Abstract
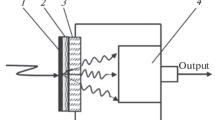
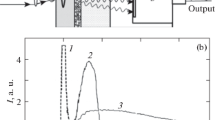
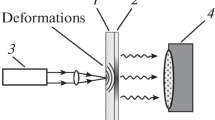
We studied the mechanoluminescence of composite materials based on polymethylmethacrylate and fine powder of Sr4Al14O25:(Eu2+,Dy3+) phosphor with a centrosymmetric crystal structure of microcrystals and fine powder of SrAl2O4:(Eu2+,Dy3+) phosphor with noncentrosymmetric structure. To study mechanoluminescence, a thin (~250–300 μm) layer of the composite material was deposited on the surface of a substrate transparent in the visible region of the spectrum. The mechanoluminescence of the composite layer was excited by the action of a mechanical striker, short laser pulses, or the dynamic pressure of a stylus sliding over the surface of the mechanoluminescent layer. The composite material based on a polymer and Sr4Al14O25:(Eu2+,Dy3+) powder with a centrosymmetric crystal lattice does not exhibit mechanoluminescence properties, while the composite material containing SrAl2O4:(Eu2+,Dy3+) exhibits pronounced mechanoluminescence. The excitation of mechanoluminescence in water begins at a much lower power density of laser pulses than in air. The resulting composite layer exhibits a high efficiency of “mechano-optical” conversion and can be used as sensor elements for sensors in mechatronic systems.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Terasaki, N., Yamada, H., and Xu, C.-N., Ultrasonic wave induced mechanoluminescence and its application for photocatalysis as ubiquitous light source, Catal. Today, 2013, vol. 201, pp. 203–208.
Chandra, B.P., Chandra, V.K., Mahobia, S.K., et al., Real time mechanoluminescence sensing of the amplitude and duration of impact stress, Sens. Actuators, A, 2012, vol. 173, pp. 9–16.
Wang, C., Dong, L., Peng, D., et al., Tactile sensors for advanced intelligent systems, Adv. Intell. Syst., 2019, vol. 1, no. 8, art. ID 1900090. https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.201900090
Qian, X., Cai, Z., Su, M., et al., Printable skin-driven mechanoluminescence devices via nanodoped matrix modification, Adv. Mater., 2018, vol. 30, art. ID 1800291.
Banishev, A.A., Lotin, A.A., and Banishev, A.F., Low temperature photoluminescence and deformation luminescence of microparticles SrAl2O4:(Eu2+,Dy3+) in a matrix of photopolymer, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B, 2014, vol. 28, no. 23, art. ID 1450154.
Banishev, A.F. and Banishev, A.A., Deformation stimulated luminescence of polymer film induced by pulsed mechanical stresses, Phys. Lett. A, 2011, vol. 375, nos. 28–29, pp. 2767–2769.
Banishev, A.F. and Banishev, A.A., Deformation stimulated luminescence of a composite produced on the basis of polymethylmethacrylate transparent in the visible region and finely dispersed powder of SrAl2O4:(Eu2+,Dy3+) phosphor, Inorg. Mater.: Appl. Res., 2019, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 647–651.
Banishev, A.F. and Banishev, A.A., Mechanoluminescence of a thin composite layer obtained by incorporation of SrAl2O4:(Eu2+,Dy3+) phosphor microparticles into a poly(methyl methacrylate) surface, Tech. Phys. Lett., 2019, vol. 45, no. 5, pp. 475–477. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063785019050201
Banishev, A.F., Banishev, A.A., and Lotin, A.A., An investigation of photo- and mechanoluminescence of SrAl2O4:(Eu2+,Dy3+) fine powder in photopolymer matrix, Fiz. Khim. Obrab. Mater., 2012, no. 5, pp. 89–92.
Leelachao, S., Muraishi, Sh., Sannomiya, T., Shi, J., and Namamura, Y., Mechanoluminescence of ZnS:Mn phosphors and its correlation to impact energy and contact geometry, Opt. Lett., 2015, vol. 40, no. 19, pp. 4468–4471.
Feng, A. and Smet, P.F., A review of mechanoluminescence in inorganic solids: Compounds, mechanisms, models and applications, Materials, 2018, vol. 11, no. 4, art. ID 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11040484
Zhang, H., Peng, D., Wang, W., et al., Mechanically induced light emission and infrared-laser-induced upconversion in the Er-doped CaZnOS multifunctional piezoelectric semiconductor for optical pressure and temperature sensing, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, vol. 119, art. ID 28136.
Wang, X., Peng, D., Huang, B., Pan, C., and Wang, Z.L., Piezophotonic effect based on mechanoluminescent materials for advanced flexible optoelectronic applications, Nano Energy, 2019, vol. 55, pp. 389–400.
Zhang, J.-C., Wang, X., Marriott, G., and Xu, C.-N., Trap-controlled mechanoluminescent materials, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2019, vol. 103, pp. 678–742.
Banishev, A.F., Banishev, A.A., Bolshukhin, V.A., Syrov, Yu.V., and Khort, A.M., Mechano- and photoluminescence of fine powders and films on the base of solid solutions of SrAl2O4:(Eu2+, Dy3+), Fiz. Khim. Obrab. Mater., 2010, no. 2, pp. 60–65.
Rahimi, M.R., Yun, G.J., Doll, G.L., and Choi, J.S., Effects of persistent luminescence decay on mechanoluminescence phenomena of SrAl2O4:(Eu2+,Dy3+) materials, Opt. Lett., 2013, vol. 38, pp. 4134–4137.
Timilsina, S., Lee, K.H., Jang, I.Y., and Kim, J.S., Mechanoluminescent determination of the mode stress intensity factor in SrAl2O4:(Eu2+, Dy3+), Acta Mater., 2013, vol. 61, pp. 7197–7206.
Banishev, A.A. and Banishev, A.F., Photoluminescence features and mechanoluminescence mechanism inherent in composite materials based on a photopolymerizing resin and finely dispersed powders of SrAl2O4:(Eu2+,Dy3+) and Sr4Al14O25:(Eu2+,Dy3+, B) luminophores, Inorg. Mater.: Appl. Res., 2018, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 484–489.
Botterman, J., van den Eeckhout, K., de Baere, I., Poelman, D., and Smet, P.F., Mechanoluminescence in BaSi2O2N2: Eu, Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 5494–5500.
Zhang, J.C., Xu, C.N., Kamimura, S., Terasawa, Y., Yamada, H., et al., An intense elastico-mechanoluminescence material CaZnOS:Mn2+ for sensing and imaging multiple mechanical stresses, Opt. Exp., 2013, vol. 21, pp. 12976–12986.
Kamimura, S., Yamada, H., and Xu, C.N., Strong reddish-orange light emission from stress-activated Srn + 1SnnO3n + 1:Sm3+ (n = 1, 2, ∞) with perovskite-related structures, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2012, vol. 101, no. 9, art. ID 091113.
Bunkin, F.V. and Prokhorov, A.M., Use of a laser energy source in producing a reactive thrust, Sov. Phys.-Usp., 1976, vol. 19, no. 7, pp. 561–573. https://doi.org/10.1070/PU1976v019n07ABEH005273
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research and the State Atomic Energy Corporation Rosatom in the framework of the scientific project no. 20-21-00066 and partially supported by the RF Ministry of Science and Higher Education in the framework of the work on the state task of the Federal Scientific Research Centre Crystallography and Photonics of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by O. Zhukova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Banishev, A.F., Banishev, A.A. An Investigation of the Mechanoluminescence of Composite Materials Based on a Polymer and a Phosphor Powder Excited by the Action of a Mechanical Striker, Stylus, and Laser Pulse. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 12, 785–789 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113321030047
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2075113321030047