Abstract
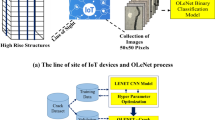
Concrete roads have high durability and long-term performance. To ensure this, proper design, good quality application and necessary maintenance are essential. Maintenance/repair activities are carried out to increase the life of the roads and the volume of traffic that they can carry safely. These activities are started by first illustrating the current condition of the road superstructure at periodic intervals and identifying damaged areas. However, this determination process is very tiring, time-consuming and costly for long distances. This study focused on detecting cracks in concrete roads for various shooting, weather conditions and illumination levels using a deep learning-based object detection method. In this way, existing cracks can be determined in a remarkably short time and inexpensive. A descriptive approach is considered to detect cracks of images captured on concrete road surfaces using a pre-trained Faster R-CNN. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, 323 images with a resolution of 4128 × 2322 pixels and an aspect ratio of 16:9 to verify the performance of damage detection on the selected concrete road surface. This experimental study produces bounding boxes of 1128 objects for the object detection process. A parametric study to verify the quality of the training level was carried out by changing the shooting conditions on the concrete road. The shooting distance and shooting height were taken as variables and crack detection analyses were carried out. The effects of the weather conditions and illumination level were also investigated. Crack detection analysis of the photographs captured on sunny, cloudy and foggy weather conditions, at sunset and moonlight times of the day, between 5:00–6:00 pm, 6:00–7:00 pm and 7:00–8:00 pm, which corresponds to dark periods of the day has been made. According to the results obtained, the number of cracks detected on a sunny day does not change on a cloudy and foggy day. It decreases by 50% for sunset and moonlight, by about 25% at 6:00–7:00 pm and by about 85% at 7:00–8:00 pm; however, it does not change at 5:00–6:00 pm.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Some or all data, models or codes that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ale L, Zhang N, Wu H et al (2019) Online proactive caching in mobile edge computing using bidirectional deep recurrent neural network. IEEE Internet Things J 6:5520–5530. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2019.2903245
Alfarrarjeh A, Trivedi D, Kim SH, Shahabi C (2019) A deep learning approach for road damage detection from smartphone images. In: Proceeding 2018 IEEE international conference on big data, (big data) 2018. pp. 5201–5204. https://doi.org/10.1109/BigData.2018.8621899
Amidi A, Amidi S (2019) CS 230: Recurrent neural networks cheatsheet. https://stanford.edu/~shervine/l/tr/teaching/cs-230/cheatsheet-recurrent-neural-networks. Accessed 16 Mar 2020
Angulo A, Vega-Fernández JA, Aguilar-Lobo LM, et al (2019) Road damage detection acquisition system based on deep neural networks for physical asset management. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including Subser Lect Notes Artif Intell Lect Notes Bioinformatics) 11835 LNAI: pp. 3–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33749-0_1
Cha YJ, Choi W, Büyüköztürk O (2017) Deep learning-based crack damage detection using convolutional neural networks. Comput-Aided Civ Infrastruct Eng 32:361–378. https://doi.org/10.1111/mice.12263
Chen S, Zhan Y, Zhang Y et al (2019) Embedded system for road damage detection by deep convolutional neural network. Math Biosci Eng 16:7982–7994. https://doi.org/10.3934/mbe.2019402
Chun C, Ryu SK (2019) Road surface damage detection using fully convolutional neural networks and semi-supervised learning. Sensors (switzerland) 19:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19245501
Embacher RA, Snyder MB (2001) Life-cycle cost comparison of asphalt and concrete pavements on low-volume roads case study comparisons. Transp Res Rec. https://doi.org/10.3141/1749-05
Girshick R (2015) Fast R-CNN. In: Proceedings IEEE international conference computer vision 2015 Inter: pp. 1440–1448. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2015.169
Karpathy A (2016) Convolutional neural networks (CNNs /ConvNets). retrieved CS231n convolutional neural networks for visual recognition. In: https://cs231n.github.io/. Accessed 15 Apr 2020
Khan S, Rahmani H, Shah SAA, Bennamoun M (2018) A guide to convolutional neural networks for computer vision. Synth Lect Comput Vision 8(1):1–207
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 51:436–444
Maeda H, Sekimoto Y, Seto T et al (2018) Road damage detection and classification using deep neural networks with smartphone images. Comput Civ Infrastruct Eng 33:1127–1141. https://doi.org/10.1111/mice.12387
Naddaf-Sh MM, Hosseini S, Zhang J et al (2019) Real-time road crack mapping using an optimized convolutional neural network. Complexity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2470735
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2017) Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(6):1137–1149
Saha U (2018) A comprehensive guide to convolutional neural networks. In: Towards data science. https://towardsdatascience.com. Accessed 28 Apr 2019
Srivastava N, Hinton GE, Krizhevsky A et al (2014) Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. J Mach Learn Res 5:1929–1958
TensorFlow (2020). https://www.tensorflow.org/. Accessed 16 Mar 2020
Tzutalin (2020) LabelImg. Git code. In: https://github.com/qaprosoft/labelImg. Accessed 28 Apr 2019
Wang W, Wu B, Yang S, Wang Z (2019) Road damage detection and classification with faster R-CNN. In: Proceedings 2018 IEEE international conference on big data, (big data) 2018: pp. 5220–5223. https://doi.org/10.1109/BigData.2018.8622354
Yang S, Fang B, Tang W, et al (2018) Faster R-CNN based microscopic cell detection. In: 2017 International conference on security pattern analysis cybern SPAC 2017 2018-January: pp. 345–350. https://doi.org/10.1109/SPAC.2017.8304302
Zhang K, Cheng HD, Zhang B (2018) Unified approach to pavement crack and sealed crack detection using preclassification based on transfer learning. J Comput Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000736
Zhang L, Yang F, Daniel Zhang Y, Zhu YJ (2016) Road crack detection using deep convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings international conference image process ICIP 2016-August: pp.3708–3712. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2016.7533052
Zhou S, Song W (2020) Deep learning-based roadway crack classification using laser-scanned range images: a comparative study on hyperparameter selection. Autom Constr 114:103171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103171
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hacıefendioğlu, K., Başağa, H.B. Concrete Road Crack Detection Using Deep Learning-Based Faster R-CNN Method. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 46, 1621–1633 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-021-00671-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-021-00671-2