Abstract
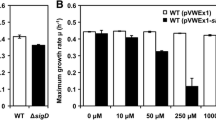
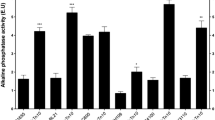
RpoS, an alternative sigma factor of RNA polymerase, regulates the expression of a great deal of genes involved in stationary-phase survival and stress response. To identify the function of RpoS homologue in Serratia marcescens FS14, in-frame deletion mutant of rpoS was constructed. It was found that RpoS activates the biosynthesis of prodigiosin in FS14 which is just opposite to what was observed in Serratia sp. ATCC 39006. We also demonstrated that RpoS positively regulates the prodigiosin production by activating the transcription of pig cluster in FS14, and the transcription of pig cluster is RpoS-dependent. Further study showed that the differences in the promoters of pig clusters in FS14 and 39006 lead to the different selection of the sigma factors and result in the different regulation mechanisms. The -10 element and the spacer region between -10 and -35 elements of the pig cluster in FS14 are vital for the RpoS recognition in FS14.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
The genome data had been deposited into NCBI GenBank with the Accession number: CP005927.
References
Harris AK, Williamson NR, Slater H, Cox A, Abbasi S, Foulds I et al (2004) The Serratia gene cluster encoding biosynthesis of the red antibiotic, prodigiosin, shows species- and strain-dependent genome context variation. Microbiology 150:3547–3560. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.27222-0
Williamson NR, Simonsen HT, Ahmed RA, Goldet G, Slater H, Woodley L et al (2005) Biosynthesis of the red antibiotic, prodigiosin, in Serratia: identification of a novel 2-methyl-3-n-amyl-pyrrole (MAP) assembly pathway, definition of the terminal condensing enzyme, and implications for undecylprodigiosin biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Mol Microbiol 56:971–989. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04602.x
Williamson NR, Simonsen HT, Harris AK, Leeper FJ, Salmond GP (2006) Disruption of the copper efflux pump (CopA) of Serratia marcescens ATCC 274 pleiotropically affects copper sensitivity and production of the tripyrrole secondary metabolite, prodigiosin. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 33:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-005-0040-9
Han R, Xiang R, Li J, Wang F, Wang C (2021) High-level production of microbial prodigiosin A review. J Basic Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.202100101
Stella NA, Fender JE, Lahr RM, Kalivoda EJ, Shanks RM (2012) The LysR transcription factor, HexS, is required for glucose inhibition of prodigiosin production by Serratia marcescens. Adv Microbiol 2:511–517. https://doi.org/10.4236/aim.2012.24065
Paget MS, Helmann JD (2003) The sigma70 family of sigma factors. Genome Biol 4:203. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2003-4-1-203
Wilf NM, Salmond GP (2012) The stationary phase sigma factor, RpoS, regulates the production of a carbapenem antibiotic, a bioactive prodigiosin and virulence in the enterobacterial pathogen Serratia sp. ATCC 39006. Microbiology 158:648–658. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.055780-0
Liu X, Wu Y, Chen Y, Xu F, Halliday N, Gao K et al (2016) RpoS differentially affects the general stress response and biofilm formation in the endophytic Serratia plymuthica G3. Res Microbiol 167:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2015.11.003
Guan J, Xiao X, Xu S, Gao F, Wang J, Wang T et al (2015) Roles of RpoS in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis stress survival, motility, biofilm formation and type VI secretion system expression. J Microbiol 53:633–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-015-0099-6
Huerta AM, Collado-Vides J (2003) Sigma70 promoters in Escherichia coli: specific transcription in dense regions of overlapping promoter-like signals. J Mol Biol 333:261–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2003.07.017
Typas A, Becker G, Hengge R (2007) The molecular basis of selective promoter activation by the sigmaS subunit of RNA polymerase. Mol Microbiol 63:1296–1306. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05601.x
Espinosa-Urgel M, Chamizo C, Tormo A (1996) A consensus structure for sigma S-dependent promoters. Mol Microbiol 21:657–659. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02573.x
Lee SJ, Gralla JD (2001) Sigma38 (rpoS) RNA polymerase promoter engagement via -10 region nucleotides. J Biol Chem 276:30064–30071. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M102886200
Fenton MS, Gralla JD (2001) Function of the bacterial TATAAT -10 element as single-stranded DNA during RNA polymerase isomerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9020–9025. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.161085798
Schaumburg CS, Tan M (2003) Mutational analysis of the Chlamydia trachomatis dnaK promoter defines the optimal -35 promoter element. Nucleic Acids Res 31:551–555. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg150
Wise A, Brems R, Ramakrishnan V, Villarejo M (1996) Sequences in the -35 region of Escherichia coli rpoS-dependent genes promote transcription by E sigma S. J Bacteriol 178:2785–2793. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.178.10.2785-2793.1996
Typas A, Hengge R (2006) Role of the spacer between the -35 and -10 regions in sigmas promoter selectivity in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 59:1037–1051. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04998.x
Qin H, Liu Y, Cao X, Jiang J, Lian W, Qiao D et al (2020) RpoS is a pleiotropic regulator of motility, biofilm formation, exoenzymes, siderophore and prodigiosin production, and trade-off during prolonged stationary phase in Serratia marcescens. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0232549
Zhang X, Wu D, Guo T, Ran T, Wang W, Xu D (2018) Differential roles for ArcA and ArcB homologues in swarming motility in Serratia marcescens FS14. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 111:609–617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0981-9
Slater H, Crow M, Everson L, Salmond GP (2003) Phosphate availability regulates biosynthesis of two antibiotics, prodigiosin and carbapenem, in Serratia via both quorum-sensing-dependent and -independent pathways. Mol Microbiol 47:303–320. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03295.x
Ruff EF, Record MT Jr, Artsimovitch I (2015) Initial events in bacterial transcription initiation. Biomolecules 5:1035–1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5021035
Bowers CW, Dombroski AJ (1999) A mutation in region 1.1 of sigma70 affects promoter DNA binding by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme. EMBO J 18:709–716. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.3.709
Li P, Kwok AH, Jiang J, Ran T, Xu D, Wang W et al (2015) Comparative genome analyses of Serratia marcescens FS14 reveals its high antagonistic potential. PLoS ONE 10:e0123061. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123061
Woodcock DM, Crowther PJ, Doherty J, Jefferson S, DeCruz E, Noyer-Weidner M et al (1989) Quantitative evaluation of Escherichia coli host strains for tolerance to cytosine methylation in plasmid and phage recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res 17:3469–3478. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/17.9.3469
Herrero M, de Lorenzo V, Timmis KN (1990) Transposon vectors containing non-antibiotic resistance selection markers for cloning and stable chromosomal insertion of foreign genes in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol 172:6557–6567. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.172.11.6557-6567.1990
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant Nos. 31770050, 31770074 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Funding
This work was supported by Grant Nos. 31770050, 31770074 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BY: Investigation, Data Curation, Visualization, Writing-original draft; FC and HL: Investigation, Formal analysis; WW: Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing-review & editing; TR: Formal analysis; DX: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Writing-review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest is declared.
Ethical Statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for Publication
All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, B., Chu, F., Li, H. et al. RpoS Activates the Prodigionsin Production by Activating the Transcription of the RpoS-Dependent Pig Gene Cluster in Serratia marcescens FS14. Indian J Microbiol 61, 355–363 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-021-00952-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-021-00952-4