Abstract
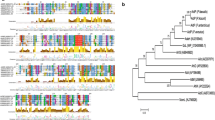
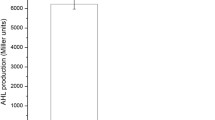
N-acylhomoserine lactones (AHLs) are autoinducers found in gram-negative bacteria and are ubiquitous in common plant pathogenic bacteria. N-acylhomoserine lactonase degrades the lactone ring of AHLs to achieve quorum quenching of phytopathogenic virulence genes. In this study, a novel AHL lactonase gene KaAhl was successfully cloned and identified from Kushneria avicenniae strain DSM 23439. KaAhl is encoded a 261-residue polypeptide belonging to the metallo-β-lactamase superfamily. The recombinant enzyme displayed maximum hydrolysis activity of 0.64 U/mg toward N-(3-oxooctanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone substrate at 30°C and pH 8.0. Besides, it had moderate thermal stability but exhibited a high salt tolerance showing approximate 50% relative activity in the presence of 35% concentrations of NaCl. Furthermore, the KaAhl was significantly promoted by Mn2+ and Ni2+, which enhanced the lactonase activity to approximate 100% extent. In addition, it was observed that recombinant Escherichia coli BL21-pET28a-KaAhl producing KaAhl proteins could effectively inhibit the plant pathogenicity of Erwinia carotovora for 72 h, which might have great potential for controlling gram-negative pathogenic bacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sitnikov, D. M., J. B. Schineller, and T. O. Baldwin (1995) Transcriptional regulation of bioluminesence genes from Vibrio fischeri. Mol. Microbiol. 17: 801–812.
Dong, Y. H., L. H. Wang, J. L. Xu, H. B. Zhang, X. F. Zhang, and L. H. Zhang (2001) Quenching quorum-sensing-dependent bacterial infection by an N-acyl homoserine lactonase. Nature. 411: 813–817.
de Kievit, T. R. and B. H. Iglewski (2000) Bacterial quorum sensing in pathogenic relationships. Infec. Immun. 68: 4839–4849.
Saeki, E. K., R. K. T. Kobayashi, and G. Nakazato (2020) Uorum sensing system: Target to control the spread of bacterial infections. Microb. Pathog. 142: 104068.
Mukherjee, S. and B. L. Bassler (2019) Bacterial quorum sensing in complex and dynamically changing environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 17: 371–382.
Uroz, S., P. M. Oger, E. Chapelle, M. T. Adeline, D. Faure, and Y. Dessaux (2008) A Rhodococcus qsdA-encoded enzyme defines a novel class of large-spectrum quorum-quenching lactonases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74: 1357–1366.
Bassler, B. L., E. P. Greenberg, and A. M. Stevens (1997) Cross-species induction of luminescence in the quorum-sensing bacterium Vibrio harveyi. J. Bacteriol. 179: 4043–4045.
Lang, J. and D. Faure (2014) Functions and regulation of quorum-sensing in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Front. Plant Sci. 5: 14.
Zhang, H. B., L. H. Wang, and L. H. Zhang (2002) Genetic control of quorum-sensing signal turnover in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 99: 4638–4643.
Chatterjee, A., Y. Cui, P. Chakrabarty, and A. K. Chatterjee (2010) Regulation of motility in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora: quorum-sensing signal controls FlhDC, the global regulator of flagellar and exoprotein genes, by modulating the production of RsmA, an RNA-binding protein. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 23: 1316–1323.
Allison, D. G., B. Ruiz, C. SanJose, A. Jaspe, and P. Gilbert (1998) Extracellular products as mediators of the formation and detachment of Pseudomonas fluorescens biofilms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 167: 179–184.
Chatterjee, A., Y. Cui, Y. Liu, C. K. Dumenyo, and A. K. Chatterjee (1995) Inactivation of rsmA leads to overproduction of extracellular pectinases, cellulases, and proteases in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora in the absence of the starvation/cell density-sensing signal, N-(3-oxohexanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 1959–1967.
Parsek, M. R. and E. P. Greenberg (2000) Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria: a signaling mechanism involved in associations with higher organisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 97: 8789–8793.
Liu, P., Y. Chen, Z. Shao, J. Chen, J. Wu, Q. Guo, J. Shi, H. Wang, and X. Chu (2019) AhlX, an N-acylhomoserine lactonase with unique properties. Mar. Drugs. 17: 387.
Rasmussen, T. B. and M. Givskov (2006) Quorum-sensing inhibitors as anti-pathogenic drugs. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 296: 149–161.
Dong, Y. H., J. L. Xu, X. Z. Li, and L. H. Zhang (2000) AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 97: 3526–3531.
Dong, Y. H., A. R. Gusti, Q. Zhang, J. L. Xu, and L. H. Zhang (2002) Identification of quorum-quenching N-acyl homoserine lactonases from Bacillus species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68: 1754–1759.
Husain, F. M., A. A. Ansari, A. Khan, N. Ahmad, A. Albadri, and T. H. Albalawi (2019) Mitigation of acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) based bacterial quorum sensing, virulence functions, and biofilm formation by yttrium oxide core/shell nanospheres: Novel approach to combat drug resistance. Sci. Rep. 9: 18476.
Lin, L., N. Qin, and L. Guan (2019) A novel cold-adapted endoglucanase (M6A) from Microbacterium kitamiense S12 isolated from Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 24: 544–551.
Waterhouse, A., M. Bertoni, S. Bienert, G. Studer, G. Tauriello, R. Gumienny, F. T. Heer, T. A. P. de Beer, C. Rempfer, L. Bordoli, R. Lepore, and T. Schwede (2018) SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 46: W296–W303.
Huang, W., Y. Lin, S. Yi, P. Liu, J. Shen, Z. Shao, and Z. Liu (2012) QsdH, a novel AHL lactonase in the RND-type inner membrane of marine Pseudoalteromonas byunsanensis strain 1A01261. PLoS One. 7: e46587.
Bergonzi, C., M. Schwab, T. Naik, and M. Elias (2019) The structural determinants accounting for the broad substrate specificity of the quorum quenching lactonase GcL. Chembiochem. 20: 1848–1855.
Zhang, J. W., C. G. Xuan, C. H. Lu, S. Guo, J. F. Yu, M. Asif, W. J. Jiang, Z. G. Zhou, Z. Q. Luo, and L. Q. Zhang (2019) AidB, a novel thermostable N-acylhomoserine lactonase from the bacterium Bosea sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 85: e02065–19.
Jones, S., B. Yu, N. J. Bainton, M. Birdsall, B. W. Bycroft, S. R. Chhabra, A. J. Cox, P. Golby, P. J. Reeves, and S. Stephens (1993) The lux autoinducer regulates the production of exoenzyme virulence determinants in Erwinia carotovora and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. EMBO J. 12: 2477–2482.
Poole, K. and R. Srikumar (2001) Multidrug efflux in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: components, mechanisms and clinical significance. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 1: 59–71.
Tahrioui, A., M. Schwab, E. Quesada, and I. Llamas (2013) Quorum sensing in some representative species of Halomonadaceae. Life (Basel). 3: 260–275.
Wang, W. Z., T. Morohoshi, N. Someya, and T. Ikeda (2012) AidC, a novel N-acylhomoserine lactonase from the potato root-associated cytophaga-flavobacteria-bacteroides (CFB) group bacterium Chryseobacterium sp. strain StRB126. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78: 7985–7992.
Wang, W. Z., T. Morohoshi, M. Ikenoya, N. Someya, and T. Ikeda (2010) AiiM, a novel class of N-acylhomoserine lactonase from the leaf-associated bacterium Microbacterium testaceum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76: 2524–2530.
Liu, P., Y. Gao, W. Huang, Z. Shao, J. Shi, and Z. Liu (2012) A novel bioassay for high-throughput screening microorganisms with N-acyl homoserine lactone degrading activity. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 167: 73–80.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Key Laboratory of Biotic Environment and Ecology Safety in Anhui Province, Innovation Team of Scientific Research Platform in Anhui Universities, Anhui Provincial Key Laboratory of Molecular Enzymology and Mechanism of Major Diseases, Key Laboratory of Biomedicine in Gene Diseases and Health of Anhui Higher Education Institutes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Y., Shao, M., Li, T. et al. KaAhl, a Novel N-Acylhomoserine Lactonase from Kushneria avicenniae and Attenuated Effect on the Virulence of Erwinia carotovora. Biotechnol Bioproc E 26, 419–426 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-020-0230-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-020-0230-3