Abstract
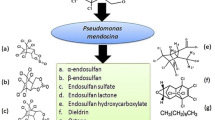
Three endosulfan-degrading bacterial strains, Pseudomonas sp. KT1, Pseudomonas sp. KT2 and Staphylococcus sp. DKT, were isolated and investigated for their degradation under anaerobic conditions. These bacteria effectively degraded endosulfans and some related compounds. All of the isolates utilized nitrate as an electron acceptor and nitrogen source. Endosulfans degradation performances by a mixed culture of Pseudomonas sp. KT2 and Staphylococcus sp. DKT changed from 25.9 ± 4.5 to 34.0 ± 5.5% and were higher than the degradation by the each individual strain. Moreover, Pseudomonas sp. KT2 was the first pure culture capable of degrading a persistent compound, endosulfan sulfate, under anaerobic conditions. The determination of degradation metabolites showed that endosulfan diol, endosulfan ether and endosulfan lactone were formed during endosulfan degradation by Pseudomonas sp. KT1 and KT2. Dehalogenase extracted from mixed culture cells also revealed effective degradation and dechlorination. The results in this study show that a mixed culture was valuable for biodegradation of endosulfans and some of their relatives under anaerobic conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Singh, V. and Singh, N., Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2014, vol. 104, pp. 189–193.
Tiwari, M.K. and Guha, S., Chemosphere, 2013, vol. 93, no. 3, pp. 567–573.
Singh, S.K. and Pandey, R.S., Ind. J. Exp. Biol., 1990, vol. 28, no. 10, pp. 953–956.
Ahmed, S. and Ahmad, M.S., Pak. Entomol., 2006, vol. 28, pp. 63–68.
Eqani, S.A., Malik, R.N., and Mohammad, A., Environ. Geochem. Health, 2011, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 33–47.
Deng, F., Xiong, B., Chen, B., Zheng, G., and Zhang, J., Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int., 2016, vol. 23, no. 13, pp. 13268–13275.
Aktar, M.W., Paramasivam, M., Sengupta, D., Purkait, S., Ganguly, M., and Banerjee, S., Environ. Monit. Assess., 2009, vol. 157, nos. 1–4, pp. 97–104.
Kumari, B., Singh, J., Singh, S., and Kathpal, T.S., Environ. Monit. Assess, 2005, vol. 105, nos. 1–3, pp. 111–120.
Kumar, M. and Philip, L., Bioremediat. J., 2006, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 179–190.
Leung, A.M., McDonough, D.M., and West, C.D., Environ. Monit. Assess., 1998, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 85–94.
Sethunathan, N., Megharaj, M., Chen Z., Singh, N., Kookana, R.S., and Naidu, R., Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol., 2002, vol. 68, no. 5, pp. 725–731.
Ito, K., Kawashima, F., Takagi, K., Kataoka, R., Kotake M., Kiyota, H., et al., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2016, vol. 473, no. 4, pp. 1094–1099.
Gupta, M., Mathur, S., Sharma, T.K., Rana, M., Gairola, A., Navani, et al., J. Hazard. Mater., 2016, vol. 301, pp. 250–258.
Mir, Z.A., Ali, S., Tyagi, A., Ali, A., Bhat, J.A., Jaiswal, P., et al., 3 Biotech., 2017, vol. 7, no. 3, p. 211.
Pradeep, V. and Subbaiah, U.M., 3 Biotech., 2016, vol. 6, no. 2, p. 124.
Zaffar, H., Ahmad, R., Pervez, A., and Naqvi, T.A., Pestic. Biochem. Phys., 2018, vol. 152, pp. 69–75.
Sutherland, T.D., Horne, I., Lacey, M.J., Harcourt, R.L., Russell, R.J., and Oakeshott, J.G., Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2000, vol. 66, no. 7, pp. 2822–2828.
Kwon, G-S., Sohn, Y., Shin, K., Kim, E., and Seo, B-I., Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2005, vol. 67, no. 6, pp. 845–850.
Guerin, T.F., Environ. Pollut., 1999, vol. 106, no. 1, pp. 13–21.
Kumar, M. and Philip, L., J. Hazard. Mater., 2006, vol. 136, no. 2, pp. 354–364.
Ha, D.D. and Nguyen T.O., Curr. Microbiol., 2019, vol. 76, no. 2, pp. 248–257.
Ha, D.D., Biodegradation, 2018, vol. 29, no. 5, pp. 499–510.
Bradford, M.M., Anal. Biochem., 1976, vol. 72, no. 1–2, pp. 248–254.
Bertani, G., J. Bact., 1951, vol. 62, no. 3, pp. 293–300.
Nijenhuis, I. and Zinder, S.H., Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 71, no. 3, pp. 1664–1667.
American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environmental Federation, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. Washington, D.C.: APHA-AWWA-WEF, 1998.
Bussian, B.M., Pandelova, M., Lehnik-Habrink, P., Aichner, B., Henkelmann, B., and Schramm, K.W., Environ. Pollut., 2015, vol. 206, pp. 661–666.
Narkhede, C.P., Patil, A.R., Koli, S., Suryawanshi, R., Wagh, N.D., Bipinchandra, K.S., and Patil, S.V., Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol., 2015, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 259–265.
Bajaj, A., Pathak, A., Mudiam, M.R., Mayilraj, S., and Manickam, N., J. Appl. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 109, no. 6, pp. 2135–2143.
Jesitha, K., Nimisha, K.M., Manjusha, C.M., and Harikumar, P.S., Environ. Process, 2015, vol. 2, pp. 225–240.
Duc, H.D., FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2019, vol. 366, no. 14. fnz174.
Ghattas, A-K., Fischer, F., Wick, A., and Ternes, T.A., Water Res., 2017, vol. 116, no. 7, 268–295.
Zhang, J., Cao, X., Xin, Y., Xue, S., and Zhang, W., World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2013, vol. 29, no. 10, pp. 1791–1799.
Camboim, E.K., Tadra-Sfeir, M.Z., de Souza, E.M., PedrosaFde, O., Andrade, P.P., McSweeney, C.S., et al., Sci. World J., 2012, ID 149893.
Bhalerao, T.S., J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2013, vol. 23, no. 11, pp. 1610–1616.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duc, H.D., Hung, N.V. & Oanh, N.T. Anaerobic Degradation of Endosulfans by a Mixed Culture of Pseudomonas sp. and Staphylococcus sp.. Appl Biochem Microbiol 57, 327–334 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683821030030
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683821030030