissipation of tet resistance genes and caused changes in the composition of soil bacteria. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 147, 455–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.08.061
Yang, S. W., & Carlson, K. (2003). Evolution of antibiotic occurrence in a river through pristine, urban and agricultural landscapes. Water Research, 37(19), 4645–4656. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0043-1354(03)00399-3
Yu, X., Liu, X., Liu, H., Chen, J., & Sun, Y. (2019a). The accumulation and distribution of five antibiotics from soil in 12 cultivars of pakchoi. Environmental Pollution, 254(Pt B), 113115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113115
Yu, Y. S., Chen, L. J., Fang, Y., Jia, X. B., & Chen, J. C. (2019b). High temperatures can effectively degrade residual tetracyclines in chicken manure through composting. Journal of Hazardous Materials. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120862
Zhang, H., Zhang, L., Wang, J., Zhu, K., & Yang, Q. (2012). Influence of oxytetracycline exposure on antibiotic resistant bacteria and enzyme activities in wheat rhizosphere soil. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 32(02), 508–516. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201012131772
Zhang, H. Y., Zhang, X. D., Li, J., & Wang, D. M. (2005). Outline of soil microbial biomass measurement methods. J Microbio, 25, 95–99. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2005.04.026
Zhang, L. H., Wang, J. J., Gao, M., Qiu, T. L., Han, M. L., & Wang, X. M. (2016). Pollution of antibiotics resistant genes in farmland amended with livestock organic manure. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 32(4), 664–669. https://doi.org/10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2016.04.023
Zhang, M. K., Gu, G. P., & Bao, C. Y. (2015). Degradation characteristics of veterinary antibiotics in soils and its relationship with soil properties. Chinese Agricultural Sciences Bulletin, 31(31), 228–236.
Zhang, X. (2012). The research on the leaching behavior of typical antibiotics in the soil. Ji'nan University.
Zhang, Y. J., Hu, H. W., Chen, Q. L., Singh, B. K., Yan, H., Chen, D. L., et al. (2019). Transfer of antibiotic resistance from manure-amended soils to vegetable microbiomes. Environment International. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.104912
Zhao, X., Wang, J. H., Zhu, L. S., & Wang, J. (2019). Field-based evidence for enrichment of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements in manure-amended vegetable soils. Science of the Total Environment, 654, 906–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.446
Zhu, K. F. (2009). Effects of antibiotic exposure on soil microorganism and soil enzyme activity. He'nan Normal University.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the reviewers of this manuscript; their insight was instrumental to improving this paper. Finally, we also thank Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People's Republic of China for the financial support necessary to make all of this work possible.
Funding
This study was funded by Fund of China Agriculture Research System (CARS-23) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD0201200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LSX and WHX conceived the study. WZW collected the data presented in the manuscript. LSX and WZW performed statistical analyses. All authors contributed to the writing and revision of the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The author(s) declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The sampling of soil and vegetable did not require permission, and the species are not classified as endangered and are not under any protection in any of the sampled areas.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, L., Wang, W. & Xu, W. Effects of tetracycline antibiotics in chicken manure on soil microbes and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). Environ Geochem Health 44, 273–284 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01004-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-01004-y