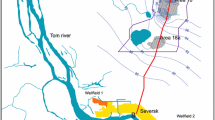
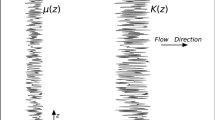
Abstract
Heterogeneity significantly effects the accuracy of flow and contaminant transport prediction in subsurface formations. The spatial correlation structure of hydraulic conductivity (K) is a crucial factor to characterize the heterogeneous architecture. In presented study, the relationship between the spatial correlation structure of K and plume dispersion is analyzed through the integration of experimental and numerical simulation approaches. A detailed description on the sedimentary facies types in a column experiment is obtained to ensure the accuracy of the heterogeneous characterization. The spatial correlation structure of K is analyzed with the components of ln(K) covariance and facies transition probability structures. Lagrangian-based models are developed to estimate solute dispersion in nonreactive tracer injection experiments. The results show that the model can predict plume spreading accurately when the spatial correlation structure is well defined. The dispersivities calculated by the Lagrangian-based model are slightly higher than those obtained from the solute transport experiments. Further, the upscaled dispersivity derived from the transition probability is dominated by the cross-transition probability structure, while the contribution of the auto-transition terms is quite small. The numerical modeling results confirm that the upscaled dispersivity can reproduce the solute breakthrough in the heterogeneous sediment well. The scale dependence of dispersion is strengthened when the flow direction is perpendicular to the bedding plane where the conductivity dramatically changes along the flow path in a layered bedding sediment.













Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data and material used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Abbreviations
- \({\alpha }_{11}^{l}\) :
-
Longitudinal dispersivity
- \({\alpha }_{22}^{l}\) :
-
Transverse dispersivity
- \({\alpha }_{33}^{l}\) :
-
Lateral dispersivity
- \({\alpha }_{11}^{e}\) :
-
Effective longitudinal dispersivities
- \({\alpha }_{11}^{ul}\) :
-
Upscaled longitudinal dispersivity
- C :
-
Concentration
- C 0 :
-
Initial concentration
- C ii(h ϕ):
-
Auto-covariance in direction ϕ
- C ij(h ϕ):
-
Cross-covariance in direction ϕ
- C Y(h ϕ):
-
Global covariance
- D :
-
Hydrodynamic dispersion coefficient
- erfc :
-
Complementary error function
- g :
-
Mean hydraulic gradient
- i, j :
-
Facies type
- I i(x):
-
Indicator space function
- J 0 :
-
Zero-order Bessel function
- J 1 :
-
First-order Bessel function
- K :
-
Hydraulic conductivity
- m i :
-
Mean
- M Y :
-
Global mean
- n :
-
Porosity
- p i :
-
Volume proportion
- R :
-
Retardation factor
- x :
-
Spatial coordinate
- t :
-
Time
- t ij(h ϕ):
-
Transition probability in direction ϕ
- U 1 :
-
Mean velocity
- v :
-
Pore velocity
- Y(x):
-
Global log conductivity
- Y i(x):
-
Log conductivity
- Z :
-
Integral variable
- σ i 2 :
-
Variance
- σ Y 2 :
-
Global variance
- δ ij :
-
Kronecker delta
- λ i :
-
Integral scale
- λ I :
-
Indicator correlation scale
- λ hi :
-
Horizontal integral scale
- λ vi :
-
Vertical integral scale
- λ Y :
-
Global integral scale
References
Abgaze TA, Sharma PK (2015) Solute transport through porous media with scale-dependent dispersion and variable mass transfer coefficient. ISH J of Hydraul Eng 21(3):298–311. https://doi.org/10.1080/09715010.2015.1021281
Al-Mansori NJH, Al-Fatlawi TJM, Othman NY, Al-Zubaidi LSA (2020) Numerical analysis of seepage in earth-fill dams. Civil Eng J 6(7):1336–1348.
Attinger S, Dentz M, Kinzelbach W (2004) Exact transverse macro dispersion coefficients for transport in heterogeneous porous media. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 18(1):9–15.
Bensoussan A (1978) Asymptotic analysis for periodic structures. North-Holland Pub. Co., Amsterdam-New York
Brenner H (1982) A general theory of taylor dispersion phenomena IV. Direct Coupling Effects Chem Eng Commun 18(5–6):355–379. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986448208939976
Carle SF, Fogg GE (1996) Transition Probability-Based Indicator Geostatistics Math Geol 28(4):453–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02083656
Carle SF, LaBolle EM, Weissmann GS, Van Brocklin D, Fogg GE (1998) Conditional simulation of hydrofacies architecture: A transition probability/Markov approach. Hydrogeologic Models of Sedimentary Aquifers 1:147–170
Dagan G (1982) Stochastic modeling of groundwater flow by unconditional and conditional probabilities: 2. The Solute Transport Water Resour Res 18(4):835–848. https://doi.org/10.1029/wr018i004p00835
Dagan G (1988) Time-dependent macrodispersion for solute transport in anisotropic heterogeneous aquifers. Water Resour Res 24(9):1491–1500. https://doi.org/10.1029/wr024i009p01491
Dagan G (1989) Flow and transport in porous formation. Springer, Berlin
Dagan G, Fiori A, Janković I (2003) Flow and transport in highly heterogeneous formations: 1. Conceptual Framework and Validity of First-Order Approximations, Water Resour Res 39(9):1268. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002WR001717
Dai Z, Ritzi RW, Huang C, Rubin YN, Dominic DF (2004a) Transport in heterogeneous sediments with multimodal conductivity and hierarchical organization across scales. J Hydrol 294(1):68–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-1694(04)00098-8
Dai Z, Ritzi RW, Dominic DF (2004b) Estimating parameters for hierarchical permeability correlation models. SEPM Spec Publ 80:41–54
Dai Z, Ritzi RW, Dominic DF (2005) Improving permeability semivariograms with transition probability models of hierarchical sedimentary architecture derived from outcrop analog studies. Water Resour Res 41(7):45–52. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004wr003515
Dai Z, Wolfsberg A, Lu Z, Deng H (2009) Scale dependence of sorption coefficients for contaminant transport in saturated fractured rock. Geophys Res Lett 36(1):17–21. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008gl036516
Dai Z, Wolfsberg A, Lu Z, Ritzi RW (2007a) Representing aquifer architecture in macrodispersivity models with an analytical solution of the transition probability matrix. Geophys Res Lett 34(20). https://doi.org/10.1029/2007gl031608
Dai Z, Wolfsberg A, Lu Z, Reimus P (2007) Upscaling matrix diffusion coefficients for heterogeneous fractured rocks. Geophys Res Lett 34(7):70–75. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007gl029332
Dai Z, Zhan C, Soltanian MR, Ritzi RW, Zhang X (2019) Identifying spatial correlation structure of multimodal permeability in hierarchical media with Markovchain approach. J Hydrol 568:703–715
Dai Z, Zhan C, Dong S, Yin S, Zhang X, Soltanian MR (2020) How does resolution of sedimentary architecture data affect plume dispersion in multiscale and hierarchical systems? J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124516
Davis JM, Lohmann RC, Phillips FM, Wilson JL, Love DW (1993) Architecture of the Sierra Ladrones Formation, central New Mexico: depositional controls on the permeability correlation structure. Geol Soc Am Bull 105(8):998–1007
Deng H, Dai Z, Wolfsberg AV, Ye M, Stauffer PH, Lu Z, Kwicklis E (2013) Upscaling retardation factor in hierarchical porous media with multimodal reactive mineral facies. Chemosphere 91(3):248–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.10.105
Dentz M, de Barros FPJ, Le Borgne T, Lester DR (2018) Evolution of solute blobs in heterogeneous porous media. J Fluid Mech 853:621–646. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2018.588
Dentz M, Kang PK, Le Borgne T (2015) Continuous time random walks for non-local radial solute transport. Adv Water Resour 82:16–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2015.04.005
Disley T, Gharabaghi B, Mahboubi AA, McBean EA (2014) Predictive equation for longitudinal dispersion coefficient. Hydrol Process 29(2):161–172. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10139
Dong S, Dai Z, Li J, Zhou W (2018) The scale dependence of dispersivity in multi-facies heterogeneous formations. Carbonates Evaporites 33(1):161–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-018-0421-6
Dou Z, Zhou Z, Wang J, Huang Y (2018) Roughness scale dependence of the relationship between tracer longitudinal dispersion and Peclet number in variable-aperture fractures. Hydrol Process 32(10):1461–1475. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11505
Fazelabdolabadi B, Golestan MH (2020) Towards Bayesian quantification of permeability in micro-scale porous structures - the database of micro networks. High Tech Innov J 1(4):148–160. https://doi.org/10.28991/HIJ-2020-01-04-02
Fiori A, Dagan G (2000) Concentration fluctuations in aquifer transport: A rigorous first-order solution and applications. J Contam Hydrol 45(1–2):139–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0169-7722(00)00123-6
Fiori A, de Barros FPJ (2015) Groundwater flow and transport in aquifers: Insights from modeling and characterization at the field scale. J Hydrol 531:1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.11.001
Freeze R, Cherry J (1979) Groundwater. PrenticeHall Inc, Englewood cliffs, New Jersey, p 604
Gelhar LW (1993) Stochastic Subsurface Hydrology. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J.
Godoy VA, Zuquette LV, Gómez-Hernández JJ (2018) Scale effect on hydraulic conductivity and solute transport: small and large-scale laboratory experiments and field experiments. Eng Geol 243:196–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.06.020
Hakoun V, Comolli A, Dentz M (2019) Upscaling and prediction of Lagrangian velocity dynamics in heterogeneous porous media. Water Resour Res 55(5):3976–3996. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018wr023810
Huang G, Huang Q, Zhan H (2006) Evidence of one-dimensional scale-dependent fractional advection–dispersion. J Contam Hydrol 85:53–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2005.12.007
Huang K, Toride N, Van Genuchten MT (1995) Experimental investigation of characteristic length scale in periodic heterogeneous porous media. Transp Porous Media 25:235–246.
Igreja I, Lima SA, Klein V (2017) Asymptotic Analysis of Three-Scale Model of pH-Dependent Flows in 1:1 Clays with Danckwerts’ Boundary Conditions. Transp Porous Media 119(2):425–450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-017-0891-3
Janković I, Fiori A, Dagan G (2003) Flow and transport in highly heterogeneous formations: 3 Numerical simulations and comparison with theoretical results. Water Resources Research. 39(9):11–14
Jury WA, Sposito G (1985) Field calibration and validation of solute transport models for the unsaturated zone. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49(6):1331–1341. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1985.03615995004900060
Kennedy CA, Lennox WC (2001) A stochastic interpretation of the tailing effect in solute transport. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 15(4):325–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004770100076
Khan UH, Jury WA (1990) A laboratory study of the dispersion scale effect in column outflow experiments. J Contam Hydrol 5(2):119–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-7722(90)90001-w
Lapidus L, Amundson NR (1952) Mathematics of adsorption in beds VI The effect of longitudinal diffusion in ion exchange and chromatographic columns. J Phys Chem 56(8):984–988. https://doi.org/10.1021/j150500a014
Libera A, Henri CV, de Barros FPJ (2019) Hydraulic conductivity and porosity heterogeneity controls on environmental performance metrics: Implications in probabilistic risk analysis. Adv Water Resour. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2019.03.002
Lu Z, Wolfsberg AV, Dai Z, Zheng C (2010) Characteristics and controlling factors of dispersion in bounded heterogeneous porous media. Water Resour Res 46(12):137–139.
Mackay DM, Freyberg DL, Roberts PV, Cherry JA (1986) A natural gradient experiment on solute transport in a sand aquifer: 1 Approach and overview of plume movement. Water Resour Res 22(13):2017–2029. https://doi.org/10.1029/wr022i013p02017
Ma Z, Dong S, Yin S, Dai Z, Zhu L, Jia W, Wallace C, Soltanian MR (2021) Experimental investigations on scale-dependent dispersivity in three-dimensional heterogeneous porous media. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12316-4
Metzger D, Kinzelbach H, Neuweiler I, Kinzelbach W (1999) Asymptotic transport parameters in a heterogeneous porous medium: Comparison of two ensemble-averaging procedures. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 13(6):396–415.r https://doi.org/10.1007/s004770050046
Noetinger B, Roubinet D, Russian A, Le Borgne T, Delay F, Dentz M, Gouze P (2016) Random walk methods for modeling hydrodynamic transport in porous and fractured media from pore to reservoir scale. Transp Porous Media 115(2):345–385. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-016-0693-z
Paleologos EK, Sarris TS (2011) Stochastic analysis of flux and head moments in a heterogeneous aquifer system. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 25(6):747–759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-011-0459-7
Porro I, Wierenga PJ, Hills RG (1993) Solute transport through large uniform and layered soil columns. Water Resour Res 29(4):1321–1330. https://doi.org/10.1029/92wr02528
Ramanathan R, Ritzi RW, Huang C (2008) Linking hierarchical stratal architecture to plume spreading in a Lagrangian-based transport model. Water Resour Res 44(4):10–19. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007wr006282
Ritzi RW, Huang L, Ramanathan R, Allen-King RM (2013) Horizontal spatial correlation of hydraulic and reactive transport parameters as related to hierarchical sedimentary architecture at the Borden research site. Water Resour Res 49:1901–1913. https://doi.org/10.1002/wrcr.20165
Ritzi RW (2000) Behavior of indicator variograms and transition probabilities in relation to the variance in lengths of hydrofacies. Water Resour Res 36(11):3375–3381. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000wr900139
Ritzi RW, Soltanian MR (2015) What have we learned from deterministic geostatistics at highly resolved field sites, as relevant to mass transport processes in sedimentary aquifers? J Hydrol 531:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.07.049
Ritzi RW, Dai Z, Dominic DF, Rubin YN (2004) Spatial correlation of permeability in cross-stratified sediment with hierarchical architecture. Water Resour Res 40(3):20–25. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003wr002420
Roberts PV, Goltz MN, Mackay DM (1986) A natural gradient experiment on solute transport in a sand aquifer: 3 Retardation estimates and mass balances for organic solutes. Water Resour Res 22(13):2047–2058. https://doi.org/10.1029/wr022i013p02047
Rubin Y (2003) Applied Stochastic Hydrogeology. Oxford University Press, New York
Rubin Y, Sun A, Maxwell R, Bellin A (1999) The concept of block effective macrodispersivity and a unified approach for grid-scale and plume-scale-dependent transport. J Fluid Mech 395:161–180. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0022112099005868
Ross K, Heße F, Musuuza JL, Attinger S (2019) Ensemble and effective dispersion in three-dimensional isotropic fractal media. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 33(11–12):2089–2107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-019-01739-2
Scaini A, Amvrosiadi N, Hissler C, Pfister L, Beven K (2019) Following tracer through the unsaturated zone using a Multiple Interacting Pathways model: implications from laboratory experiments. Hydrol Process. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13466
Shakir AO, Ali HA (2019) The effect of lining material on the permeability of clayey soil. Civil Eng J 5(3):662–678. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-2019-03091277
Soltanian MR, Behzadi F, de Barros FP (2020) Dilution Enhancement in Hierarchical and Multiscale Heterogeneous Sediments. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125025
Soltanian MR, Ritzi RW (2014) A new method for analysis of variance of the hydraulic and reactive attributes of aquifers as linked to hierarchical and multiscaled sedimentary architecture. Water Resour Res 50(12):9766–9776. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014wr015468
Soltanian MR, Ritzi RW, Huang C, Dai Z (2015) Relating reactive solute transport to hierarchical and multiscale sedimentary architecture in a L agrangian-based transport model: 1 Time-dependent effective retardation factor. Water Resour Res 51(3):1586–1600
Soltanian MR, Ritzi RW, Huang C, Dai Z (2015) Relating reactive solute transport to hierarchical and multiscale sedimentary architecture in a Lagrangian-based transport model: 2. Particle Displacement Variance Water Resour Res 51(3):1601–1618. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014wr016354
Soltanian MR, Ritzi RW, Dai Z, Huang C (2015) Reactive solute transport in physically and chemically heterogeneous porous media with multimodal reactive mineral facies: The Lagrangian approach. Chemosphere 122:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.11.064
Soltanian MR, Ritzi RW, Dai Z, Huang C, Dominic D (2015) Transport of kinetically sorbing solutes in heterogeneous sediments with multimodal conductivity and hierarchical organization across scales. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 29(3):709–726. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-014-0922-3
Soltanian MR, Sun A, Dai Z (2017) Reactive transport in the complex heterogeneous alluvial aquifer of Fortymile Wash, Nevada. Chemosphere 179:379–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.136
Sternberg SPK, Cushman JH, Greenkorn RA (1996) Laboratory observation of nonlocal dispersion. Transp Porous Media 23(2):135–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00178123
Sternberg SPK (2004) Dispersion measurements in highly heterogeneous laboratory-scale porous media. Transp Porous Media 54(1):107–124
Sudicky EA (1986) A natural gradient experiment on solute transport in a sand aquifer: Spatial variability of hydraulic conductivity and its role in the dispersion process. Water Resour Res 22(13):2069–2082
Sudicky EA, Illman W (2011) Lessons learned from a suite of CFB Borden experiments. Groundwater 49(5):630–648. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2011.00843.x
Taylor SR, Howard KWF (1987) A field study of scale-dependent dispersion in a sandy aquifer. J Hydrol 90:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(87)90170-3
Thibodeaux LJ, Donald M (2011) Handbook of chemical mass transport in the environment. Crc Press Inc.
Tu T, Ercan A, Kavvas ML (2018) Time-space fractional governing equations of transient groundwater flow in confined aquifers: Numerical investigation. Hydrol Process 32(10):1406–1419. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11500
Vik B, Bastesen E, Skauge A (2013) Evaluation of representative elementary volume for a vuggy carbonate rock—part: Porosity, permeability and dispersivity. J Pet Sci Eng 112:36–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2013.03.029
Wu Z, Li Z, Zeng L, Shao L, Tang H, Yang Q, Chen G (2011) Environmental dispersivity in free-water-surface-effect dominated wetland: multi-scale analysis. Front Environ Sci Eng China 5(4):597–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-011-0311-9
Zhang R, Huang K, Xiang J (1994) Solute movement through homogeneous and heterogeneous soil columns. Adv Water Resour 17(5):317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/0309-1708(94)90034-5
Zhang R, Li Q, Chow TL, Li S, Danielescu S (2012) Baseflow separation in a small watershed in New Brunswick, Canada, using a recursive digital filter calibrated with the conductivity mass balance method. Hydrol Process 27(18):2659–2665. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9417
Zhao J, Liu S (2016) An optimal filtering method for a time-fractional inverse advection-dispersion problem. J Inverse Ill-Posed Probl 24(1):51–54. https://doi.org/10.1515/jiip-2013-0081
Zheng L, Wang L (2018) Scale-dependent poiseuille flow alternatively explains enhanced dispersion in geothermal environments. Hydrol Process 33(4):527–534. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13339
Acknowledgements
This work was jointly supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC1800900), the Program for Jilin University (JLU) Science and Technology Innovative Research Team (No. 2019TD-35), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 41772253, 41972249) and the Graduate Innovation Fund of Jilin University (101832020CX233). Additional funding was provided by the Engineering Research Center of Geothermal Resources Development Technology and Equipment, Ministry of Education, China.
Funding
This work was jointly supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC1800900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 41772253, 41972249), the Program for Jilin University (JLU) Science and Technology Innovative Research Team (No. 2019TD-35) and the Graduate Innovation Fund of Jilin University (101832020CX233). Additional funding was provided by the Engineering Research Center of Geothermal Resources Development Technology and Equipment, Ministry of Education, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Ziqi Ma, Zhenxue Dai; Methodology: Ziqi Ma, Zhenxue Dai, Xiaoying Zhang; Formal analysis and investigation: Ziqi Ma, Chuanjun Zhan, Lin Zhu; Writing—original draft preparation: Ziqi Ma, Chuanjun Zhan; Writing – review and editing: Zhenxue Dai, Huili Gong, Corey Wallace, Mohamad Reza Soltanian; Funding acquisition: Zhenxue Dai, Xiaoying Zhang; Supervision: Zhenxue Dai.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Z., Dai, Z., Zhang, X. et al. Dispersivity variations of solute transport in heterogeneous sediments: numerical and experimental study. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 36, 661–677 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-021-02040-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-021-02040-x