Abstract
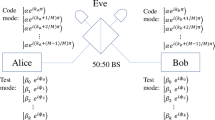
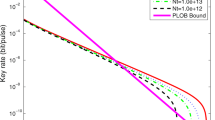
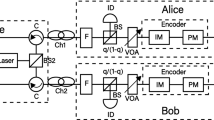
Twin-field quantum key distribution (TF-QKD) can overcome the fundamental rate-loss limit without quantum repeaters, which has stimulated intense research interests both in theory and experiment. Recently, TF-QKD protocols with discrete-phase-randomized sources have been widely studied. However, all these protocols require the phase postselection step in the test mode. To bypass this step, we propose a discrete-phase-randomized TF-QKD protocol without phase postselection in the test mode, which reduces the amount of information transmitted in the classical post-processing stage and thus reduces the consumption of secret keys in the authentication of classical information. Moreover, the numerical simulation of our protocol can be easily solved by linear programming. Simulation results show that, with only a few number of discrete phases, our protocol can beat the rate-loss bound and approximate the case of continuous phases, which is very practical in some real-life implementations of TF-QKD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C. H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing. pp. 175–179 (1984)
Acín, A., Brunner, N., Gisin, N., Massar, S., Pironio, S., Scarani, V.: Device-independent security of quantum cryptography against collective attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 230501 (2007)
Lo, H.K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130503 (2012)
Braunstein, S.L., Pirandola, S.: Side-channel-free quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130502 (2012)
Lim, C.C.W., Portmann, C., Tomamichel, M., Renner, R., Gisin, N.: Device-independent quantum key distribution with local Bell test. Phys. Rev. X 3, 031006 (2013)
Takesue, H., Sasaki, T., Tamaki, K., Koashi, M.: Experimental quantum key distribution without monitoring signal disturbance. Nat. Photonics. 9, 827–831 (2015)
Fan-Yuan, G.J., Chen, W., Lu, F.Y., Yin, Z.Q., Wang, S., Guo, G.C., Han, Z.F.: A universal simulating framework for quantum key distribution systems. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 63, 180504 (2020)
Ma, X., Fung, C.H.F., Razavi, M.: Statistical fluctuation analysis for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 86, 052305 (2012)
Yin, Z.-Q., Fung, C.H.F., Ma, X., Zhang, C.-M., Li, H.-W., Chen, W., Han, Z.-F.: Mismatched-basis statistics enable quantum key distribution with uncharacterized qubit sources. Phys. Rev. A 90, 052319 (2014)
Li, H.-W., Yin, Z.-Q., Chen, W., Wang, S., Guo, G.-C., Han, Z.-F.: Quantum key distribution based on quantum dimension and independent devices. Phys. Rev. A 89, 032302 (2014)
Zhou, Y.-H., Yu, Z.-W., Wang, X.-B.: Making the decoy-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution practically useful. Phys. Rev. A 93, 042324 (2016)
Rubenok, A., Slater, J.A., Chan, P., Lucio-Martinez, I., Tittel, W.: Real-world two-photon interference and proof-of-principle quantum key distribution immune to detector attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 130501 (2013)
Tang, Z., Liao, Z., Xu, F., Qi, B., Qian, L., Lo, H.-K.: Experimental demonstration of polarization encoding measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 190503 (2014)
Comandar, L.C., Lucamarini, M., Fröhlich, B., Dynes, J.F., Sharpe, A.W., Tam, S.W., Yuan, Z.L., Penty, R.V., Shields, A.J.: Quantum key distribution without detector vulnerabilities using optically seeded lasers. Nat. Photonics. 10, 312–315 (2016)
Yin, H.-L., Chen, T.-Y., Yu, Z.-W., Liu, H., You, L.-X., Zhou, Y.-H., Chen, S.-J., Mao, Y., Huang, M.-Q., Zhang, W.-J., Chen, H., Li, M.-J., Nolan, D., Zhou, F., Jiang, X., Wang, Z., Zhang, Q., Wang, X.-B., Pan, J.-W.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution over a 404 km optical fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 190501 (2016)
Takeoka, M., Guha, S., Wilde, M.M.: Fundamental rate-loss trade-off for optical quantum key distribution. Nat. Commun. 5, 5235 (2014)
Pirandola, S., Laurenza, R., Ottaviani, C., Banchi, L.: Fundamental limits of repeaterless quantum communications. Nat. Commun. 8, 15043 (2017)
Lucamarini, M., Yuan, Z.L., Dynes, J.F., Shields, A.J.: Overcoming the rate-distance limit of quantum key distribution without quantum repeaters. Nature 557, 400–403 (2018)
Tamaki, K., Lo, H.-K., Wang, W., Lucamarini, M.: Information theoretic security of quantum key distribution overcoming the repeaterless secret key capacity bound. arXiv:p.1805.05511 (2018)
Ma, X., Zeng, P., Zhou, H.: Phase-matching quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. X 8, 31043 (2018)
Wang, X.-B., Yu, Z.-W., Hu, X.-L.: Twin-field quantum key distribution with large misalignment error. Phys. Rev. A 98, 062323 (2018)
Curty, M., Azuma, K., Lo, H.K.: Simple security proof of twin-field type quantum key distribution protocol. npj Quantum Inf. 5, 64 (2019)
Cui, C., Yin, Z.-Q., Wang, R., Chen, W., Wang, S., Guo, G.-C., Han, Z.-F.: Twin-field quantum key distribution without phase postselection. Phys. Rev. Appl. 11, 034053 (2019)
Lin, J., Lütkenhaus, N.: Simple security analysis of phase-matching measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 98, 42332 (2018)
Yin, H.-L., Fu, Y.: Measurement-device-independent twin-field quantum key distribution. Sci. Rep. 9, 3045 (2019)
Wang, R., Yin, Z.-Q., Lu, F.-Y., Wang, S., Chen, W., Zhang, C.-M., Han, Z.-F.: Optimized protocol for twin-field quantum key distribution. Commun. Phys. 3, 149 (2020)
Minder, M., Pittaluga, M., Roberts, G.L., Lucamarini, M., Dynes, J.F., Yuan, Z.L., Shields, A.J.: Experimental quantum key distribution beyond the repeaterless secret key capacity. Nat. Photonics 13, 334–338 (2019)
Wang, S., He, D.-Y., Yin, Z.-Q., Lu, F.-Y., Cui, C.-H., Chen, W., Han, Z.-F.: Beating the fundamental rate-distance limit in a proof-of-principle quantum key distribution system. Phys. Rev. X 9, 021046 (2019)
Zhong, X., Hu, J., Curty, M., Qian, L., Lo, H.-K.: Proof-of-principle experimental demonstration of twin-field type quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 123, 100506 (2019)
Fang, X.-T., Zeng, P., Liu, H., Zou, M., Wu, W., Tang, Y.-L., Pan, J.-W.: Implementation of quantum key distribution surpassing the linear rate-transmittance bound. Nat. Photonics 14, 422–425 (2020)
Liu, Y., Yu, Z.-W., Zhang, W., Guan, J.-Y., Chen, J.-P., Zhang, C., Pan, J.-W.: Experimental twin-field quantum key distribution through sending or not sending. Phys. Rev. Lett. 123, 100505 (2019)
Chen, J.-P., Zhang, C., Liu, Y., Jiang, C., Zhang, W., Hu, X.-L., Pan, J.-W.: Sending-or-not-sending with independent lasers: secure twin-field quantum key distribution over 509 km. Phys. Rev. Lett. 124, 070501 (2020)
Xu, F., Qi, B., Ma, X., Xu, H., Zheng, H., Lo, H.K.: Ultrafast quantum random number generation based on quantum phase fluctuations. Opt. Express. 20, 12366–12377 (2012)
Abellán, C., Amaya, W., Jofre, M., Curty, M., Acín, A., Capmany, J., Mitchell, M.W.: Ultra-fast quantum randomness generation by accelerated phase diffusion in a pulsed laser diode. Opt. Express 22, 1645–1654 (2014)
Tang, Z., Liao, Z., Xu, F., Qi, B., Qian, L., Lo, H.K.: Experimental demonstration of polarization encoding measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 190503 (2014)
Cao, Z., Zhang, Z., Lo, H.-K., Ma, X.: Discrete-phase-randomized coherent state source and its application in quantum key distribution. New J. Phys. 17, 053014 (2015)
Cao, Z.: Discrete-phase-randomized measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 101, 062325 (2020)
Currás-Lorenzo, G., Wooltorton, L., Razavi, M.: Twin-field quantum key distribution with fully discrete phase randomization. Phys. Rev. Appl. 15, 014016 (2021)
Zhang, C.-M., Xu, Y.-W., Wang, R., Wang, Q.: Twin-field quantum key distribution with discrete-phase-randomized sources. Phys. Rev. Appl. 14, 064070 (2020)
Jiang, C., Yu, Z.W., Hu, X.-L., Wang, X.-B.: Sending-or-not-sending twin-field quantum key distribution with discrete-phase-randomized weak coherent states. Phys. Rev. Res. 2, 043304 (2020)
Walenta, N.: Concepts, components and implementations for quantum key distribution over optical fibers. Doctoral dissertation, University of Geneva (2013)
Christandl, M., König, R., Renner, R.: Postselection technique for quantum channels with applications to quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 020504 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2019T120446, 2018M642281), Jiangsu Planned Projects for Postdoctoral Research Funds (2018K185C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, YW., Wang, R. & Zhang, CM. Discrete-phase-randomized twin-field quantum key distribution without phase postselection in the test mode. Quantum Inf Process 20, 199 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03135-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-021-03135-8