Abstract
Purpose
This research presents experimental results of dredged lakebed sediment-stabilised with ordinary Portland cement (OPC) and fly ash (FA) for use as pavement materials in road infrastructure. The work also proposed empirical correlations for the strength and stiffness parameters of chemically stabilised dredged sediments intended for pavement engineering.
Materials and methods
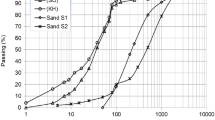
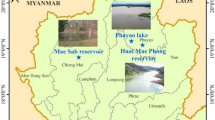
The dredged sediment was collected from the drop-off area around Phayao Lake in Thailand. The sediment’s optimal moisture content was determined by a Proctor compaction test. The OPC and FA content ranged from 3 to 10% and 5 to 20% per dry weight of sediment. The shear strength of treated sediments at different curing time was measured using the unconfined compression (UC) test.
Results and discussion
The optimum FA content proved to be most effective in generating the highest material strengths and stiffnesses from the stabilised sediments, regardless of OPC contents and curing duration. A suitable replacement ratio of cement with fly ash was 15%. The results were compared with data on other types of chemically stabilised sediments available in literature. Correlations between engineering properties and design parameters such as UCS, E50, \({\upvarepsilon }_{f}\), and eot can be suggested based on the comprehensive experimental results.
Conclusions
Using OPC and FA as admixes together provided the greatest improvement in the strength characteristic of dredged sediment. In addition, the study presented an empirical correlation between the strength and stiffness of adding fly ash on cement-stabilised lakebed sediment for using in geotechnical and pavement works.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
References
ASTM C 618 (2019) Standard specification for coal fly ash and raw or calcined natural Pozzolan for use in concrete. ASTM Int. https://doi.org/10.1520/C0618-19
AOAC (2005) Official methods of analysis of the Association of Analytical Chemists International, 18th ed. Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC), Gathersburg, MD, USA
ASTM D 1557 (2012) Standard test methods for laboratory compaction characteristics of soil using modified effort (56,000 ft-lbf/ft3 (2700 kN-m/m3)). ASTM International. https://doi.org/10.1520/D1557-12E01
ASTM D 2166, D 2166M (2016) Standard test method for unconfined compressive strength of cohesive soil. ASTM Int. https://doi.org/10.1520/D2166_D2166M-16
Chompoorat T, Likitlersuang S (2016) Assessment of shrinkage characteristic in blended cement and fly ash admixed soft clay. 15th Asian Regional Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering. Japan Geotech Soc Spec Publ 2(6):311–316. https://doi.org/10.3208/jgssp.THA-01
Chompoorat T, Maikhun T, Likitlersuang S (2019) Cement improved lake bed sedimentary soil for road construction. Proc Inst Civil Eng - Ground Improv 172(3):192–201. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgrim.18.00076
Chompoorat T, Thanawong K, Likitlersuang S (2021) Swell-shrink behaviour of cement with fly-ash stabilised lakebed sediment. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80:2617–2628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-02069-2
DOH (Department of Highways) (1989) Standard of soil cement subbase. [In Thai] DH-S 206/2532. Bangkok, Thailand: DOH
Dontriros S, Likitlersuang S, Janjaroen D (2020) Mechanisms of chloride and sulfate removal from municipal-solid-waste-incineration fly ash (MSWI FA): Effect of acid-base solutions. Waste Manage 101:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.09.033
Du YJ, Jiang NJ, Liu SY, Jin F, Singh DN, Puppala AJ (2013) Engineering properties and microstructural characteristics of cement-stabilized zinc-contaminated kaolin. Can Geotech J 51:289–302. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2013-0177
Güllü H (2014) Factorial experimental approach for effective dosage rate of stabilizer: application for fine-grained soil treated with bottom ash. Soils Foundations 54(3):462–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2014.04.017
Horpibulsuk S, Rachan R, Raksachon Y (2009) Role of fly ash on strength and microstructure development in blended cement stabilized silty clay. Soils Foundations 49(1):85–98. https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf.49.85
Horpibulsuk S, Rachan R, Suddeepong A (2011) Assessment of strength development in blended cement admixed Bangkok clay. Construction Building Mater 25(4):1521–1531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.08.006
Jamsawang P, Charoensil S, Namjan T, Jongpradist P, Likitlersuang S (2020) Mechanical and microstructural properties of dredged sediments treated with cement and fly ash for use as road materials. Road Mater Pavement Design. https://doi.org/10.1080/14680629.2020.1772349
Jamsawang P, Nuansrithongb N, Voottipruexc P, Songpiriyakijd S, Jongpradiste P (2017) Laboratory investigations on the swelling behavior of composite expansive clays stabilized with shallow and deep clay-cement mixing methods. Appl Clay Sci 148:83–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.08.013
Jongpradist P, Jamsawang P, Kongkitkul W (2019) Equivalent void ratio controlling the mechanical properties of cementitious material-clay mixtures with high water content. Mar Georesourc Geotechnol 37(10):1151–1162. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2018.1539534
Jongpradist P, Jumlongrach N, Youwai S, Chucheepsakul S (2010) Influence of fly ash on unconfined compressive strength of cement-admixed clay at high water content. J Mater Civil Eng 22(1):49–58. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0899-1561(2010)22:1(49)
Julphunthong P, Thongdetsri T, Chompoorat T (2018) Stabilisation of soft Bangkok clay using Portland cement and calcium sulfoaluminate-belite cement. Key Eng Mater 775:582–588. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.775.582
Kang X, Kang GC, Chang KT, Ge L (2014) Chemically stabilized soft clays for road-base construction. J Mater Civil Eng 27(7). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0001156
Leelarungroj K, Likitlersuang S, Chompoorat T, Janjaroen D (2018) Leaching mechanisms of heavy metals from fly ash stabilised soils. Waste Manage Res 36(7):616–623. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X18775494
Lorenzo GA, Bergado DT (2004) Fundamental parameters of cement-admixed clay: new approach. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 130(10):1042–1050. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2004)130:10(1042)
Moghal AAB, Sivapullaiah PV (2011) Effect of pozzolanic reactivity on compressibility characteristics of stabilized low lime fly ashes. Geotech Geol Eng 29(5):665–673. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-011-9408-y
NNEB (2004) Notification of the National Environmental Board No. 25 (BE 2547, AD 2004) issued under the National Environmental Quality Promotion and Preservation Act BE 2535. Soil quality standard. Published in Royal Gazette 121, special session 119, Ngor. (In Thai)
Tastan EO, Edil TB, Benson CH, Aydilek AH (2011) Stabilization of organic soils with fly ash. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 137(9):819–833. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000502
Voottipruex P, Jamsawang P (2014) Characteristics of expansive soils improved with cement and fly ash in Northern Thailand. Geomech Eng 6(5):437–453. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2014.6.5.437
Wang D, Abriak NE, Zentar R (2013) Strength and deformation properties of Dunkirk marine sediments solidified with cement, lime and fly ash. Eng Geol 166:90–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.09.007
Yoobanpot N, Jamsawang P, Horpibulsuk S (2017) Strength behavior and micro-structural characteristics of soft clay stabilized with cement kiln dust and fly ash residue. App Clay Sci 141:146–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.02.028
Yoobanpot N, Jamsawang P, Poorahong H, Jongpradist P, Likitlersuang S (2020a) Multiscale laboratory investigation of the mechanical and microstructural properties of dredged sediments stabilized with cement and fly ash. Eng Geol 267https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105491
Yoobanpot N, Jamsawang P, Simarat P, Jongpradist P, Likitlersuang S (2020b) Sustainable reuse of dredged sediments as pavement materials by cement and fly ash stabilization. J Soils Sediments 20:3807–3823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02635-xx
Zhang T, Yue X, Deng Y, Zhang D, Liu S (2014) Mechanical behaviour and micro-structure of cement-stabilised marine clay with a metakaolin agent. Construct Build Mater 73:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.09.041
Funding
This research was supported by the National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT): NRCT5-RSA63001-05; and the Ratchadapisek Sompoch Endowment Fund (2020), Chulalongkorn University (763014 Climate Change and Disaster Management Cluster). The first author acknowledges the annual government statement of expenditure fund from the University of Phayao.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Victor Magar
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chompoorat, T., Thepumong, T., Taesinlapachai, S. et al. Repurposing of stabilised dredged lakebed sediment in road base construction. J Soils Sediments 21, 2719–2730 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02974-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02974-3