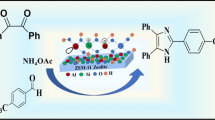
Abstract
Efficient and reusable ZS-1 zeolite as a novel catalyst was successfully synthesized by the hydrothermal method. Characterizations of catalysts were carried out using diverse analysis techniques such as XRD, FT-IR, FESEM, EDAX, HRTEM, BET, and NH3TPD. Promoted as an environment-friendly protocol for the facile synthesis of various substituted 1-amidoalkyl-2-naphthols through the reaction of β-naphthol, aldehyde, and amides under solvent-free conditions. This catalyst provides many advantages such as shorter reaction times, operational simplicity, reusability, an excellent yield of the product, facile work-up, and easily recoverable. Moreover, the recovered catalyst can be recycled and reused for the next five runs without significant loss of catalytic activity.
Graphic Abstract












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Manuscript including all data correct and unpublished.
References
Singh RK, Duvedi R (2018) Environment-friendly green chemistry approaches for an efficient synthesis of 1-amidoalkyl-2-naphthols catalyzed by tannic acid. Arab J Chem 11:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.08.022
Zhang Q, Gao Y-H, Qin S-L, Wei H-X (2017) Facile one-pot synthesis of amidoalkyl naphtholsand benzopyrans using magnetic nanoparticle-supported acidic ionic liquid as a highly efficientand reusable catalyst. Catalysts 7:351. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal7110351
Erfaninia N, Tayebee R, Foletto EL, Amini MM, Dusek M, Zonoz M (2018) Preparation of magnetically recyclable ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles by easy single-step co-precipitation methodand their catalytic performance in the synthesis of 2-aminothiophenes. Appl Organomet Chem 32:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4047
Li B, Tayebee R, Esmaeili E, Namaghi MS, Maleki B (2020) Selective photocatalytic oxidation of aromatic alcohols to aldehydes with air by magnetic WO3ZnO/Fe3O4. In situ photochemical synthesis of 2-substituted benzimidazoles. RSC Adv 10:40725–40738. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA08403D
Rekunge DS, Bendale HS, Chaturbhuj GU (2018) Activated Fuller’s earth: an efficient, inexpensive, environmentallybenign, and reusable catalyst for rapid solvent-free synthesis of1-(amido/amino)alkyl-2-naphthols. Monatsh Chem 149:1991–1997. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-018-2247-2
Hashemzadeh A, Amini MM, Tayebee R, Sadeghian A, Durndell LJ, Isaacs MA, Osatiashtiani A, Parlett CMA (2017) Amagnetically separable H3PW12O40@Fe3O4/EN-MIL-101 catalyst for the one-pot solventless synthesis of 2H-indazolo [2,1-b] phthalazine-triones. Mol Catal 440:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2017.07.010
Tayebee R, Pejhan A, Ramshini H et al (2018) Equisetum arvense as an abundant source of silica nanoparticles. SiO2/H3PW12O40 nanohybrid material as an efficient andenvironmental benign catalyst in the synthesis of 2-amino-4H-chromenes under solvent-free conditions. Appl Organomet Chem 32:e3924. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.3924
Tayebee R, Mojtaba FA, Nasrin E et al (2019) Phosphotungstic acid grafted zeolite imidazolate framework as an effective heterogeneous nanocatalystfor the one-pot solvent-free synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidinones. Appl Organomet Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4959
Benito HE, Alamilla RG, Enríquez JMH et al (2015) Porous silicates modified with zirconium oxide and sulfate ions for alcohol dehydration Reactions. Adv Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/325463
Mahdizadeh Ghohe N, Tayebee R, Amini MM (2019) Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous Nb-Zr/KIT-6 as a productive catalyst for the synthesis of benzylpyrazolyl coumarins. Mater Chem Phys 223:268–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.10.067
Yang G, Pidko EA, Hensen EJM (2013) Structure, stability, and lewis acidity of mono and double Ti, Zr, and Sn framework substitutions in BEA zeolites: a periodic density functional theory study. J Phys Chem C 117:3976–3986. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp310433r
Dipake SS, Lande MK, Rajbhoj AS, Gaikwad ST (2021) Zeolite ZSM-11 as a reusable and efficient catalyst promoted improved protocol for synthesis of 2,4,5-triarylimidazole derivatives under solvent-free condition. Res Chem Intermed. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-021-04423-9
Gadekar SP, Dipake SS, Gaikwad ST, Lande MK (2018) Solid acid TS-1 catalyst: an efficient catalyst in Knoevenagel condensation for the synthesis of 5-arylidene-2,4-thiazolidinediones/Rhodanines in aqueous medium. Res Chem Intermed 44:7509–7518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-3570-2
Narenji-Sani F, Tayebee R, Chahkandi M (2020) New task-specific and reusable ZIF-like grafted H6P2W18O62 catalyst for the effective esterification of free fatty acids. ACS Omega 5:9999–10010. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00358
Moliner M (2014) State of the art of Lewis acid-containing zeolites:lessons fromfine chemistry to new biomasstransformation processes. Dalt Trans 43:4197–4208. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3dt52293h
KEYSER DJ, Guillem AF (12) (2015) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0258769 A1 lifted-off layer Patent Application Publication
Lambert SL, 1994, Patent Number: 5,338,527, US005338527A
Cioc RC, Ruijter E, Orru RVA (2014) Multicomponent reactions: advanced tools forsustainable organic synthesis. Green Chem 16:2958–2975. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4GC00013G
Tayebee R, Fattahi Abdizadeh M, Maleki B, Shahri E (2017) Heteropolyacid-based ionic liquid [Simp] 3PW12O40 nanoparticles as a productive catalyst for the one-pot synthesis of 2H-indazolo [2,1-b] phthalazine-triones under solvent-free conditions. J Mol Liq 241:447–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.06.033
Tayebee R, Amini MM, Rostamian H, Aliakbari A (2014) Preparation and characterization of a novel Wells–Dawson heteropolyacid-based magneticinorganic–organic nanohybrid catalyst H6P2W18O62/pyridino-Fe3O4 for the efficient synthesis of 1-amidoalkyl-2-naphthols under solvent-free conditions. Dalt Trans 43:1550–1563. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3DT51594J
Taghrir H, Ghashang M, Biregan MN (2016) Preparation of 1-amidoalkyl-2-naphthol derivatives using bariumphosphate nano-powders. Chin Chem Lett 27:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2015.08.011
Gupta A, Kour D, Gupta VK, Kapoor KK (2016) Graphene oxide mediated solvent-free three component reaction for the synthesis of 1-amidoalkyl-2-naphthols and 1,2-dihydro-1-arylnaphth [1,2-e][1,3] oxazin-3-on. Tetrahedron Lett 57:4869–4872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.09.067
Pourmousavi SA, Moghimi P, Ghorbani F, Zamani M (2017) Sulfonated polynaphthalene as an effective and reusable catalyst for the one-pot preparation of amidoalkyl naphthols: DFT and spectroscopic studies. J Mol Struct 1144:87–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2017.05.010
Tayebee R, Amini MM, Akbari M, Aliakbari A (2015) A novel inorganic–organic nanohybrid materialH4SiW12O40/pyridino-MCM-41 as efficient catalystfor the preparation of 1-amidoalkyl-2-naphtholsunder solvent-free conditions. Dalt Trans 44:9596–9609. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5dt00368g
Gong K, Wang H, Ren X et al (2015) β-Cyclodextrin-butane sulfonic acid: an efficientand reusable catalyst for the multicomponent synthesis of 1-amidoalkyl-2-naphthols under solvent-free conditions. Green Chem 17:3141–3147. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5gc00384a
Nasresfahani Z, Kassaee MZ, Eidi E (2016) Homopiperazine sulfamic acid functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs-HPZ-SO3H)as an efficient catalyst for one-pot synthesis of1-amidoalkyl-2-naphthols. New J Chem 40:4720–4726. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nj02974k
Zolfagharinia S, Kolvari E, Salehi M (2017) Highly efficient and recyclable phosphoric acid functionalized zirconia encapsulated-Fe3O4 nanoparticles: clean synthesis of 1,4-dihydropyridineand 1-amidoalkyl-2-naphthol derivatives. Reac Kinet Mech Cat. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-017-1186-y
Kiasat AR, Hemat-Alian L, Saghanezhad SJ (2016) Nano Al2O3: an efficient and recyclable nanocatalystfor the one-pot preparation of 1-amidoalkyl-2-naphthols under solvent-free conditions. Res Chem Intermed 42:915–922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-015-2062-x
Khodaei MM, Khosropour AR, Moghanian H (2006) A simple and efficient procedure for the synthesis of amidoalkyl naphthols by p-TSA in solution or under solvent-free conditions. Synlett. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-939034
Shaterian HR, Yarahmadi H, Ghashang M (2009) One-pot synthesis of amidoalkyl naphthols using NaHSO4.SiO2as an efficient and recyclable heterogeneous catalyst. Turkish J Chem 33:449–457. https://doi.org/10.3906/kim-0812-67
Shaterian HR, Yarahmadi H, Ghashang M (2008) Silica supported perchloric acid (HClO4eSiO2): an efficientand recyclable heterogeneous catalyst for the one-potsynthesis of amidoalkyl naphthols. Tetrahedron 64:1263–1269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2007.11.070
Jesudoss SK, Vijaya JJ, Kaviyarasu K et al (2017) Anti-cancer activity of hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolitessynthesized from rice-based waste materials. RSC Adv 8:481–490. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA11763A
Li Y, Sun H, Feng R et al (2015) Synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite from diatomite for fluid catalyticcracking (FCC) application. Appl Petrochem Res 5:347–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13203-015-0113-2
Gadekar SP, Lande MK (2018) Solid acid catalyst TS-1 zeolite-assisted solvent-free one-pot synthesis of poly-substituted 2,4,6-triaryl-pyridines. Res Chem Intermed 44:3267–3278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-3305-4
Bortun AI, Bortun LN, Clearfield A (1997) Hydrothermal synthesis of sodium zirconium silicatesand characterization of their properties. Chem Mater 9:1854–1864
Ko YS, Ahn WS (1998) Synthesis and characterization of zirconium silicalite-1. Korean J Chem Eng 15:423–428
Franklin KR, Lowe BM (1987) Hydrothermal crystallization of piperazine- ZSM-39, vol 7. Butterworth & Co. Ltd, Oxford, pp 0144–2449
Treacy MMJ, Higgins JB (2007) Collection of simulated XRD powder patterns zeolites, 5th edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Chen H, Zhang X, Zhang J, Wang Q (2017) Controllable synthesis of hierarchical ZSM-5 for hydro conversion of vegetable oil to aviation fuel-like hydrocarbons. RSC Adv 7:46109–46117. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra08867a
Shao J, Cheng S, Li Z, Huang B (2020) Enhanced catalytic performance of hierarchical MnOx/ZSM-5 catalyst for the low-temperature NH3-SCR. Catalysts 10:311
Peng B, Zou H, He L, Wang P, Shi Z, Zhu L, Wang R, Zhang Z (2013) Engineering growth defects: a new route towards hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolite with high-density intracrystalline mesopores. CrystEngComm 00:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1039/x0xx00000x
Na J, Liu G, Ding TZG, Hu S, Wang L et al (2013) Synthesis and catalytic performance of ZSM-5/MCM-41 zeolites with varying mesopore size by surfactant-directed recrystallization. Catal Lett 143:267–275
Subramanian N, Vijaya JJ, Sivasanker S, Arjunan A (2014) Enhanced selectivity to benzaldehyde in the liquid phase oxidationof benzyl alcohol using nanocrystalline ZSM-5 zeolite catalyst. J Porous Mater 21:633–641
Ansari SAMK, Sangshetti JN, Kokare ND (2010) Oxalic acid catalyzed solvent-free synthesis of α-amidoalkyl-β-naphthols. Indian J Chem Technol 17:71–73
Mahdavinia GH, Bigdeli MA (2009) Wet cyanuric chloride promoted efficient synthesis of amidoalkyl naphthols under solvent-free conditions. Chin Chem Lett 20:383–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2008.12.018
Patil SB, Singh PR, Surpur MP, Samant SD (2007) Ultrasound-promoted synthesis of 1-amidoalkyl-2-naphthols via a three-component condensation of 2-naphthol, ureas/amides, and aldehydes, catalyzed by sulfamic acid under ambient conditions. Ultrason Sonochem 14:515–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2006.09.006
Nandi GC, Samai S, Kumar R, Singh MS (2009) Atom-efficient and environment-friendly multicomponent synthesisof amidoalkyl naphthols catalyzed by P2O5. Tetrahedron Lett 50:7220–7222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.10.055
Sheik Mansoor S, Aswin K, Logaiya K, Sudhan SPN (2016) ZrOCl2Æ8H2O: an efficient and recyclable catalystfor the three-component synthesis of amidoalkylnaphthols under solvent-free conditions. J Saudi Chem Soc 20:138–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2012.06.003
Kantevari S, Vuppalapati SVN, Nagarapu L (2007) Montmorillonite K10 catalyzed efficient synthesis of amidoalkyl naphthols under solvent free conditions. Catal Commun 8:1857–1862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2007.02.022
Srihari G, Nagaraju M, Murthy MM (2007) Solvent-free one-pot synthesis of amidoalkyl naphthols catalyzed by silicasulfuric acid. Helv Chim Acta 90:1497–1504. https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.200790156
Nagarapu L, Baseeruddin M, Apuri S, Kantevari S (2007) Potassium dodecatungstocobaltate trihydrate (K5CoW12O40.3H2O): a mild and efficient reusable catalyst for the synthesis of amidoalkyl naphthols in solution and under solvent-free conditions. Catal Commun 8:1729–1734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2007.02.008
Lei M, Ma L, Hu L (2009) Thiamine hydrochloride as a efficient catalyst for the synthesis of amidoalkyl naphthols. Tetrahedron Lett 50:6393–6397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.08.081
Acknowledgements
One of the authors, Mr. Sudarshan S. Dipake, gratefully thankful to the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi for the award of fellowship and the Department of Chemistry, Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University, Aurangabad-431004 (M.S.), India. for support and providing the necessary laboratory facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SSD-conduct the whole experiment, writing an original draft. SPG-investigation. PBT-investigation. MKL-review and editing. ASR-review and editing. STG-writing, review, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Consent to Participate
All Authors are agreed for submission.
Consent for Publication
Agreed to submission.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dipake, S.S., Gadekar, S.P., Thombre, P.B. et al. ZS-1 Zeolite as a Highly Efficient and Reusable Catalyst for Facile Synthesis of 1-amidoalkyl-2-naphthols Under Solvent-Free Conditions. Catal Lett 152, 755–770 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-021-03684-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-021-03684-8