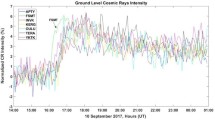
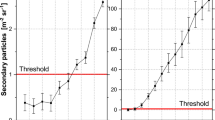
Abstract
In this work an improved approach of existing approximations on the coupling function between primary and ground-level cosmic-ray particles is presented. The proposed coupling function is analytically derived based on a formalism used in Quantum Field Theory calculations. It is upgraded compared to previous versions with the inclusion of a wider energy spectrum that is extended to lower energies, as well as an altitude correction factor, also derived analytically. The improved approximations are applied to two cases of Forbush decreases detected in March 2012 and September 2017. In the analytical procedure for the derivation of the primary cosmic-ray spectrum during these events, we also consider the energy spectrum exponent \(\gamma \) to be varied with time. For the validation of the findings, we present a direct comparison between the primary spectrum and the amplitude values derived by the proposed method and the obtained time series of the cosmic-ray intensity at the rigidity of 10 GV obtained from the Global Survey Method. The two sets of results are found to be in very good agreement for both events as denoted by the Pearson correlation factors and slope values of their scatter plots. In such way we determine the validity and applicability of our method to Forbush decreases as well as to other cosmic-ray phenomena, thus introducing a new, alternative way of inferring the primary cosmic-ray intensity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostinelli, S., Allison, J., Amako, K., Apostolakis, J., Araujo, H., Arce, P., et al.: 2003, Geant4-a simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 506, 250. DOI.
Belov, A.: 2008, Forbush effects and their connection with solar, interplanetary and geomagnetic phenomena. In: Proc. of the IAU 4, 439. DOI.
Belov, A., Abunin, A., Abunina, M., Eroshenko, E., Oleneva, V., Yanke, V., Papaioannou, A., Mavromichalaki, H., Gopalswamy, N., Yashiro, S.: 2014, Coronal mass ejections and non-recurrent Forbush decreases. Solar Phys. 289, 3949. DOI.
Belov, A., Eroschenko, E., Yanke, V., Oleneva, V., Abunin, A., Abunina, M., Papaioannou, A., Mavromichalaki, H.: 2018, The global survey method applied to ground-level cosmic ray measurements. Solar Phys. 293, 68. DOI.
Bilal, A.: 2011, Advanced quantum field theory: renormalization, non-abelian gauge theories and anomalies. In: Lect. Notes Brus.
Brown, R.: 1957, Neutron yield functions of the nucleonic component of cosmic radiation. Nuovo Cimento 6, 2816.
Caballero-Lopez, R., Moraal, H.: 2012, Cosmic-ray yield and response functions in the atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 117, 12103. DOI.
Cane, H.V.: 2000, Coronal mass ejections and Forbush decreases. Space Sci. Rev. 93, 55. DOI.
Clem, J.M., Dorman, L.I.: 2000, Neutron monitor response functions. Space Sci. Rev. 93, 335. DOI.
Desorgher, L., Flückiger, E.O., Gurtner, M., Moser, M.R., Bütikofer, R.: 2005, Atmocosmics: a Geant 4 code for computing the interaction of cosmic rays with the Earth’s atmosphere. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 20, 6802. DOI.
Dorman, L.I.: 1957, Cosmic Ray Variations, State Publishing House for Technical and Theoretical Literature, Moscow, 102.
Dorman, L.I.: 1974, Cosmic Rays Variations and Space Explorations, North-Holland, Amsterdam.
Dorman, L.I., Villoresi, G., Iucci, N., et al.: 2000, Cosmic ray survey to Antarctica and coupling functions for neutron component near solar minimum (1996–1997): 3. Geomagnetic effects and coupling functions. J. Geophys. Res. 105(A9), 21047. DOI.
Flückiger, E.O., Moser, M.R., Pirard, B., Bütikofer, R., Desorgher, L.: 2008, A parameterized neutron monitor yield function for space weather applications. In: Proc. 30 th ICRC 2007, 1289.
Fonger, W.: 1953, Cosmic radiation intensity-time variations and their origin. II. Energy dependence of 27-day variation. Phys. Rev. 91, 351.
Forbush, S.E.: 1937, On the effects in cosmic-ray intensity observed during the recent magnetic storm. Phys. Rev. 51, 1108. DOI.
Forbush, S.E.: 1954, Worldwide cosmic ray variations, 1937–1952. J. Geophys. Res. 59, 525. DOI.
Griffiths, D.: 2008, Introduction to Elementary Particles, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 9783527406012.
Kumar, A., Badruddin: 2014, Cosmic-ray modulation due to high-speed solar-wind streams of different sources, speed, and duration. Solar Phys. 289, 4267. DOI.
Kurt, V., Kudela, K., Mavromichalaki, H., Kashapova, L., Yushkov, B., Sgouropoulos, C.: 2019, Onset time of the GLE 72 observed at neutron monitors and its relation to electromagnetic emissions. Solar Phys. 294, 18. DOI.
Lingri, D., Mavromichalaki, H., Belov, A., Eroshenko, E., Yanke, V., Abunin, A., Abunina, M.: 2016, Solar activity parameters and associated Forbush decreases during the minimum between cycles 23 and 24 and the ascending phase of Cycle 24. Solar Phys. 291, 1025. DOI.
Livada, M., Mavromichalaki, H.: 2020, Spectral analysis of Forbush decreases using a new yield function. Solar Phys. 295, 115. DOI.
Livada, M., Mavromichalaki, H., Plainaki, C.: 2018, Galactic cosmic ray spectral index: the case of Forbush decreases of March 2012. Astrophys. Space Sci. 363, 8. DOI.
Lockwood, J.A.: 1971, Forbush decreases in the cosmic radiation. Space Sci. Rev. 12, 658. DOI.
Maurin, D., Cheminet, A., Derome, L., Ghelfi, A., Hubert, G.: 2015, Neutron monitors and muon detectors for solar modulation studies: interstellar flux, yield function, and assessment of critical parameters in count rate calculations. Adv. Space Res. 55(1), 363. DOI.
Mavromichalaki, H.: 2012, The physics of cosmic rays applied to space weather. In: Maris, G., Demetrescu, C. (eds.) Advances in Solar and Solar-Terrestrial Physics, 135, ISBN 978-81-308-0483-5.
Mavromichalaki, H., Souvatzoglou, G., Sarlanis, C., Mariatos, G., Papaioannou, A., Belov, A., Eroshenko, E., Yanke, V., for the NMDB team: 2010, Implementation of the ground level enhancement alert software at NMDB database. New Astron. 15, 744. DOI.
Mavromichalaki, H., Papaioannou, A., Plainaki, C., Sarlanis, C., Souvatzoglou, G., Gerontidou, M., Papailiou, M., Eroshenko, E., Belov, A., Yanke, V., Flückiger, E.O., Bütikofer, R., et al.: 2011, Applications and usage of the real – time neutron monitor database. Adv. Space Res. 47, 2210. DOI.
Mavromichalaki, H., Gerontidou, M., Paschalis, P., Paouris, E., Tezari, A., Sgouropoulos, C., Crosby, N., Dierckxsens, M.: 2018, Real-time detection of the ground level enhancement on 10 September 2017 by A.Ne.Mo.S.: system report. Space Weather 16, 1797. DOI.
Mishev, A.L., Koldobskiy, S.A., Kovaltsov, G.A., Gil, A., Usoskin, I.G.: 2020, Updated neutron-monitor yield function: bridging between in situ and ground-based cosmic ray measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 125, e2019JA02743. DOI.
National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA): Technical Note 3182, Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere, Calculations by the NACA, International Civil Aviation Organization Montreal, Canada and Langley Aeronautical Laboratory Langley Field, VA, USA.
Papaioannou, A., Belov, A., Abunina, M., Eroshenko, E., Abunin, A., Anastasiadis, A., Patsourakos, S., Mavromichalaki, H.: 2020, Interplanetary coronal mass ejections as the driver of non-recurrent Forbush decreases. Astrophys. J. 890, 101. DOI.
Patsourakos, S., Georgoulis, M.K., et al.: 2016, The major geoeffective solar eruptions of 2012 March 7: comprehensive Sun-to-Earth analysis. Astrophys. J. 817, 1. DOI.
Peskin, M.E., Schroeder, D.V.: 1995, An Introduction to Quantum Field Theory, Perseus Books, Cambridge.
Seinfeld, J.H., Pandis, S.: 2006, Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, Wiley, New York, ISBN 1118947401.
Simpson, J.A.: 1948, The latitude dependence of neutron densities in the atmosphere as a function of altitude. Phys. Rev. 73, 11. DOI.
Simpson, J.A.: 2000, The cosmic ray nucleonic component: the invention and scientific uses of the neutron monitor. Space Sci. Rev. 93, 11. DOI.
Srednicki, M.: 2007, Quantum Field Theory, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. DOI.
Usoskin, I.G., Kovaltsov, G.A., Adriani, O., Barbarino, G.C., Basilevskaya, G.A., et al.: 2015, Force-field parameterization of the galactic cosmic ray spectrum: validation for Forbush decreases. Adv. Space Res. 55, 2940. DOI.
Venkatesan, D., Badruddin: 1990, Cosmic-ray intensity variations in the 3-dimensional heliosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 52, 121. DOI.
Villoresi, G., Dorman, L.I., Iucci, N., Ptitsyna, N.G.: 2000, Cosmic ray survey to Antarctica and coupling functions for neutron component near solar minimum (1996–1997): 1. Methodology and data quality assurance. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 21. DOI.
Weinberg, S.: 1995, The Quantum Theory of Fields, vol. I, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Xaplanteris, L., Livada, M., Mavromichalaki, H., Dorman, L.I.: 2020, A new approximate coupling function: the case of Forbush decreases. New Astron. 82, 101453. DOI.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to our collaborators of the Neutron Monitor stations for kindly providing the cosmic-ray data used in this work in the frame of the high-resolution real-time Neutron Monitor Database (NMDB), funded under the European Union’s FP7 Program (contract no. 213007). Athens Neutron Monitor Station (A.Ne.Mo.S.) is supported by the Special research account of the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens. We are also particularly thankful to the anonymous referee whose insightful comments have helped us improve the manuscript significantly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xaplanteris, L., Livada, M., Mavromichalaki, H. et al. Improved Approach in the Coupling Function Between Primary and Ground Level Cosmic Ray Particles Based on Neutron Monitor Data. Sol Phys 296, 91 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01836-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-021-01836-y