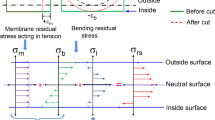
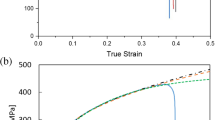
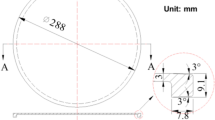
Abstract
Rectangular and square hollow steel sections can be manufactured using either a “direct forming” or an “indirect forming” method. The production route for both “direct forming” and “indirect forming” techniques can be conducted at room temperature (cold forming) or elevated temperature (hot forming). It might also start by forming at room temperature and subsequently followed by heat treatment (hot-finishing). The manufacturing method and production route choice cause the final products that are roll-formed from the same material to possess different mechanical properties. One of the main reasons for the disparity of mechanical properties is the variation of residual stress induced during forming processes. In this paper, available numerical and experimental studies of different rectangular and square steel hollow sections manufacturing methods and production routes on residual stresses are comprehensively reviewed. Furthermore, studies on the effects of roll-forming parameters on product quality and residual stresses are integrated. Moreover, future research activities aiming to manufacture residual stresses-free rectangular and square hollow sections are recommended.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- b :
-
Rectangular or square section width
- DF:
-
Direct formed
- D S :
-
Diameter of side roll
- D T :
-
Diameter of top roll
- IF:
-
Indirect formed
- r i :
-
Inside corner radius
- S a :
-
Average of height and width of corner
- S x :
-
Width of corner
- S y :
-
Height of corner
- t :
-
Section thickness
- σ b :
-
Bending residual stress
- σ b ,in :
-
Bending residual stress on inner surface
- σ b ,out :
-
Bending residual stress outer surface
- σ long :
-
Longitudinal residual stress
- σ long ,corner :
-
Longitudinal residual stress on the corner area
- σ long ,flat :
-
Longitudinal residual stress on the flat face
- σ long ,in :
-
Longitudinal residual stress on inner surface
- σ long ,avg :
-
Average longitudinal residual stress
- σ long ,out :
-
Longitudinal residual stress on outer surface
- σ m :
-
Membrane residual stress
- σ rs :
-
Combined residual stress
- σ trans :
-
Transversal residual stress
- σ trans ,avg :
-
Average transversal residual stress
- σ y :
-
Material yield stress
- σ y ,corner :
-
Material yield stress on the corner area
- σ y ,flat :
-
Material yield stress on the flat face
- σ 0 .2 :
-
Static 0.2% tensile proof stress
- σ 0 .2,corner :
-
Static 0.2% tensile proof stress the corner area
- σ 0 .2,flat :
-
Static 0.2% tensile proof stress on the flat face
- ɛ :
-
Total strain
- ɛ b :
-
Bending residual strain
- ɛ m :
-
Membrane residual strain
References
Halmos GT. Roll forming handbook. 2005. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420030693.
Sweeney K, Grunewald U. The application of roll forming for automotive structural parts. J Mater Process Technol. 2003;132:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00193-0.
Groche P, Henkelmann M, Götz P, Berner S. Cold rolled profiles for vehicle construction. Arch Civ Mech Eng. 2008;8:31–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1644-9665(12)60191-5.
Kacar I, Ozturk F. Roll forming applications for automotive industry. In: Automot. Technol. Congr. 2014. pp. 1–6.
Kuchta K, Tylek I. Rational application of hot finished rectangular hollow sections in steel structures. In: MATEC Web Conf. 2018. pp. 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201816307005.
Sedlmaier A, Dietl T. 3D roll forming center for automotive applications. Proc Manuf. 2018;15:767–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2018.07.319.
Gronostajski Z, Pater Z, Madej L, Gontarz A, Lisiecki L, Łukaszek-Sołek A, Łuksza J, Mróz S, Muskalski Z, Muzykiewicz W, Pietrzyk M, Śliwa RE, Tomczak J, Wiewiórowska S, Winiarski G, Zasadziński J, Ziółkiewicz S. Recent development trends in metal forming. Arch Civ Mech Eng. 2019;19:898–941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2019.04.005.
Abambres M, Quach WM. Residual stresses in steel members: a review of available analytical expressions. Int J Struct Integr. 2016;7:70–94. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSI-12-2014-0070.
Li SH, Zeng G, Ma YF, Guo YJ, Lai XM. Residual stresses in roll-formed square hollow sections. Thin Walled Struct. 2009;47:505–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2008.10.015.
Sun M, Packer JA. Direct-formed and continuous-formed rectangular hollow sections - comparison of static properties. J Constr Steel Res. 2014;92:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2013.09.013.
Zhang XZ, Liu S, Zhao MS, Chiew SP. Comparative experimental study of hot-formed, hot-finished and cold-formed rectangular hollow sections. Case Stud Struct Eng. 2016;6:115–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csse.2016.09.001.
Standard for cold galvanized steel tubes. https://www.cnspipes.com/info/standard-for-cold-galvanized-steel-tubes-32456283.html.
Neves FO, Oliviera TLL, Braga DU, Da Silva ASC. Influence of heat treatment on residual stress in cold-forged parts. Adv Mater Sci Eng. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/658679.
Hui X, Wang X. Forming quality analysis on the cold roll forming C-channel steel. Materials. 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11101911.
Sun Y, Li Y, Daniel WJT, Meehan PA, Liu Z, Ding S. Longitudinal strain development in Chain-die forming AHSS products: analytical modelling, finite element analysis and experimental verification. J Mater Process Technol. 2017;243:322–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.12.019.
Heinilä S, Björk T, Marquis G. The influence of residual stresses on the fatigue strength of cold-formed structural tubes. J ASTM Int. 2008;5:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1520/JAI101570.
Jandera M, Machacek J. Residual stress influence on material properties and column behaviour of stainless steel SHS. Thin Walled Struct. 2014;83:12–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2014.03.013.
Ma JL, Chan TM, Young B. Material properties and residual stresses of cold-formed high strength steel hollow sections. J Constr Steel Res. 2015;109:152–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2015.02.006.
Shiozaki T, Tamai Y, Urabe T. Effect of residual stresses on fatigue strength of high strength steel sheets with punched holes. Int J Fatigue. 2015;80:324–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2015.06.018.
Tong L, Hou G, Chen Y, Zhou F, Shen K, Yang A. Experimental investigation on longitudinal residual stresses for cold-formed thick-walled square hollow sections. J Constr Steel Res. 2012;73:105–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2012.02.004.
Peng XF, Han JT, Liu J, Li DY, Yan PJ. Key technical analysis of roll forming for high strength rectangular tube. Adv Mater Res. 2014;941–944:1812–6. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.941-944.1812.
Tayyebi K, Sun M, Karimi K. Residual stresses of heat-treated and hot-dip galvanized RHS cold-formed by different methods. J Constr Steel Res. 2020;169:106071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2020.106071.
Yao Y, Quach WM, Young B. Finite element-based method for residual stresses and plastic strains in cold-formed steel hollow sections. Eng Struct. 2019;188:24–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2019.03.010.
Key PW, Hancock GJ. Non-linear analysis of cold-formed sections using the finite strip method. In: Ninth Int. Spec. Conf. Cold-Formed Steel Struct. 1988. pp. 75–96.
Key PW, Hancock GJ. A theoretical investigation of the column behaviour of cold-formed square hollow sections. Thin Walled Struct. 1993;16:31–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/0263-8231(93)90040-H.
Clarin M, Lagerqvist O. Residual stresses in square hollow sections made of high strength steel. In: Fourth Int. Conf. Adv. Steel Struct. II. 2005. pp. 1577–1582. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-008044637-0/50235-3.
Cruise RB, Gardner L. Residual stress analysis of structural stainless steel sections. J Constr Steel Res. 2008;64:352–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2007.08.001.
Gardner L, Cruise RB. Modeling of residual stresses in structural stainless steel sections. J Struct Eng. 2009;135:42–53. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2009)135:1(42).
Gardner L, Saari N, Wang F. Comparative experimental study of hot-rolled and cold-formed rectangular hollow sections. Thin Walled Struct. 2010;48:495–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2010.02.003.
Li W, Zhang X, Kou H, Wang R, Fang D. Theoretical prediction of temperature dependent yield strength for metallic materials. Int J Mech Sci. 2016;105:273–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2015.11.017.
Somodi B, Kövesdi B. Residual stress measurements on cold-formed HSS hollow section columns. J Constr Steel Res. 2017;128:706–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2016.10.008.
Han ZW, Liu C, Lu WP, Ren LQ. The effects of forming parameters in the roll-forming of a channel section with an outer edge. J Mater Process Technol. 2001;116:205–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(01)01041-X.
Tavares TB, Rodrigues DG, Santos DB. Effect of warm rolling and annealing on microstructure, texture, and mechanical properties of a 2205 Duplex stainless steel. Steel Res Int. 2020;91:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201900543.
Chen Y, Zhang X, Cai Z, Ding H, Pan M, Wei W, Liu Y. Effects of rolling temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a High-Mn austenitic steel for cryogenic applications. Steel Res Int. 2020;1900660:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.201900660.
Stamenkovic A, Gardner MJ. Effect of residual stresses on the column behaviour of hot-finished steel structural hollow sections. Proc Inst Civ Eng. 1983;75:599–616. https://doi.org/10.1680/iicep.1984.1196.
Kwak SY, Hwang HY. Effect of heat treatment residual stress on stress behavior of constant stress beam. J Comput Des Eng. 2018;5:137–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcde.2017.07.001.
Li GW, Li YQ. Overall stability behavior of annealed cold-formed thick-walled SHS and RHS steel tubes. J Constr Steel Res. 2019;157:260–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2019.02.033.
Sun M, Ma Z. Effects of heat-treatment and hot-dip galvanizing on mechanical properties of RHS. J Constr Steel Res. 2019;153:603–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2018.11.012.
Sun M, Packer JA. Hot-dip galvanizing of cold-formed steel hollow sections: a state-of-the-art review. Front Struct Civ Eng. 2019;13:49–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-017-0448-0.
Kang W, Zhao Y, Yu W, Wang S, Ma Y, Yan P. Numerical simulation and parameters analysis for roll forming of martensitic steel MS980. Proc Eng. 2014;81:251–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2014.09.159.
Abeyrathna B, Rolfe B, Weiss M. The effect of process and geometric parameters on longitudinal edge strain and product defects in cold roll forming. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2017;92:743–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-0164-x.
Nagamachi T, Kitawaki T, Matsumura K. Effects of ellipse preforming on cross-sectional shapes of square steel pipe formed by roll forming. Mater Trans. 2013;54:2189–94. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.P-M2013834.
Bayoumi LS, Attia AS. Determination of the forming tool load in plastic shaping of a round tube into a square tubular section. J Mater Process Technol. 2009;209:1835–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.04.047.
Nagamachi T, Nakako T, Nakamura D. Effects of forming conditions of roll offset method on sectional shape at the corner of square steel pipe. Mater Trans. 2013;54:1703–8. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.P-M2013815.
Li GW, Li YQ, Xu J, Cao X. Experimental investigation on the longitudinal residual stress of cold-formed thick-walled SHS and RHS steel tubes. Thin Walled Struct. 2019;138:473–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2018.09.036.
Chen MT, Young B. Material properties and structural behavior of cold-formed steel elliptical hollow section stub columns. Thin Walled Struct. 2019;134:111–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2018.07.055.
Tebedge N, Alpsten G, Tall L. Residual-stress measurement by the sectioning method. Exp Mech. 1973;13:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02322389.
Sun Y, Luzin V, Daniel WJT, Meehan PA, Zhang M, Ding S. Development of the slope cutting method for determining the residual stresses in roll formed products. Meas J Int Meas Confed. 2017;100:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2016.12.036.
Wald MJ, Considine JM, Turner KT, Service USF. Measuring the elastic modulus of soft thin films on substrates. Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, vol. 6, pp. 741–747. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9792-0.
Zaroog OS, Yap C, Ken W, Noorlina A, Manap A. Current and challenge of residual stress measurement techniques. Int J Sci Res. 2014;3:210–6.
Rossini NS, Dassisti M, Benyounis KY, Olabi AG. Methods of measuring residual stresses in components. Mater Des. 2012;35:572–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.08.022.
Modeling FE. Finite element modeling. SpringerBriefs Appl Sci Technol. 2015;21:53–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14986-8_7.
Pastor MM, Bonada J, Roure F, Casafont M. Residual stresses and initial imperfections in non-linear analysis. Eng Struct. 2013;46:493–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2012.08.013.
Guo J, Fu H, Pan B, Kang R. Recent progress of residual stress measurement methods: a review. Chin J Aeronaut. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2019.10.010.
Huang X, Liu Z, Xie H. Recent progress in residual stress measurement techniques. Acta Mech Solida Sin. 2013;26:570–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0894-9166(14)60002-1.
Withers PJ, Bhadeshia HKDH. Residual stress part 2 - nature and origins. Mater Sci Technol. 2001;17:366–75. https://doi.org/10.1179/026708301101510087.
Safdarian R, Moslemi Naeini H. The effects of forming parameters on the cold roll forming of channel section. Thin Walled Struct. 2015;92:130–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2015.03.002.
Billur E, Altan PDT. Challenges in forming advanced high strength steels. New Dev. Sheet Met. Form. 2010. pp. 285–304.
Bhargava M, Tewari A, Mishra SK. Forming limit diagram of advanced high strength steels (AHSS) based on strain-path diagram. Mater Des. 2015;85:149–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.06.147.
Simpson N, Van Rooyen GT. Corner cracking associated with the production of square tubing from low carbon ferritic stainless steel. J S Afri Inst Min Metall. 2003;103:641–4.
Han F, Wang Y, Wang ZL. Mechanical bending property of ultra-high strength steel sheets in roll forming process. Int J Precis Eng Manuf. 2018;19:1885–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-018-0216-7.
Wang H, Yan Y, Jia F, Han F. Investigations of fracture on DP980 steel sheet in roll forming process. J Manuf Process. 2016;22:177–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2016.03.008.
Brnic J, Canadija M, Turkalj G, Lanc D, Pepelnjak T, Barisic B, Vukelic G, Brcic M. Tool material behavior at elevated temperatures. Mater Manuf Process. 2009;24:758–62. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426910902809800.
Pandre S, Morchhale A, Kotkunde N, Singh SK. Influence of processing temperature on formability of thin-rolled DP590 steel sheet. Mater Manuf Process. 2020;35:901–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2020.1743854.
Saito N, Fukahori M, Hisano D, Hamasaki H, Yoshida F. Effects of temperature, forming speed and stress relaxation on springback in warm forming of high strength steel sheet. Procedia Eng. 2017;207:2394–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.10.1014.
Karren K, Winter G. Investigation of effects of cold forming on mechanical properties. Center for Cold-Formed Steel Structures Library; 1964, p. 13. https://scholarsmine.mst.edu/ccfss-library/13.
Chajes A, Warren K. Effects of cold work in cold-formed steel structural members. Center for Cold-Formed Steel Structures Library; 1970, p. 70. https://scholarsmine.mst.edu/ccfsslibrary/170.
Xu D, Wan X, Yu J, Xu G, Li G. Effect of cold deformation on microstructures and mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steel. Metals. 2018;8:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8070522.
Nie Z, Li Y, Wang Y. Mechanical properties of steels for cold-formed steel structures at elevated temperatures. Adv Civ Eng. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9627357.
Paralikas J, Salonitis K, Chryssolouris G. Optimization of roll forming process parameters-a semi-empirical approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2010;47:1041–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-009-2252-z.
Liu X, Cao J, Chai X, Liu J, Zhao R, Kong N. Investigation of forming parameters on springback for ultra high strength steel considering Young’s modulus variation in cold roll forming. J Manuf Process. 2017;29:289–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.08.001.
Badr OM, Rolfe B, Weiss M. Effect of the forming method on part shape quality in cold roll forming high strength Ti-6Al-4V sheet. J Manuf Process. 2018;32:513–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.03.022.
Son JY, Yoon HS, Park WK, Shim DS. Fundamental study on the development of a new incremental roll forming process for structural pipe manufacturing. J Korean Soc Precis Eng. 2017;34:217–24. https://doi.org/10.7736/KSPE.2017.34.3.217.
Bui QV, Ponthot JP. Numerical simulation of cold roll-forming processes. J Mater Process Technol. 2008;202:275–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.08.073.
Mohammdi Najafabadi H, Moslemi Naeini H, Safdarian R, Kasaei MM, Akbari D, Abbaszadeh B. Effect of forming parameters on edge wrinkling in cold roll forming of wide profiles. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2019;101:181–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-018-2885-x.
Shirani Bidabadi B, Moslemi Naeini H, Salmani Tehrani M, Barghikar H. Experimental and numerical study of bowing defects in cold roll-formed, U-channel sections. J Constr Steel Res. 2016;118:243–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2015.11.007.
Miller AG. Review of limit loads of structures containing defects. Int J Press Vessel Pip. 1988;32:197–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/0308-0161(88)90073-7.
Zhu XK, Joyce JA. Review of fracture toughness (G, K, J, CTOD, CTOA) testing and standardization. Eng Fract Mech. 2012;85:1–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2012.02.001.
Abvabi A, Rolfe B, Hodgson PD, Weiss M. The influence of residual stress on a roll forming process. Int J Mech Sci. 2015;101–102:124–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2015.08.004.
Cai Y, Quach WM, Chen MT, Young B. Behavior and design of cold-formed and hot-finished steel elliptical tubular stub columns. J Constr Steel Res. 2019;156:252–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2019.02.006.
Liu W, Rasmussen KJR, Zhang H. Modelling and probabilistic study of the residual stress of cold-formed hollow steel sections. Eng Struct. 2017;150:986–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.08.004.
Qiang X, Bijlaard F, Kolstein H. Dependence of mechanical properties of high strength steel S690 on elevated temperatures. Constr Build Mater. 2012;30:73–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.12.018.
Chen J, Young B. Design of high strength steel columns at elevated temperatures. J Constr Steel Res. 2008;64:689–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2007.09.004.
ASTM. Standard practice for safeguarding against embrittlement of hot-dip galvanized structural steel products and procedure for detecting. American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1520/A0143.
Jandera M, Machacek J. Residual stress pattern of stainless steel SHS. In: Tubul. Struct. XIII - Proc. 13th Int. Symp. Tubul. Struct. 2010. pp. 265–272. https://doi.org/10.1201/b10564-37.
Yun X, Gardner L. Numerical modelling and design of hot-rolled and cold-formed steel continuous beams with tubular cross-sections. Thin Walled Struct. 2018;132:574–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2018.08.012.
Wang J, Afshan S, Gkantou M, Theofanous M, Baniotopoulos C, Gardner L. Flexural behaviour of hot-finished high strength steel square and rectangular hollow sections. J Constr Steel Res. 2016;121:97–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcsr.2016.01.017.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express our appreciation to Elsevier, the Japan Society for Technology Plasticity (JSTP), and The Korean Society for Precision Engineering for their permission of figure reproduction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abathun, M.Z., Han, J. & Yu, W. Effects of manufacturing methods and production routes on residual stresses of rectangular and square hollow steel sections: a review. Archiv.Civ.Mech.Eng 21, 100 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-021-00193-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-021-00193-8