Abstract
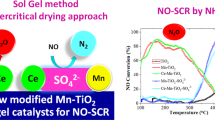
New mesoporous and well-structured aerogel catalysts (CeO2–TiO2, WO3–TiO2 and WO3–CeO2–TiO2) were elaborated via the sol–gel method, characterized by means of various techniques (XRD; N2-Physisorption at 77 K; NH3-TPD; H2-TPR; DRUV–Vis spectroscopy) and evaluated in the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO by NH3. The results reveal that all the aerogel catalysts develop essentially the diffraction peaks of TiO2 anatase phase and are classified as mesoporous materials with a high surface area (70 < SBET < 106 m2 g−1), large porosity (0.27 < VPT < 0.46 cm3 g−1) and nanometer size of crystallites (8–15 nm). The addition of Ce and/or W influences differently the structure, texture, crystallites size, surface oxygen concentration, total acidity and redox ability of aerogel samples and clearly affects their NO-SCR activity which follows this order: TiO2 < WO3–TiO2 < CeO2–TiO2 < WO3–CeO2–TiO2. It was also found that cerium species are more active in the low temperature NO-SCR reaction than tungsten ones (NO conversions obtained at 300 °C using CeO2–TiO2 and WO3–TiO2 were 75 and 0%, respectively). On the other hand, it was suggested that the interactions between Ce and W species play a key role in improving the reactivity of WO3–CeO2–TiO2 catalyst in the SCR of NO by NH3. Interestingly, the NO conversion into N2 reaches 85% at 300 °C and exceeds 90% between 320 and 400 °C over this novel meso-structured aerogel catalyst.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Z.M. Liu, H. Su, J.H. Li, Y. Li, Novel MoO3/CeO2–ZrO2 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Catal. Commun. 65, 51–54 (2015)
C.Z. Sun, H. Liu, W. Chen, D.Z. Chen, S.H. Yu, A.N. Liu, L. Dong, S. Feng, Insights into the Sm/Zr co-doping effects on N2 selectivity and SO2 resistance of a MnOx–TiO2 catalyst for the NH3-SCR reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 347, 27–40 (2018)
Y. Peng, J.H. Li, X. Huang, X. Li, W.K. Su, X. Sun, D.Z. Wang, J. Hao, Deactivation mechanism of potassium on the V2O5/CeO2 catalysts for SCR reaction: acidity, reducibility and adsorbed-NOx. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 4515–4520 (2014)
L. Chen, D. Weng, Z. Si, X. Wu, Synergistic effect between ceria and tungsten oxide on WO3–CeO2–TiO2 catalysts for NH3-SCR reaction. Prog. Nat. Sci. 22, 265–272 (2012)
G. Zhang, W. Han, H. Zhao, L. Zong, Z. Tang, Solvothermal synthesis of well-designed ceria–tin–titanium catalysts with enhanced catalytic performance for wide temperature NH3-SCR reaction. Appl. Catal. B 226, 117–126 (2018)
W. Shan, F. Liu, Y. Yu, H. He, The use of ceria for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Chin. J. Catal. 35, 1251–1259 (2014)
Y. Jiang, C.Z. Bao, Q. Liu, G. Liang, M. Lu, S. Ma, A novel CeO2–MoO3–WO3/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Catal. Commun. 103, 96–100 (2018)
X. Gao, Y. Jiang, Y. Zhong, Z.Y. Luo, K. Cen, The activity and characterization of CeO2–TiO2 catalysts prepared by the sol–gel method for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Hazard. Mater. 174, 734–739 (2010)
P. Li, Y. Xin, Q. Li, Z.P. Wang, Z.L. Zhang, L.R. Zheng, Ce–Ti amorphous oxides for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: confirmation of Ce–O–Ti active sites . Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 9600–9605 (2012)
Z. Wang, Z. Qu, X. Quan, H. Wang, Selective catalytic oxidation of ammonia to nitrogen over ceria–zirconia mixed oxides. Appl. Catal. A 411–412, 131–138 (2012)
Y.S. Shen, S.M. Zhu, T. Qiu, A novel catalyst of CeO2/Al2O3 for selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Catal. Commun. 11, 20–23 (2009)
R. Qu, X. Gao, K. Cen, J. Li, Relationship between structure and performance of a novel cerium–niobium binary oxide. Appl. Catal. B 142–143, 290–297 (2013)
G. Qi, R.T. Yang, R. Chang, MnOx–CeO2 mixed oxides prepared by co-precipitation for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 at low temperatures. Appl. Catal. B 51, 93–106 (2004)
L. Chen, J.H. Li, M.F. Ge, Mechanism of selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over CeO2–WO3 catalysts. Chin. J. Catal. 32, 836–841 (2011)
H.Q. Wang, X.B. Chen, X.L. Weng, Enhanced catalytic activity for selective catalytic reduction of NO over titanium nanotube-confined CeO2 catalyst. Catal. Commun. 12, 1042–1045 (2011)
W.E.J. van Kooten, B. Liang, H.C. Krijnsen, Ce-ZSM-5 catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx in stationary diesel exhaust gas. Appl. Catal. B 21, 203–213 (1999)
L.L. Zhu, B.C. Huang, W.H. Wang, Low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3 over CeO2 supported on modified activated carbon fibers. Catal. Commun. 12, 394–398 (2011)
X.B. Chen, S. Gao, H.Q. Wang, Selective catalytic reduction of NO over carbon nanotubes supported CeO2. Catal. Commun. 14, 1–5 (2011)
A. Zhou, D. Yu, L. Yang, Z. Sheng, Combined effects Na and SO2 in flue gas on Mn–Ce/TiO2 catalyst for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 simulated by Na2SO4 doping. Appl. Surf. Sci. 378, 167–173 (2016)
Z. Wu, Y. Zeng, F. Song, S. Zhang, Q. Zhong, Active sites assembly effect on CeO2–WO3–TiO2 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Mol. Catal. 479, 110549 (2019)
L. Chen, J. Li, M. Ge, R. Zhu, Enhanced activity of tungsten modified CeO2–TiO2 for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia. Catal. Today 153, 77–83 (2010)
S. Zhang, Q. Zhong, Y. Shen, L. Zhu, J. Ding, New insight into the promoting role of process on the CeO2–WO3/TiO2 catalyst for NO reduction with NH3 at low-temperature. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 448, 417–426 (2015)
L. Chen, D. Weng, J. Wang, D. Weng, L. Cao, Low-temperature activity and mechanism of WO3‐modified CeO2–TiO2 catalyst under NH3–NO/NO2 SCR conditions. Chin. J. Catal. 39, 1804–1813 (2018)
L. Zong, G. Zhang, H. Zhao, J. Zhang, Z. Tang, One pot synthesized CeO2–WO3–TiO2 catalysts with enriched TiO2 (001) facets for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 by evaporation-induced self-assembly method. Chem. Eng. J. 354, 295–303 (2018)
W. Xie, G. Zhang, B. Mu, Z. Tang, J. Zhang, The promoting effect of palygorskite on CeO2–WO3–TiO2 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Appl. Clay Sci. 192, 105641 (2020)
L. Chen, J.H. Li, M.F. Ge, Promotional effect of Ce-doped V2O5–WO3/TiO2 with low vanadium loadings for selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 21177–21184 (2009)
E. Tronconi, I. Nova, C. Ciardelli, Redox features in the catalytic mechanism of the ‘“standard”’ and ‘“fast”’ NH3-SCR of NOX over a V-based catalyst investigated by dynamic methods. J. Catal. 245, 1–10 (2007)
C. Liu, J.W. Shi, C. Gao, C. Niu, Manganese oxide-based catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: a review. Appl. Catal. A 522, 54–69 (2016)
C. Liu, L. Chen, H. Chang, L. Ma, Y. Peng, H. Arandiyan, J. Li, Characterization of CeO2–WO3 catalysts prepared by different methods for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Catal. Commun. 40, 145–148 (2013)
W. Gao, Z. Zhang, J. Li, Y. Ma, Y. Qu, Surface engineering on CeO2 nanorods by chemical redox etching and their enhanced catalytic activity for CO oxidation. Nanoscale 7, 11686–11691 (2015)
H. Jensen, A. Soloviev, Z. Li, E.G. Søgaard, XPS and FTIR investigation of the surface properties of different prepared titania nano-powders. Appl. Surf. Sci. 246, 239–249 (2005)
J. Arfaoui, A. Ghorbel, C. Petitto, G. Delahay, Novel V2O5–CeO2–TiO2–SO42– nanostructured aerogel catalyst for the low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 in excess O2. Appl. Catal. B 224, 264–275 (2018)
J. Arfaoui, A. Ghorbel, C. Petitto, G. Delahay, A new V2O5–MoO3–TiO2–SO42– nanostructured aerogel catalyst for diesel DeNOx technology. N. J. Chem. 44, 16119–16134 (2020)
K. Cheng, J. Liu, T. Zhang, J. Li, Z. Zhao, Y. Wei, G. Jiang, A. Duan, Effect of Ce doping of TiO2 support on NH3-SCR activity over V2O5–WO3/CeO2–TiO2 catalyst. J. Environ. Sci. 26, 2106–2113 (2014)
Z. Li, J. Li, S. Liu, X. Ren, J. Ma, W. Su, Y. Peng, Ultra hydrothermal stability of CeO2–WO3/TiO2 for NH3-SCR of NO compared to traditional V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalyst. Catal. Today 258, 11–16 (2015)
Y. Iida, S. Ozak, Grain growth and phase transformation of titanium oxide during calcination. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 44, 120–127 (1961)
S. Petrović, L. Rožić, S. Stojadinović, B. Grbić, R. Vasilić, Z. Vuković, N. Radić, The effect of sintering temperature on mesoporous structure of WO3 doped TiO2 powders. Sci. Sinter. 50, 123–132 (2018)
IUPAC, Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 57, 603–619 (1985)
G. Imran, R. Maheswari, Mn-incorporated SBA-1 cubic mesoporous silicates: synthesis and characterization. Mater. Chem. Phys. 161, 237–242 (2015)
M.A. López-Mendoza, R. Nava, C. Peza-Ledesma, B. Millán-Malo, R. Huirache-Acuña, P. Skewes, E.M. Rivera-Muñoz, Characterization and catalytic performance of Co–Mo–W sulfide catalysts supported on SBA-15 and SBA-16 mechanically mixed. Catal. Today 271, 114–126 (2016)
M. Kang, T.H. Yeon, E.D. Park, J.E. Yie, J.M. Kim, Novel MnOx catalysts for NO reduction at low temperature with ammonia. Catal. Lett. 106, 77–80 (2006)
Y. Segura, L. Chmielarz, P. Kustrowski, P. Cool, R. Dziembaj, E.F. Vansant, Characterisation and reactivity of vanadia–titania supported SBA-15 in the SCR of NO with ammonia. Appl. Catal. B 61, 69–78 (2005)
R. Huirache-Acuña, B. Pawelec, E. Rivera-Muñoz, R. Nava, J. Espino, J.L.G. Fierro, Comparison of the morphology and HDS activity of ternary Co–Mo–W catalysts supported on P-modified SBA-15 and SBA-16 substrates. Appl. Catal. B 92, 168–184 (2009)
R. Huirache-Acuña, B. Pawelec, E.M. Rivera-Muñoz, R. Guil López, J.L.G. Fierro, Characterization and HDS activity of sulfided Co–Mo–W/SBA-16 catalysts: effects of P addition and Mo/(Mo + W) ratio. Fuel 198, 145–158 (2017)
T.I. Bhuiyan, P. Arudra, M.N. Akhtar, A.M. Aitani, R.H. Abudawoud, M.A. Al-Yami, S.S. Al-Khattaf, Metathesis of 2-butene to propylene over W-mesoporous molecular sieves: a comparative study between tungsten containing MCM-41 and SBA-15. Appl. Catal. A 467, 224–234 (2013)
X.L. Yang, W.L. Dai, R. Gao, H. Chen, H. Li, Y. Cao, K. Fan, Synthesis, characterization and catalytic application of mesoporous W-MCM-48 for the selective oxidation of cyclopentene to glutaraldehyde. J. Mol. Catal. A 241, 205–214 (2005)
J. Arfaoui, A. Ghorbel, C. Petitto, G. Delahay, New MoO3–CeO2–ZrO2 and WO3–CeO2–ZrO2 nanostructured mesoporous aerogel catalysts for the NH3-SCR of NO from diesel engine exhaust. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 95, 182–189 (2021)
J. Arfaoui, A. Ghorbel, C. Petitto, G. Delahay, New Mn–TiO2 aerogel catalysts for the low temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx. J. Sol–Gel Sci. Technol. 97, 302–310 (2021)
J.R. Sohn, J.H. Bae, Characterization of tungsten oxide supported on TiO2 and activity for acid catalysis. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 17, 86–92 (2000)
Z. Liu, S. Zhang, J. Li, J. Zhu, L. Ma, Novel V2O5–CeO2/TiO2 catalyst with low vanadium loading for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Appl. Catal. B 158–159, 11–19 (2014)
C. Gannoun, R. Delaigle, P. Eloy, D.P. Debecker, A. Ghorbel, E.M. Gaigneaux, Effect of support on V2O5 catalytic activity in chlorobenzene oxidation. Appl. Catal. A 447–448, 1–6 (2012)
Y. Peng, J.H. Li, L. Chen, J.H. Chen, J. Han, H. Zhang, W. Han, Alkali metal poisoning of a CeO2–WO3 catalyst used in the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: an experimental and theoretical study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 2864–2869 (2012)
Z.R. Ma, D. Weng, X.D. Wu, Z.C. Si, Effect of WOx modification on the activity, adsorption and redox properties of CeO2 catalyst for NOx reduction with ammonia. J. Environ. Sci. 24, 1305–1316 (2012)
Z. Song, L. Yin, Q. Zhang, P. Ning, Y. Duan, J. Wang, X. Liu, K. Long, Z. Huang, Relationship between the WO3 states and reaction pathway over CeO2–ZrO2–WO3 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Mol. Catal. 437, 95–104 (2017)
P. Forzatti, Present status and perspectives in de-NOx SCR catalysis. Appl. Catal. A 222, 221–236 (2001)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their sincere thanks to Thomas Cacciaguerra for XRD analysis. Laboratory of Chemistry of Materials and Catalysis (LCMC) of Tunisia and FrancoTunisian Cooperation (French Institute of Tunisia, SSHN Grant) are gratefully acknowledged for the financial support.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arfaoui, J., Ghorbel, A., Petitto, C. et al. New CeO2–TiO2, WO3–TiO2 and WO3–CeO2–TiO2 mesoporous aerogel catalysts for the low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. J Porous Mater 28, 1535–1543 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-021-01102-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-021-01102-3