Abstract
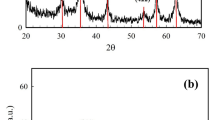
This paper focused on the synthesis of Fe3O4@NiO core–shell magnetic nanoparticles for the highly efficient removal of Alizarin red S dye from contaminated effluent. The physicochemical properties of as-synthesized nanoparticles were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, vibrating sample magnetometer, transmission electron microscopy, N2 adsorption–desorption, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy instrumental analysis. Many adsorption parameters, i.e., contact time, adsorbent dosage, pH solution, initial Alizarin red S concentration, and process temperature, were applied to interpret the dye adsorption mechanism. Also, the reuse efficiency of Fe3O4@NiO in six cycles of adsorption–desorption was investigated. By applying many isotherms and kinetic models of adsorption, it was concluded that Alizarin red S removal using Fe3O4@NiO followed pseudo-second-order kinetic equation (R2 = 0.9985) and Freundlich isotherm model (R2 = 0.9947) with a maximum adsorption capacity of 223.30 mg/g. The effect of coexisting ions (bicarbonate, phosphate, sulfate, nitrate ions) on the removal of Alizarin red S was investigated. The results indicated that adsorption capacity has decreased by increasing the concentration of co-anions in the solution. The affinity sequence for the anion adsorption on the adsorbent is \({\text{NO}}_{{3}}^{ - }\) > \({\text{HCO}}_{{3}}^{ - }\) > \({\text{PO}}_{{4}}^{{{3} - }}\) > \({\text{SO}}_{{4}}^{2 - }\). Overall, as-synthesized Fe3O4@NiO core–shell magnetic nanoparticles indicated an efficient performance in dye adsorption, specifically Alizarin red S dye from contaminated wastewater, which may be useful for practical applications in large quantities.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Absalan G, Bananejad A, Ghaemi M (2017) Removal of alizarin red and purpurin from aqueous solutions using Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem Res 4:65–77
Aksakal O, Ucun H (2010) Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the biosorption of textile dye (reactive red 195) onto Pinus sylvestris L. J Hazard Mater 181:666–672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.064
Aksu Z (2005) Application of biosorption for the removal of organic pollutants: a review. Process Biochem 40:997–1026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.04.008
Aksu Z, Ertuǧrul S, Dönmez G (2010) Methylene blue biosorption by rhizopus arrhizus: effect of SDS (sodium dodecylsulfate) surfactant on biosorption properties. Chem Eng J 158:474–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.01.029
Asgari G, Ramavandi B, Sahebi S (2014) Removal of a cationic dye from wastewater during purification by Phoenix dactylifera. Desalin Water Treat 52:7354–7365. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.823358
Asgher M, Bhatti HN (2012) Evaluation of thermodynamics and effect of chemical treatments on sorption potential of citrus waste biomass for removal of anionic dyes from aqueous solutions. Ecol Eng 38:79–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.10.004
Awad AM, Shaikh SMR, Jalab R et al (2019) Adsorption of organic pollutants by natural and modified clays: a comprehensive review. Sep Purif Technol 228:115719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115719
Aydin H, Baysal G (2006) Adsorption of acid dyes in aqueous solutions by shells of bittim (Pistacia khinjuk Stocks). Desalination 196:248–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.11.025
Azari A, Nabizadeh R, Nasseri S et al (2020) Comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of dyes adsorption by carbon-based adsorbent materials: classification and analysis of last decade studies. Chemosphere 250:126238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126238
Baghapour MA, Mahvi AH, Pourfadakari S (2013) Thermodynamic analysis of reactive red 198 removal from synthetic wastewater by using multiwall carbon nanotubes. Health Scope 2:149–155. https://doi.org/10.17795/jhealthscope-13438
Cheruiyot GK, Wanyonyi WC, Kiplimo JJ, Maina EN (2019) Adsorption of toxic crystal violet dye using coffee husks: equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics study. Scientific African 5:e00116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2019.e00116
Fan L, Zhang Y, Li X et al (2012) Removal of alizarin red from water environment using magnetic chitosan with Alizarin Red as imprinted molecules. Colloids Surf, B 91:250–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.11.014
Farahani A, Rahbar-Kelishami A, Shayesteh H (2021) Microfluidic solvent extraction of Cd(II) in parallel flow pattern: optimization, ion exchange, and mass transfer study. Sep Purif Technol 258:118031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.118031
Fayazi M, Ghanei-Motlagh M, Taher MA (2015) The adsorption of basic dye (Alizarin red S) from aqueous solution onto activated carbon/γ-Fe2O3 nano-composite: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Mater Sci Semicond Process 40:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.06.044
Fu F, Gao Z, Gao L, Li D (2011) Effective adsorption of anionic dye, alizarin red S, from aqueous solutions on activated clay modified by iron oxide. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:9712–9717. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie200524b
Garba ZN, Zhou W, Lawan I et al (2019) An overview of chlorophenols as contaminants and their removal from wastewater by adsorption: a review. J Environ Manag 241:59–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.04.004
Gautam RK, Mudhoo A, Chattopadhyaya MC (2013) Kinetic, equilibrium, thermodynamic studies and spectroscopic analysis of Alizarin Red S removal by mustard husk. J Environ Chem Eng 1:1283–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.09.021
Gautam RK, Gautam PK, Chattopadhyaya MC, Pandey JD (2014) Adsorption of alizarin Red S onto biosorbent of lantana camara: kinetic, equilibrium modeling and thermodynamic studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Secton A Phys Sci 84:495–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-014-0154-4
Gholivand MB, Yamini Y, Dayeni M et al (2015) Adsorptive removal of alizarin red-S and alizarin yellow GG from aqueous solutions using polypyrrole-coated magnetic nanoparticles. J Environ Chem Eng 3:529–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.01.011
Gupta VK, Suhas (2009) Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—a review. J Environ Manag 90:2313–2342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2008.11.017
Habiba U, Siddique TA, Joo TC et al (2017) Synthesis of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/zeolite composite for removal of methyl orange, Congo red and chromium(VI) by flocculation/adsorption. Carbohyd Polym 157:1568–1576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.11.037
Hadi M, Samarghandi MR, McKay G (2010) Equilibrium two-parameter isotherms of acid dyes sorption by activated carbons: Study of residual errors. Chem Eng J 160:408–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.03.016
Hashemian S, Rahimi M, Kerdegari AA (2016) CuFe2O4@ graphene nanocomposite as a sorbent for removal of alizarine yellow azo dye from aqueous solutions. Desalin Water Treat 57:14696–14707
Hassan SSM, Kamel AH, Hassan AA et al (2020) A sno2/ceo2 nano-composite catalyst for alizarin dye removal from aqueous solutions. Nanomaterials 10:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020254
Huo Y, Wu H, Wang Z et al (2018) Preparation of core/shell nanocomposite adsorbents based on amine polymer-modified magnetic materials for the efficient adsorption of anionic dyes. Colloids Surf, A 549:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.04.021
Ighalo JO, Adeniyi AG (2020) Adsorption of pollutants by plant bark derived adsorbents: an empirical review. J Water Process Eng 35:101228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101228
Islam MA, Benhouria A, Asif M, Hameed BH (2015) Methylene blue adsorption on factory-rejected tea activated carbon prepared by conjunction of hydrothermal carbonization and sodium hydroxide activation processes. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 52:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.02.010
Jalilvand P, Rahbar-Kelishami A, Mohammadi T, Shayesteh H (2020) Optimizing of malachite green extraction from aqueous solutions using hydrophilic and hydrophobic nanoparticles. J Mol Liq 308:113014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113014
Kausar A, Iqbal M, Javed A et al (2018) Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: a review. J Mol Liq 256:395–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.034
Khashan S, Dagher S, Tit N et al (2017) Novel method for synthesis of Fe3O4@TiO2 core/shell nanoparticles. Surf Coat Technol 322:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.05.045
Konicki W, Sibera D, Mijowska E et al (2013) Equilibrium and kinetic studies on acid dye Acid Red 88 adsorption by magnetic ZnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 398:152–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.02.021
Konicki W, Hełminiak A, Arabczyk W, Mijowska E (2018) Adsorption of cationic dyes onto Fe@graphite core–shell magnetic nanocomposite: equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics. Chem Eng Res Des 129:259–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.11.004
Lai KC, Lee LY, Hiew BYZ et al (2019) Environmental application of three-dimensional graphene materials as adsorbents for dyes and heavy metals: review on ice-templating method and adsorption mechanisms. J Environ Sci (china) 79:174–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.11.023
Li D, Liu Q, Ma S et al (2011) Adsorption of alizarin red S onto nano-sized silica modified with γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Adsorpt Sci Technol 29:289–300. https://doi.org/10.1260/0263-6174.29.3.289
Li Y, Bi HY, Liang YQ et al (2019) A magnetic core-shell dodecyl sulfate intercalated layered double hydroxide nanocomposite for the adsorption of cationic and anionic organic dyes. Appl Clay Sci 183:105309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2019.105309
Liang YD, He YJ, Zhang YH (2018) Adsorption property of alizarin red S by NiFe2O4/polyaniline magnetic composite. J Environ Chem Eng 6(1):416–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.12.022
Liu QS, Zheng T, Wang P et al (2010) Adsorption isotherm, kinetic and mechanism studies of some substituted phenols on activated carbon fibers. Chem Eng J 157:348–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.11.013
López-Ortiz A, Collins-Martínez VH, Hernández-Escobar CA et al (2008) Protection of NiO nanoparticles against leaching in acid medium by grafting of polyacrylic acid. Mater Chem Phys 109:306–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2007.11.031
Machado FM, Carmalin SA, Lima EC et al (2016) Adsorption of alizarin red S dye by carbon nanotubes: an experimental and theoretical investigation. J Phys Chem C 120:18296–18306. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b03884
Mahmoudi E, Behnajady MA (2018) Synthesis of Fe3O4@NiO core-shell nanocomposite by the precipitation method and investigation of Cr(VI) adsorption efficiency. Colloids Surf, A 538:287–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.11.020
Mohebali S, Bastani D, Shayesteh H (2018) Methylene blue removal using modified celery (Apium graveolens) as a low-cost biosorbent in batch mode: kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. J Mol Struct 1173:541–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.07.016
Mohebali S, Bastani D, Shayesteh H (2019) Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of a low-cost biosorbent for the removal of Congo red dye: acid and CTAB-acid modified celery (Apium graveolens). J Mol Struct 1176:181–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.08.068
Morshedi D, Mohammadi Z, Akbar Boojar MM, Aliakbari F (2013) Using protein nanofibrils to remove azo dyes from aqueous solution by the coagulation process. Colloids Surf, B 112:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.08.004
Nodehi R, Shayesteh H, Kelishami AR (2020) Enhanced adsorption of congo red using cationic surfactant functionalized zeolite particles. Microchem J 153:104281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104281
Paul Guin J, Bhardwaj YK, Varshney L (2017) Mineralization and biodegradability enhancement of methyl orange dye by an effective advanced oxidation process. Appl Radiat Isot 122:153–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2017.01.018
Qu F, Wang Y, Liu J et al (2014) Fe3O4-NiO core-shell composites: hydrothermal synthesis and toluene sensing properties. Mater Lett 132:167–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2014.06.060
Raghu S, Lee CW, Chellammal S et al (2009) Evaluation of electrochemical oxidation techniques for degradation of dye effluents-A comparative approach. J Hazard Mater 171:748–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.063
Rahman-Setayesh MR, Rahbar-Kelishami A, Shayesteh H (2020) Equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic applications for methylene blue removal using Buxus sempervirens leaf powder as a powerful low-cost adsorbent. J Particle Sci Technol 5:161–170. https://doi.org/10.22104/jpst.2020.3909.1160
Rehman R, Mahmud T (2013) Sorptive elimination of alizarin red-S dye from water using Citrullus lanatus peels in environmentally benign way along with equilibrium data modeling. Asian J Chem 25:5351
Roosta M, Ghaedi M, Mohammadi M (2014) Removal of Alizarin Red S by gold nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon combined with ultrasound device: optimization by experimental design methodology. Powder Technol 267:134–144
Saeed A, Sharif M, Iqbal M (2010) Application potential of grapefruit peel as dye sorbent: kinetics, equilibrium and mechanism of crystal violet adsorption. J Hazard Mater 179:564–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.03.041
Sarbisheh F, Norouzbeigi R, Hemmati F, Shayesteh H (2017) Application of response surface methodology for modeling and optimization of malachite green adsorption by modified sphagnum peat moss as a low cost biosorbent. Desalin Water Treat 59:230–242. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2016.1728
Sepehr MN, Amrane A, Karimaian KA et al (2014) Potential of waste pumice and surface modified pumice for hexavalent chromium removal: characterization, equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic study. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45:635–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2013.07.005
Setyaningsih N, Yanasin S, Supardi ZAI, Taufiq A (2019) Phase and magnetic properties of Fe3O4/SiO2 natural materials-based using polyethylene glycol media. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering. IOP Publishing, p 12017
Shayesteh H, Rahbar-Kelishami A, Norouzbeigi R (2016) Adsorption of malachite green and crystal violet cationic dyes from aqueous solution using pumice stone as a low-cost adsorbent: kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. Desalin Water Treat 57:12822–12831. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1054315
Wibowo NA, Juharni J, Alfansuri T et al (2020) Core-shell Fe3O4@ Ag magnetic nanoparticles detection using spin-valve GMR sensing element in the wheatstone bridge circuit. Mater Res Express 7:126102
Yang J-Y, Jiang X-Y, Jiao F-P, Yu J-G (2018) The oxygen-rich pentaerythritol modified multi-walled carbon nanotube as an efficient adsorbent for aqueous removal of alizarin yellow R and alizarin red S. Appl Surf Sci 436:198–206
Yu X, Shang L, Wang D et al (2018) Plasmon-resonance-enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity of Ag quantum dots/TiO2 microspheres for methyl orange degradation. Solid State Sci 80:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2018.03.014
Zhang Z, Chen H, Wu W et al (2019) Efficient removal of Alizarin Red S from aqueous solution by polyethyleneimine functionalized magnetic carbon nanotubes. Biores Technol 293:122100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122100
Zheng Y, Cheng B, Fan J et al (2021) Review on nickel-based adsorption materials for Congo red. Elsevier
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Iran University of Science and Technology for providing the support for this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Senthil Kumar Ponnusamy.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nodehi, R., Shayesteh, H. & Rahbar-Kelishami, A. Fe3O4@NiO core–shell magnetic nanoparticle for highly efficient removal of Alizarin red S anionic dye. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 2899–2912 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03399-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03399-8