Abstract
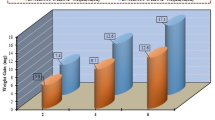
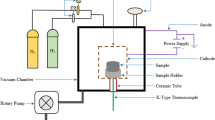
Active screen plasma nitriding is a newly developed technique utilized to enhance low alloy steel's surface property by placing them inside a steel case and supplying biased voltage to the cage. In this work, low alloy steel EN24 samples are plasma nitrided using active screen at different process parameters to improve its surface properties. The EN24 samples are treated at 500˚C and 550˚C treatment temperature for 2 h, 4 h and 6 h with gas flow ratio of \({H}_{2}/{N}_{2}=4:1\).The active screen plasma-nitrided samples are analyzed with various analytical techniques such as SEM, XRD, EDS, microhardness test, weight loss technique and potentiodynamic polarization test. From the SEM analysis, it is found that the compound layers vary from 12.680 to 22.025 µm. Further, the SEM analysis also reveals the formation of transformed austenite phases with increasing temperature and treatment time. Phase identification is performed on treated samples by XRD, which reveals the formation of \(\varepsilon ({Fe}_{2-3}N)\) and \(\upgamma ({Fe}_{4}N)\) on the surface of the samples. Using the microhardness test, it is found that the hardness value of treated samples has increased by 3.5 times (approx.) from the base material. From the weight loss technique, the minimum weight loss is seen for the treated sample at 500˚C for 6 h. Finally, it is observed from the potentiodynamic polarization test of the sample treated at 550˚C for 6 h has the minimum corrosion rate of 446.20 mm/year × 10−3.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves Jr C, Da Silva E.F, Martinelli A.E, Surf Coat Technol 139 (2001) 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(00)01146-4
Ahangarani Sh, Mahboubi F, and Sabour AR, Vacuum 80 (2006) 1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2006.01.013
Li CX, Bell T, Dong H, Surf Eng 18 (2002) 174. https://doi.org/10.1179/026708401225005250
Kumar N, Ganguli B, Roy B, and Deb B, Trans Indian Inst Met (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02191-z
Zhao C, Li CX, Dong H, and Bell T. Surf Coat Technol 201 (2006) 2320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2006.04.014
Rao K.R.M, Nouveau C, and Trinadh K, Trans Indian Inst Met 73 (2020)1695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-02013-8
Li CX, Bell T, Wear 256 (2004)1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2003.07.006
Cleugh D, Surf Eng 18(2) (2002) 133. https://doi.org/10.1179/026708402225002802
Perumal G, Geetha M, Asokamani R, Alagumurthi N, Trans Indian Inst Met 66 (2013)109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-012-0234-6
Berg M, Budtz-Jørgensen CV, Reitz H, Schweitz KO, Chevallier J, Kringhøj P, et al. Surf Coat Technol 124 (2000) 25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(99)00472-7
Borgioli F, Galvanetto E, Fossati A, and Bacci T, Surf Coat Technol 162 (2002) 61. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(02)00574-1
C. X. Li, Surf Eng 26(3) (2010) 1. https://doi.org/10.1179/174329409X439032
De Sousa R.R.M, De Araújo F.O, Gontijo L.C, Da Costa J.A.P, and Jr Alves C, Vacuum 86 (2012) 2048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2012.05.008
Wang L, Li Y, and Wu X, Appl. Surf Sci 254 (2008) 6595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.04.027
Figueroa U, Oseguera J, Schabes-Retchkinam P.S, Surf Coat Technol 728 (1996) 86. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(96)03058-7
Metin E, O.T. Inal J Mater Sci 22 (1987) 2783. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01086471
Corengia P, Ybarra G, Moina C, Cabo A, and Broitman E, Surf Coat Technol 200 (2005) 2391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2005.01.060
Saeed A, Khan A W, Jan F, Abrar M, Khalid M, Zakaullah M, Appl Surf Sci 273 (2013) 173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.02.008
Gautam D, Ganguli B, and Sharma S, Mater Perform Characterization 6 (2017) 581. https://doi.org/10.1520/MPC20160084
Bell T, Sun Y, and Suhadi A, Vacuum 59 (2000) 14. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0042-207X(00)00250-5
Wöhrle T, Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Phase Transformations in the Fe-N-C System, Dissertation. Stuttgart: Fakultät Chemie der Universität Stuttgart, 2012 (142 pp.), (2012).
Lei M.K, Zhang Z.L, Surf Coat Technol 91 (1997) 25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(96)03155-6
Liapina T, Leineweber E.J, and Mittemeijer A, Metall Mater Trans A 37 (2006) 319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-006-0003-4
Nikolussi M, Leineweber A, Bischoff E, Mittemeijer E.J, Int J Mat Red 98 (2007) 1086. https://doi.org/10.3139/146.101576
Lampe T, S Eisenberg, and Laudien G, Surf Eng 9 (1993) 69. https://doi.org/10.1179/sur.1993.9.1.69
Jacobs H, Rechenbach D, and Zachwieja U, J Alloys Comp 227 (1995) 10. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-8388(95)01610-4
Ahangarani Sh, Sabour A.R, Mahboubi F, and Shahrabi T, J Alloys Comp 484 (2009) 222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.03.161
C.X. Li, T. Bell, Corrosion Science 46 (6) (2004) 1527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2003.09.015
Nakata K, Yamauchi W, Akamatsu K, Ushio M, Surf Coat Technol 174 (2003) 1206. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(03)00459-6
Asadi Z.S, Mahboubi F, Mater & Des. 34 (2012) 516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.04.066
Kniess C T, Lima J C D and Prates P B, in Sintering – Methods and Products, (ed) Shatokha V, London (2012) p 294.
Ramboa K D M, Ferreira M C M, J Braz Chem Soc 26 (2015) 1491. http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.201
Shen H, Wang L, Surf Coat Technol 378 (2019)124953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.124953
Liang W, Bin X, Zhiwei Y, & Yaqin S, Surf Coat Technol 130 (2000) 304. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(00)00713-1
Naeem M, Shafiq M, Zaka-ul-Islam M, Ashiq A, Díaz-Guillén J C, Shahzad M, Zakaullah M, Mater & Des 108 (2016) 745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.07.044
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the contribution of Mr. Hardik Patel, Scientific Assistant-C, Institute for Plasma Research Gandhinagar, India, Mr. Subrat Kumar Das, Scientific Assistant-C (for SEM) and Mr. Vyom Desai, PhD scholar (for XRD analysis) from Facilitation Centre for Industrial Plasma Technologies Gandhinagar, India, in this study.
Funding
This study does not contain any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare no conflict of interest involved in the present study.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, N., Roy, B., Ganguli, B. et al. Influence of Treatment Time and Temperature on Surface Property of Active Screen Plasma-Nitrided EN24 Low Alloy Steel. Trans Indian Inst Met 74, 2027–2041 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02299-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-021-02299-2