Abstract
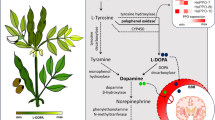
The relationship of the genes of PAL (phenylalanine ammonia-lyase) and scopoletin was explored to reveal the key gene involved in PAL activity, PAL expression and scopoletin accumulation in noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) leaves and fruit. Our results display how the enzyme activity of PAL in noni fruit and leaves increases gradually with the leaves maturity, and exogenous ethephon induces PAL activity in noni leaves, which is consistent with the scopoletin accumulation law. Based on our previous transcriptome data, three PAL fragments were retrieved, and their full lengths were cloned via RACE; named as McPAL1, McPAL2 and McPAL3. The analysis of qRT-PCR showed that McPAL3 is expressed in the leaves and mature fruit, McPAL2 in the leaves only and McPAL1 mainly in the young stage of fruit. Ethephon induced the expression of McPAL2 and McPAL3 in the leaves, and McPAL1 and McPAL3 in the fruit. In noni fruit treated with ethephon, the expression pattern of McPAL3 was consistent with the trend of the scopoletin content and total PAL activity. We conclude that McPAL3 is the key gene involved in the accumulation of scopoletin, which can be induced by ethylene (ETH).






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PAL:
-
Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- RACE:
-
Rapid-amplification of cDNA ends
- HCl:
-
Hydrochloric acid
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- LSD:
-
Least significance difference
- ETH:
-
Ethylene
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
Assanga SBI, Luján LML, Rivera-Castañeda EG, Gilsalido AA, Acostasilva AL, Rubiopino JL (2013) Effect of maturity and harvest season on antioxidant activity, phenolic compounds and ascorbic acid of Morinda citrifolia L. (noni) grown in Mexico (with track change). Afr J Biotechnol 12:4630–4639. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB12.1881
Barry CS, Llop-Tous MI, Grierson D (2000) The regulation of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase gene expression during the transition from system-1 to system-2 ethylene synthesis in tomato. Plant Physiol 123:979–986. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.123.3.979
Boo HO, Chon SU, Lee SY (2006) Effects of temperature and plant growth regulators on anthocyanin synthesis and phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activity in chicory (Cichorium intybus L.). J Hortic Sci Biotech 81:478–482. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2006.11512091
Brown AC (2012) Anticancer activity of Morinda citrifolia (Noni) fruit: a review. Phytother Res 26:1427–1440. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.4595
Cochrane FC, Davin LB, Lewis NG (2004) The arabidopsis phenylalanine ammonia lyase gene family: kinetic characterization of the four PAL isoforms. Phytochemistry 65:1557–1564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2004.05.006
De PA, Pignone D, Morgese A, Sonnante G (2010) Characterization and differential expression analysis of artichoke phenylalanine ammonia-lyase-coding sequences. Physiol Plant 132:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2007.00996.x
Deng S, West BJ, Jarakae JC (2010) A quantitative comparison of phytochemical components in global noni fruits and their commercial products. Food Chem 122:267–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.01.031
Espley RV, Leif D, Plunkett B, Mcghie TK, Henrykirk RA, Hall M, Johnston JW, Punter MP, Boldingh H, Nardozza S, Volz RK, O’Donnell S, Allan AC (2019) Red to brown: an elevated anthocyanic response in apple drives ethylene to advance maturity and fruit flesh browning. Front Plant Sci 10:1248. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01248
Given NK, Venis MA, Grierson D (1998) Purification and properties of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase from strawberry fruit and its synthesis during ripening. J Plant Physiol 133:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0176-1617(88)80080-4
Jia DD, Lan ZQ, Wu T (2020) Ethylene is the key signal in the accumulation process of scopoletin in Noni (Morinda citrifolia). Sci Hortic. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108980
Jong DF, Hanley SJ, Beale MH, Karp A (2015) Characterisation of the willow phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) gene family reveals expression differences compared with poplar. Phytochemistry 11:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2015.06.005
Kao YY (2002) Differential expression of two distinct phenylalanine ammonia-lyase genes in condensed tannin-accumulating and lignifying cells of quaking aspen. Plant Physiol 130:796–807. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.006262
Kostenyuk IA, Zon J, Burns JK (2002) Phenylalanine ammonia lyase gene expression during abscission in citrus. Physiol Plant 116:106–112. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2002.1160113.x
Kumar A, Ellis BE (2001) The phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene family in raspberry. Structure, expression, and evolution. Plant Physiol 127:230–239. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.127.1.230
Li ZH, Gemma HS, Iwahori SC (2002) Stimulation of ‘Fuji’ apple skin color by ethephon and phosphorus-calcium mixed compounds in relation to flavonoid synthesis. Sci Hortic 94:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4238(01)00363-6
Lin SY, Liao YY, Roan SF, Chen LZ, Chen PA (2014) Growth of noni fruits (Morinda citrifolia L.) and accumulation of phenolic compounds during fruit development. Sci Hortic 178:168–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.08.013
Lopez-Galvez G, Saltveit ME, Cantwell MI (1996) Wound-induced phenylalanine ammonia lyase activity: factors affecting its induction and correlation with the quality of minimally processed lettuce. Postharv Biol Technol 9:223–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(96)00050-6
Macdonald MJ, Dcunha GB (2007) A modern view of phenylalanine ammonia lyase. Biochem Cell Biol 85:273–282. https://doi.org/10.1139/o07-018
Mao XF, Xu X, Yang XX, Li ZX, Yang JH, Liu ZY (2019) Molecular and functional characterization of ApPGRP from Anatolica polita in the immune response to Escherichia coli. Gene 690:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.12.036
Merchante C, Alonso JM, Stepanova AN (2013) Ethylene signaling: simple ligand, complex regulation. Curr Opin Plant Biol 16:554–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2013.08.001
Ng TB, Liu F, Lu YH, Chen CHK, Wang ZT (2003) Antioxidant activity of compounds from the medicinal herb Aster tataricus. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 136:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1532-0456(03)00170-4
Reichert A, He XZ, Dixon RA (2009) Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) from tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum): characterization of the four tobacco PAL genes and active heterotetrameric enzymes. Biochem J 424:233–242. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20090620
Sharma K, Pachauri SD, Khandelwal K, Ahma H, Arya A, Biala P, Agrawal S, Pandey RR, Srivastava AK, Srivastav A, Saxena JK, Dwivedi AK (2016) Anticancer effects of extracts from the fruit of Morinda citrifolia (Noni) in breast cancer cell lines. Drug Res 66:141–147. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0035-1555804
Shaw CY, Chen CH, Hsu CC, Chen CC, Tsai YC (2003) Antioxidant properties of scopoletin isolated from Sinomonium acutum. Phytother Res 17:823–825. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.1170
Shi R, Shuford CM, Wang JP, Sun YHS, Yang ZC, Chen HSC, Tunlayaanukit S, Li QZ, Liu J, Muddiman DC, Sederoff RR, Chiang VL (2013) Regulation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) gene family in wood forming tissue of Populus trichocarpa. Planta 238:487–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1905-1
Siddiqui BS, Sattar FA, Begum S, Dar A, Nadeem M, Gilani AH, Rehman Mandukhail S, Ahmad A, Tauseef S (2014) A note on anti-leishmanial, spasmolytic and spasmogenic, antioxidantand antimicrobial activities of fruits, leaves and stem of Morinda citrifolia Linn. an important medicinal and food supplement plant. Med Aromat Plants 3:1–3. https://doi.org/10.4172/2167-0412.1000159
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tsai CJ, Harding SA, Tschaplinski TJ, Lindroth RL, Yuan YN (2010) Genome-wide analysis of the structural genes regulating defense phenylpropanoid metabolism in Populus. New Phytol 172:47–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01798.x
Wan Osman WN, Che Ahmad Tantowi NA, Lau SF, Mohamed S (2019) Epicatechin and scopoletin rich Morinda citrifolia (Noni) leaf extract supplementation, mitigated Osteoarthritis via anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative, and anti-protease pathways. J Food Biochem 43:e12755. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.12755
Wang J, Liang SJ, Ma HL, Zhang PP, Shi WN (2016) Effects of ethephon on fresh in-husk walnut preservation and its possible relationship with phenol metabolism. J Food Sci 81:1921–1927. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.13370
Wang MY, West BJ, Jensen CJ, Nowicki D, Su C, Palu AK, Anderson G (2002) Morinda citrifolia (Noni): a literature review and recent advances in Noni research. Acta Pharmacol Sin 3:1127–1141. https://doi.org/10.1097/00007890-199602270-00002
Wu T, Li M, Lan ZQ (2019) Reveal the variation patterns of chemical composition in the fruit of Morinda citrifolia (noni) during postharvest storage through metabolomic characterization. Trop Plant Biol 12:85–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12042-019-09222-6
Zhang WM, Wang W, Zhang JJ, Wang ZR, Wang Y, Hao WJ, Huang WY (2016) Antibacterial constituents of Hinan Morinda citrifolia (Noni) leaves. J Food Sci 81:1192–1196. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.13302
Zhu YC, Wang K, Wu CX, Zhao Y, Yin XR, Zhang B, Grierson D, Chen KS, Xu CJ (2019) Effect of ethylene on cell wall and lipid metabolism during alleviation of postharvest chilling injury in peach. Cells 8:1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8121612
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Extension Project of State Administration of Forestry and Grassland, China (No. [2019]27) and the fund of China Scholarship Council (201908535030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Qingfen Wang, Fei Yang, Dandan Jia and Juan Liu performed the experiment, and Wang analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. Tian Wu designed the experiment and modified the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Liu, J., Yang, F. et al. The phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene McPAL3: the key gene involved in the scopoletin accumulation of Morinda citrifolia L.. Braz. J. Bot 44, 663–670 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-021-00717-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-021-00717-9