Abstract
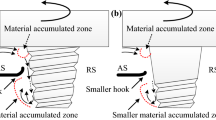
T-lap joints are widely utilized in connecting various structural elements owing to their efficient application. Typically, the mechanical properties of the joints are critical in maintaining an effective connection. In this study, we examined the role of the interface morphology in failure behavior of the dissimilar friction stir welded (FSWed) T-lap joints of 7075/5083 aluminum alloys. The experimental results verified that the morphology of interface of the joints was sensitive to the number of welding passes and tool offset. Additionally, the kissing bonds (KBs) were minimized significantly when the tool offset was combined with the double-pass welding. Furthermore, both the tensile and fatigue strengths of the joints were extremely sensitive to the interface geometry. We performed a quantitative analysis using a simplified fracture mechanics model and finite element method to clarify the failure behavior of the FSWed T-lap joints that must be optimized in terms of both the size and geometry of the KBs by altering the welding conditions.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
[1]R.M.F. Paulo, P. Carlone, V. Paradiso, R.A.F. Valente, and F. Teixeira-Dias: Thin-Walled Struct., 2017, vol. 120, pp. 297–306.
[2]C. Li, H. Ren, Z. Zhu, and C. Guedes Soares: Thin-Walled Struct., 2018, vol. 127, pp. 221–234.
[3]A. Heinz, A. Haszler, C. Keidel, S. Moldenhauer, R. Benedictus, and W. Miller: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2000, vol. 280, pp. 102–107.
[4]D. Frank, H. Remes, and J. Romanoff: Int. J. Fatigue, 2011, vol. 33, pp. 102–114.
[5]D.M. Costa, J.S. Jesus, A. Loureiro, J.A.M. Ferreira, and L.P. Borrego: Int. J. Fatigue, 2014, vol. 61, pp. 244–254.
[6]J.S. Jesus, J.M. Costa, A. Loureiro, and J.M. Ferreira: Int. J. Fatigue, 2017, vol. 97, pp. 124–134.
[7]O.T. Ola, F.E. Doern: Mater. Des., 2015, vol. 77, pp. 50–58.
[8]H. Yonetani: Weld. Int., 2008, vol. 46, pp. 43–47.
[9]H. Li, J. Zou, J. Yao, H. Peng: J. Alloys Comp., 2017, vol. 727, pp. 531–539.
[10]S.C. Wu, C. Yu, P.S. Yu, J.Y. Buffière, L. Helfen, Y.N. Fu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, vol. 651, pp. 604–614.
W.M. Thomas, E.D. Nicholas, J.C. Needham, M.G. Murch, P. Temple-Smith, and C.J. Dawes: UK Patent Office, London, 1991.
[12]R.S. Mishra, and Z.Y. Ma: Mater. Sci. Eng. R, 2005, vol. 50, pp. 1–78.
[13]I. Kalemba-Rec, C. Hamilton, M. Kopyściański, D. Miara, K. Krasnowski, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, vol. 26, pp. 1032–1043.
[14]M.M.Z. Ahmed, A.M.M. Sabbah, S. El-Sayed, H.R. Ammar, E. Ahmed: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2017, vol. 242, pp. 77–91.
[15]I. Kalemba-Rec, M. Kopyściański, D. Miara, K. Krasnowski: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2018, vol. 97, pp. 2767–2779.
[16]L. Fratini, F. Micari, A. Squillace, and G. Giorleo: Key Eng. Mater. 2007, vol. 344, pp. 751-758.
[17]L. Fratini, G. Buffa, F. Micari, and R. Shivpuri: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, vol. 44, 570–578.
D.D. Hao, M. Okazaki, and T.H. Tra: JSME-Mech. Eng. J., 2019, 10.1299/mej.19-00091.
[19]L. Cui, X. Yang, G. Zhou, X. Xu, and Z. Shen: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 543, pp. 58–68.
[20]J.S. Jesus, J.M. Costa, A. Loureiro, and J.M. Ferreira: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2018, vol. 255, pp. 387–399.
[21]D.D. Hao, M. Okazaki, and T.H. Tra: Mater. Manuf. Process., 2020, vol. 36, pp. 693–701.
[22]E.E. Feistauer, L.A. Bergmann, and J.F. dos Santos: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2018, vol. 731, pp. 454–464.
D.D. Hao, M. Okazaki, and T.H. Tra: JSME-Mech. Eng. J., 2020, 10.1299/mej.19-00490.
H.D. Duong, M. Okazaki, T.H. Tran, Int. J. Fatigue, 2021, 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.106090.
M.M.Z. Ahmed, M.M. El-SayedSeleman, Z.A. Zidan, R.M. Ramadan, S. Ataya, N.A. Alsaleh: Metals, 2021, 10.3390/met11010128.
T. Suna, M.J. Roy, D. Strong, C. Simpson, P.J. Withers, P.B. Prangnell: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2019, vol. 263, pp. 256–265.
J.P. Martin, C. Stanhope, S. Gascoyne: In book: Friction Stir Welding and Processing VI, 2011, pp. 177–86.
[28]R.M.F. Paulo, F. Rubino, R.A.F. Valente, F. Teixeira-Dias, P. Carlone: Thin-Walled Struct., 2020, vol. 157, 107128.
[29]H. Liu, Y. Hu, Y. Peng, C. Dou, and Z. Wang: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2016, vol. 238, pp. 244–254.
[30]J.F.C. Moraes, R.I. Rodriguez, J.B. Jordon, and X. Su: Int. J. Fatigue, 2017, vol. 100, pp. 1–11.
[31]X. Meng, Z. Xu, Y. Huang, Y. Xie, Y. Wang, L. Wan, Z. Lv, and J. Cao: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol.. 2017, vol. 94, pp. 1253–1261.
[32]M.I. Costa, D. Verdera, J.D. Costa, C. Leitao, and D.M. Rodrigues: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2015, vol. 225, pp. 385–392.
[33]S.H. Chowdhury, D.L. Chen, S.D. Bhole, X. Cao, and P. Wanjara: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 556, pp. 500–509.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Test methods for tension testing of metallic materials, E08, ASTM International, 2004.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Standard Practice for Conducting Force Controlled Constant Amplitude Axial Fatigue Tests of Metallic Materials, E466, ASTM International, 2004.
[36]Y.S. Sato, H. Takauchi, S.H.C. Park, and H. Kokawa: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, vol. 405, pp. 333-338.
[37]D. Frank, H. Remes, and J. Romanoff: Int. J. Fatigue, 2013, vol. 47, pp. 340–350.
[38]P. Gallo, M. Guglielmo, J. Romanoff, and H. Remes: Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, vol. 136, pp. 112–123.
[39]P. Gallo, H. Remes, and J. Romanoff: Int. J. Fatigue, 2017, vol. 99, pp. 125–136.
M. Janssen, J. Zuidema, and R.J.H. Wanhill: Fracture mechanics, 2nd ed., Delft University Press, Washington, DC, 2004, p. 41.
[41]H. Nisitani: JSME, 1975, vol. 41, pp. 1103–1111.
Y. Murakami: Stress Intensity Factors, Handbook, 1987, vol. 1.
J.P. Benthem, and W.T. Koiter: Mech. Fract. 1973, vol. 1.
[44]G. Irwin: J. Appl. Mech., 1957, vol. 24, pp. 361–364.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express deep gratitude to Prof. Okazaki Masakazu at Nagaoka University of Technology, Japan for his support. This work was supported finance by Nha Trang University through Grant-in-aid #TR2020-13-21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted September 3, 2020; accepted April 19, 2021.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duong, H.D., Tran, T.H. Effect of Interface Morphology on the Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded T-lap Joints of 7075/5083 Aluminum Alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 52, 3023–3033 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-021-06296-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-021-06296-4