Abstract
pH-sensitive hydrogels are classified as soft materials that can be employed for future imaginative applications due to their interesting characteristics. Smart hydrogels undergo large deformation under exterior stimuli. However, the swelling behaviors of hydrogels that can be harnessed for microfluidic applications are not well perceived. In this paper, the functionality of an assortment of micro-valves which are composed of pH-sensitive cylindrical hydrogel jackets coated on rigid pillars is inspected considering fully coupled fluid–solid interaction analysis. Therefore, in order to introduce the theory of transient swelling of a pH-sensitive micro-check valve, a transient constitutive model capturing electrical, chemical, and mechanical fields for the hydrogel domain is utilized with fluid fields passing around the micro-valve. In this regard, the Nernst–Planck equation is employed to describe the ions’ diffusion, and Gent hyperelastic model is used to account for the large deformation of the hydrogel. Implementing this nonlinear finite element framework, we examine the performance of one cylindrical jacket and also three patterns of multiple cylindrical valves considering transient 3D FSI behavior of the hydrogel micro-valve. The foremost emphasized novelty of this paper is considering three-dimensional geometry, new designs of micro-valves, and time-dependent swelling of hydrogels by coupling ions diffusion and their large deformation.
Article Highlights
-
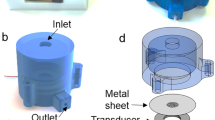
Three-dimensional single and multiple pH-sensitive hydrogel micro-valves
-
Electro-chemo-mechanical theory for pH-sensitive hydrogels to predict their transient swelling
-
Fluid–solid interaction of Newtonian fluid and hydrogel which can undergo large reversible deformation









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability and material
There is no material data to be shared.
References
Arbabi, N., Baghani, M., Abdolahi, J., Mazaheri, H., Mosavi-Mashhadi, M.: Study on pH-sensitive hydrogel micro-valves: A fluid–structure interaction approach. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 28(12), 1589–1602 (2017)
Banerjee, H., Suhail, M., Ren, H.: Hydrogel actuators and sensors for biomedical soft robots: brief overview with impending challenges. Biomimetics 3(3), 15 (2018)
Bayat, M.R., Baghani, M.: Fully-coupled transient fluid–solid interaction simulation of the pH-sensitive hydrogel-based microvalve. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 11(07), 1950071 (2019)
Bayat, M.R., Dolatabadi, R., Baghani, M.: Transient swelling response of pH-sensitive hydrogels: a monophasic constitutive model and numerical implementation. Int. J. Pharm. 577, 119030 (2020)
Beebe, D.J., Moore, J.S., Bauer, J.M., Yu, Q., Liu, R.H., Devadoss, C., Jo, B.-H.: Functional hydrogel structures for autonomous flow control inside microfluidic channels. Nature 404(6778), 588–590 (2000)
De, S.K., Aluru, N.R.: A chemo-electro-mechanical mathematical model for simulation of pH sensitive hydrogels. Mech. Mater. 36(5–6), 395–410 (2004)
De, S.K., Aluru, N.R., Johnson, B., Crone, W.C., Beebe, D.J., Moore, J.: Equilibrium swelling and kinetics of pH-responsive hydrogels: Models, experiments, and simulations. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 11(5), 544–555 (2002)
Dolatabadi, R., Mohammadi, A., Baghani, M.: A computational simulation of electromembrane extraction based on Poisson Nernst–Planck equations. Anal. Chim. Acta 1158, 338414 (2021a)
Dolatabadi, R., Mohammadi, A., Nojavan, S., Yaripour, S., Tafakhori, A., Shirangi, M.: Electromembrane extraction-high-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection of phenobarbital and phenytoin in human plasma, saliva, and urine. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. (2021b). https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.202100016
Drozdov, A.D.: Swelling of pH-responsive cationic gels: Constitutive modeling and structure–property relations. Int. J. Solids Struct. 64, 176–190 (2015)
Gerami, A., Alzahid, Y., Mostaghimi, P., Kashaninejad, N., Kazemifar, F., Amirian, T., Mosavat, N., Warkiani, M.E., Armstrong, R.T.: Microfluidics for porous systems: fabrication, microscopy and applications. Transp. Porous Media 130(1), 277–304 (2019)
Ghasemkhani, A., Mazaheri, H., Amiri, A.: Fluid-structure interaction simulations for a temperature-sensitive functionally gradedhydrogel-based micro-channel. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 32(6), 661–677 (2020)
Ghoshal, U.K., Bhattacharyya, S., Gopmandal, P.P., De, S.: Nonlinear effects on electrophoresis of a soft particle and sustained solute release. Transp. Porous Media 121(1), 121–133 (2018)
Horgan, C.O., Saccomandi, G.: Constitutive models for compressible nonlinearly elastic materials with limiting chain extensibility. J. Elast. 77(2), 123–138 (2004)
Huang, R., Zheng, S., Liu, Z., Ng, T.Y.: Recent advances of the constitutive models of smart materials—Hydrogels and shape memory polymers. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 12(02), 2050014 (2020)
Huyghe, J., Janssen, J.D.: Thermo-chemo-electro-mechanical formulation of saturated charged porous solids. Transp. Porous Media 34(1), 129–141 (1999)
Jeans, J.: Mathematical theory of electricity and magnetism. Cambridge University Press (1925)
Jeon, M.-K., Kim, S., Hosseini Zadeh, A., Kwon, T.-H.: Study on viscous fluid flow in disordered-deformable porous media using hydro-mechanically coupled pore-network modeling. Transp. Porous Media 133, 207–227 (2020)
Kim, D., Beebe, D.J.: A bi-polymer micro one-way valve. Sens. Actuat. A 136(1), 426–433 (2007)
Kurnia, J.C., Birgersson, E., Mujumdar, A.S.: Analysis of a model for pH-sensitive hydrogels. Polymer 53(2), 613–622 (2012)
Marcombe, R., Cai, S., Hong, W., Zhao, X., Lapusta, Y., Suo, Z.: A theory of constrained swelling of a pH-sensitive hydrogel. Soft Matter 6(4), 784–793 (2010)
Mazaheri, H., Namdar, A.H., Amiri, A.: Behavior of a smart one-way micro-valve considering fluid–structure interaction. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 29(20), 3960–3971 (2018)
Mazaheri, H., Ghasemkhani, A., Namdar, A.H.: Behavior of photo-thermal sensitive polyelectrolyte hydrogel micro-valve: analytical and numerical approaches. J. Stress Anal. 5(1), 21–30 (2020)
Nguyen, N.-T., Truong, T.-Q., Wong, K.-K., Ho, S.-S., Low, C.L.-N.: Micro check valves for integration into polymeric microfluidic devices. J. Micromech. Microeng. 14(1), 69 (2003)
Shojaeifard, M., Baghani, M.: On the finite bending of functionally graded light-sensitive hydrogels. Meccanica 54(6), 841–854 (2019)
Shojaeifard, M., Baghani, M.: Finite deformation swelling of a temperature-sensitive hydrogel cylinder under combined extension-torsion. Appl. Math. Mech. 41(3), 409–424 (2020)
Shojaeifard, M., Bayat, M.R., Baghani, M.J.A.M.: Swelling-induced finite bending of functionally graded pH-responsive hydrogels: a semianalytical method. Appl. Math. Mech. 40(5), 679–694 (2019a).
Shojaeifard, M., Rouhani, F., Baghani, M.: A combined analytical–numerical analysis on multidirectional finite bending of functionally graded temperature-sensitive hydrogels. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 30(13), 1882–1895 (2019b).
Shojaeifard, M., Tahmasiyan, S., Baghani, M.: Swelling response of functionally graded temperature-sensitive hydrogel valves: Analytic solution and finite element method. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 31(3), 457–474 (2019c).
Shojaeifard, M., Dolatabadi, R., Sheikhi, S., Baghani, M.: Coupled thermo-mechanical swelling of a thermo-responsive hydrogel hollow cylinder underextension-torsion: Analytical Solution and FEM. J. Int. Mat. Syst. Struct. 32(2), 140–55 (2021)
Shojaeifard, M., Wang, K., Baghani, M.: Large deformation of hyperelastic thick-walled vessels under combined extension-torsion-pressure: analytical solution and FEM. Mech. Based Design Struct. Mach. 1–18 (2020a)
Shojaeifard, M., Sheikhi, S., Baniassadi, M., Baghani, M.: On finite bending of visco-hyperelastic materials: A novel analytical solution and FEM. Acta Mechanica 231(8), 3435–3450 (2020b)
Soha, N.M., Mostafa, S.: Baghani PH-sensitive hydrogel-based valves: A transient fully-coupledfluid-solid interaction study. J. Int. Mat. Syst. Struct. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X211011671
Standnes, D.C., Evje, S., Andersen, P.Ø.: A novel relative permeability model based on mixture theory approach accounting for solid–fluid and fluid–fluid interactions. Transp. Porous Media 119(3), 707–738 (2017)
Sweijen, T., Nikooee, E., Hassanizadeh, S.M., Chareyre, B.: The effects of swelling and porosity change on capillarity: DEM coupled with a pore-unit assembly method. Transp. Porous Media 113(1), 207–226 (2016)
Valiollahi, A., Shojaeifard, M., Baghani, M.: Implementing stretch-based strain energy functions in large coupled axial and torsional deformations of functionally graded cylinder. Int. J. Appl. Mech. 11(04), 1950039 (2019a)
Valiollahi, A., Shojaeifard, M., Baghani, M.: Closed form solutions for large deformation of cylinders under combined extension-torsion. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 157, 336–347 (2019b)
Wang, X.-Q., Tai, Y.-C.: A normally closed in-channel micro check valve. Proceedings IEEE thirteenth annual international conference on micro electro mechanical systems (Cat. No.00CH36308), 68–73 (2000)
Wang, Y., Toyoda, K., Uesugi, K., Morishima, K.: A simple micro check valve using a photo-patterned hydrogel valve core. Sens. Actuat. A 304, 111878 (2020)
Zheng, S., Li, Z., Liu, Z.: The fast homogeneous diffusion of hydrogel under different stimuli. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 137, 263–270 (2018)
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The first draft of the manuscript was written by Mohammad Shojaeifard and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Code availability
There is no code to be shared
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niroumandi, S., Shojaeifard, M. & Baghani, M. On Single and Multiple pH-Sensitive Hydrogel Micro-valves: A 3D Transient Fully Coupled Fluid–Solid Interaction Study. Transp Porous Med 142, 295–316 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-021-01625-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-021-01625-y