Abstract
The Notch signalling pathway is one of the main regulators of endothelial biology. In the last 20 years the critical function of Notch has been uncovered in the context of angiogenesis, participating in tip-stalk specification, arterial-venous differentiation, vessel stabilization, and maturation processes. Importantly, pharmacological compounds targeting distinct members of the Notch signalling pathway have been used in the clinics for cancer therapy. However, the underlying mechanisms that support the variety of outcomes triggered by Notch in apparently opposite contexts such as angiogenesis and vascular homeostasis remain unknown. In recent years, advances in -omics technologies together with mosaic analysis and high molecular, cellular and temporal resolution studies have allowed a better understanding of the mechanisms driven by the Notch signalling pathway in different endothelial contexts. In this review we will focus on the main findings that revisit the role of Notch signalling in vascular biology. We will also discuss potential future directions and technologies that will shed light on the puzzling role of Notch during endothelial growth and homeostasis. Addressing these open questions may allow the improvement and development of therapeutic strategies based on modulation of the Notch signalling pathway.


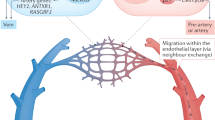
source and lower Notch activity. Tip cell specification has been shown to be transient and oscillatory. ECs at the leading edge are exposed to varying growth and biophysical factors, which makes them having different abilities to compete for the tip position. This continuous sensing and reaction to the surrounding tissue microenvironment results in a dynamic exchange among tip and stalk cells during angiogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmeliet P (2005) Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature 438:932–936
Risau W, Flamme I (1995) Vasculogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 11:73–91
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2011) Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 473:298–307
Andersson ER, Sandberg R, Lendahl U (2011) Notch signaling: simplicity in design, versatility in function. Development 138:3593–3612
Kopan R, Ilagan MX (2009) The canonical Notch signaling pathway: unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell 137:216–233
Hori K, Sen A, Artavanis-Tsakonas S (2013) Notch signaling at a glance. J Cell Sci 126:2135–2140
Bray SJ (2006) Notch signalling: a simple pathway becomes complex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:678–689
Palomero T, Lim WK, Odom DT, Sulis ML, Real PJ, Margolin A, Barnes KC, O’Neil J, Neuberg D, Weng AP et al (2006) NOTCH1 directly regulates c-MYC and activates a feed-forward-loop transcriptional network promoting leukemic cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103(48):18261–18266. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0606108103
Luo W, Garcia-Gonzalez I, Fernández-Chacón M, Casquero-Garcia V, Sanchez-Muñoz MS, Mühleder S, Garcia-Ortega L, Andrade J, Potente M, Benedito R (2021) Arterialization requires the timely suppression of cell growth. Nature 589(7842):437–441
Aranguren XL, Agirre X, Beerens M, Coppiello G, Uriz M, Vandersmissen I, Benkheil M, Panadero J, Aguado N, Pascual-Montano A, Segura V, Prósper F, Luttun A (2013) Unraveling a novel transcription factor code determining the human arterial-specific endothelial cell signature. Blood 122(24):3982–3992
Pontes-Quero S, Fernandez-Chacon M, Luo W, Lunella FF, Casquero-Garcia V, Garcia-Gonzalez I, Hermoso A, Rocha SF, Bansal M, Benedito R (2019) High mitogenic stimulation arrests angiogenesis. Nat Commun 10:2016
Hofmann JJ, Iruela-Arispe ML (2007) Notch signaling in blood vessels: who is talking to whom about what? Circ Res 100(11):1556–1568
Nolan DJ, Ginsberg M, Israely E, Palikuqi B, Poulos MG, James D, Ding BS, Schachterle W, Liu Y, Rosenwaks Z et al (2013) Molecular signatures of tissue-specific microvascular endothelial cell heterogeneity in organ maintenance and regeneration. Dev Cell 26:204–219
Halpern KB, Shenhav R, Massalha H, Toth B, Egozi A, Massasa EE, Medgalia C, David E, Giladi A, Moor AE et al (2018) Paired-cell sequencing enables spatial gene expression mapping of liver endothelial cells. Nat Biotechnol 36:962–970
Jabs M, Rose AJ, Lehmann LH, Taylor J, Moll I, Sijmonsma TP, Herberich SE, Sauer SW, Poschet G, Federico G et al (2018) Inhibition of endothelial Notch signaling impairs fatty acid transport and leads to metabolic and vascular remodeling of the adult heart. Circulation 137:2592–2608
Duarte A, Hirashima M, Benedito R, Trindade A, Diniz P, Bekman E, Costa L, Henrique D, Rossant J (2004) Dosage-sensitive requirement for mouse Dll4 in artery development. Genes Dev 18:2474–2478
Krebs LT, Shutter JR, Tanigaki K, Honjo T, Stark KL, Gridley T (2004) Haploinsufficient lethality and formation of arteriovenous malformations in Notch pathway mutants. Genes Dev 18:2469–2473
Xue Y, Gao X, Lindsell CE, Norton CR, Chang B, Hicks C, Gendron-Maguire M, Rand EB, Weinmaster G, Gridley T (1999) Embryonic lethality and vascular defects in mice lacking the Notch ligand Jagged1. Hum Mol Genet 8:723–730
Hrabe de Angelis M, McIntyre J 2nd, Gossler A (1997) Maintenance of somite borders in mice requires the Delta homologue DII1. Nature 386:717–721
Jiang R, Lan Y, Chapman HD, Shawber C, Norton CR, Serreze DV, Weinmaster G, Gridley T (1998) Defects in limb, craniofacial, and thymic development in Jagged2 mutant mice. Genes Dev 12(7):1046–1057
Ridgway J, Zhang G, Wu Y, Stawicki S, Liang WC, Chanthery Y, Kowalski J, Watts RJ, Callahan C, Kasman I et al (2006) Inhibition of Dll4 signalling inhibits tumour growth by deregulating angiogenesis. Nature 444:1083–1087
Noguera-Troise I, Daly C, Papadopoulos NJ, Coetzee S, Boland P, Gale NW, Lin HC, Yancopoulos GD, Thurston G (2006) Blockade of Dll4 inhibits tumour growth by promoting non-productive angiogenesis. Nature 444:1032–1037
Chiorean EG, LoRusso P, Strother RM, Diamond JR, Younger A, Messersmith WA, Adriaens L, Liu L, Kao RJ, DiCioccio AT, Kostic A, Leek R, Harris A, Jimeno A (2015) A phase i first-in-human study of enoticumab (REGN421), a fully human delta-like ligand 4 (Dll4) monoclonal antibody in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 21(12):2695–2703
Lafkas D, Shelton A, Chiu C, de Leon Boenig G, Chen Y, Stawicki SS, Siltanen C, Reichelt M, Zhou M, Wu X, Eastham-Anderson J, Moore H, Roose-Girma M, Chinn Y, Hang JQ, Warming S, Egen J, Lee WP, Austin C, Wu Y, Siebel CW (2015) Therapeutic antibodies reveal Notch control of transdifferentiation in the adult lung. Nature 528(7580):127–131
Wu Y, Cain-Hom C, Choy L, Hagenbeek TJ, de Leon GP, Chen Y, Finkle D, Venook R, Wu X, Ridgway J, Schahin-Reed D, Dow GJ, Shelton A, Stawicki S, Watts RJ, Zhang J, Choy R, Howard P, Kadyk L, Yan M, Siebel CW (2010) Therapeutic antibody targeting of individual Notch receptors. Nature 464(7291):1052–1057
Moore G, Annett S, McClements L, Robson T (2020) Top Notch in cancer: a detailed overview of recent insights and current perspectives. Cells 9(6):1503
Oka C, Nakano T, Wakeham A, de la Pompa JL, Mori C, Sakai T, Okazaki S, Kawaichi M, Shiota K, Mak TW, Honjo T (1995) Disruption of the mouse RBP-J kappa gene results in early embryonic death. Development 121(10):3291–3301
Krebs LT, Xue Y, Norton CR, Shutter JR, Maguire M, Sundberg JP, Gallahan D, Closson V, Kitajewski J, Callahan R et al (2000) Notch signaling is essential for vascular morphogenesis in mice. Genes Dev 14(11):1343–1352
Limbourg FP, Takeshita K, Radtke F, Bronson RT, Chin MT, Liao JK (2005) Essential role of endothelial Notch1 in angiogenesis. Circulation 111:1826–1832
Buono KD, Robinson GW, Martin C, Shi S, Stanley P, Tanigaki K, Honjo T, Hennighausen L (2006) The canonical Notch/RBP-J signaling pathway controls the balance of cell lineages in mammary epithelium during pregnancy. Dev Biol 293(2):565–580
Vasyutina E, Lenhard DC, Wende H, Erdmann B, Epstein JA, Birchmeier C (2007) RBP-J (Rbpsuh) is essential to maintain muscle progenitor cells and to generate satellite cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(11):4443–4448
Li F, Lan Y, Wang Y, Wang J, Yang G, Meng F, Han H, Meng A, Wang Y, Yang X (2011) Endothelial Smad4 maintains cerebrovascular integrity by activating N-cadherin through cooperation with Notch. Dev Cell 20(3):291–302
Castel D, Mourikis P, Bartels SJ, Brinkman AB, Tajbakhsh S, Stunnenberg HG (2013) Dynamic binding of RBPJ is determined by Notch signaling status. Genes Dev 27:1059–1071
Diaz-Trelles R, Scimia MC, Bushway P, Tran D, Monosov A, Monosov E, Peterson K, Rentschler S, Cabrales P, Ruiz-Lozano P et al (2016) Notch-independent RBPJ controls angiogenesis in the adult heart. Nat Commun 7:12088
Diéguez-Hurtado R, Kato K, Giaimo BD, Nieminen-Kelhä M, Arf H, Ferrante F, Bartkuhn M, Zimmermann T, Bixel MG, Eilken HM, Adams S, Borggrefe T, Vajkoczy P, Adams RH (2019) Loss of the transcription factor RBPJ induces disease-promoting properties in brain pericytes. Nat Commun 10(1):2817
Hellstrom M, Phng LK, Hofmann JJ, Wallgard E, Coultas L, Lindblom P, Alva J, Nilsson AK, Karlsson L, Gaiano N et al (2007) Dll4 signalling through Notch1 regulates formation of tip cells during angiogenesis. Nature 445:776–780
Lobov IB, Renard RA, Papadopoulos N, Gale NW, Thurston G, Yancopoulos GD, Wiegand SJ (2007) Delta-like ligand 4 (Dll4) is induced by VEGF as a negative regulator of angiogenic sprouting. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:3219–3224
Suchting S, Freitas C, le Noble F, Benedito R, Breant C, Duarte A, Eichmann A (2007) The Notch ligand Delta-like 4 negatively regulates endothelial tip cell formation and vessel branching. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:3225–3230
Benedito R, Roca C, Sorensen I, Adams S, Gossler A, Fruttiger M, Adams RH (2009) The Notch ligands Dll4 and Jagged1 have opposing effects on angiogenesis. Cell 137:1124–1135
Benedito R, Rocha SF, Woeste M, Zamykal M, Radtke F, Casanovas O, Duarte A, Pytowski B, Adams RH (2012) Notch-dependent VEGFR3 upregulation allows angiogenesis without VEGF-VEGFR2 signalling. Nature 484:110–114
Adams RH (2003) Molecular control of arterial-venous blood vessel identity. J Anat 202:105–112
Adams RH, Alitalo K (2007) Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:464–478
Lawson ND, Vogel AM, Weinstein BM (2002) sonic hedgehog and vascular endothelial growth factor act upstream of the Notch pathway during arterial endothelial differentiation. Dev Cell 3:127–136
Seo S, Kume T (2006) Forkhead transcription factors, Foxc1 and Foxc2, are required for the morphogenesis of the cardiac outflow tract. Dev Biol 296:421–436
Villa N, Walker L, Lindsell CE, Gasson J, Iruela-Arispe ML, Weinmaster G (2001) Vascular expression of Notch pathway receptors and ligands is restricted to arterial vessels. Mech Dev 108:161–164
Lawson ND, Scheer N, Pham VN, Kim CH, Chitnis AB, Campos-Ortega JA, Weinstein BM (2001) Notch signaling is required for arterial-venous differentiation during embryonic vascular development. Development 128(19):3675–3683
Su T, Stanley G, Sinha R, D’Amato G, Das S, Rhee S, Chang AH, Poduri A, Raftrey B, Dinh TT et al (2018) Single-cell analysis of early progenitor cells that build coronary arteries. Nature 559:356–362
Gridley T (2010) Notch signaling in the vasculature. Notch signaling. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 277–309
Swift MR, Weinstein BM (2009) Arterial-venous specification during development. Circ Res 104(5):576–588
You LR, Lin FJ, Lee CT, Demayo FJ, Tsai MJ, Tsai SY (2005) Suppression of Notch signalling by the COUP-TFII transcription factor regulates vein identity. Nature 435:98–104
Carlson TR, Yan Y, Wu X, Lam MT, Tang GL, Beverly LJ, Messina LM, Capobianco AJ, Werb Z, Wang R (2005) Endothelial expression of constitutively active Notch4 elicits reversible arteriovenous malformations in adult mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U. S. A 102:9884–9889
Murphy PA, Kim TN, Lu G, Bollen AW, Schaffer CB, Wang RA (2012) Notch4 normalization reduces blood vessel size in arteriovenous malformations. Sci Transl Med 4(117):117ra8
Trindade A, Kumar SR, Scehnet JS, Lopes-da-Costa L, Becker J, Jiang W, Liu R, Gill PS, Duarte A (2008) Overexpression of delta-like 4 induces arterialization and attenuates vessel formation in developing mouse embryos. Blood 112(5):1720–1729
Venkatesh DA, Park KS, Harrington A, Miceli-Libby L, Yoon JK, Liaw L (2008) Cardiovascular and hematopoietic defects associated with Notch1 activation in embryonic Tie2-expressing populations. Circ Res 103(4):423–431
Wang HU, Chen Z-F, Anderson DJ (1998) Molecular distinction and angiogenic interaction between embryonic arteries and veins revealed by ephrin-B2 and its receptor Eph-B4. Cell 93:741–753
Kim YH, Hu H, Guevara-Gallardo S, Lam MT, Fong SY, Wang RA (2008) Artery and vein size is balanced by Notch and ephrin B2/EphB4 during angiogenesis. Development 135(22):3755–3764
D’Amato G, Luxan G, del Monte-Nieto G, Martinez-Poveda B, Torroja C, Walter W, Bochter MS, Benedito R, Cole S, Martinez F et al (2016) Sequential Notch activation regulates ventricular chamber development. Nat Cell Biol 18:7–20
Travisano SI, Oliveira VL, Prados B, Grego-Bessa J, Pineiro-Sabaris R, Bou V, Gomez MJ, Sanchez-Cabo F, MacGrogan D, de la Pompa JL (2019) Coronary arterial development is regulated by a Dll4-Jag1-EphrinB2 signaling cascade. Elife 8:e49977
Hasan SS, Tsaryk R, Lange M, Wisniewski L, Moore JC, Lawson ND, Wojciechowska K, Schnittler H, Siekmann AF (2017) Endothelial Notch signalling limits angiogenesis via control of artery formation. Nat Cell Biol 19:928–940
Pitulescu ME, Schmidt I, Giaimo BD, Antoine T, Berkenfeld F, Ferrante F, Park H, Ehling M, Biljes D, Rocha SF et al (2017) Dll4 and Notch signalling couples sprouting angiogenesis and artery formation. Nat Cell Biol 19:915–927
Xu C, Hasan SS, Schmidt I, Rocha SF, Pitulescu ME, Bussmann J, Meyen D, Raz E, Adams RH, Siekmann AF (2014) Arteries are formed by vein-derived endothelial tip cells. Nat Commun 5:5758
Lavina, B., Castro, M., Niaudet, C., Cruys, B., Alvarez-Aznar, A., Carmeliet, P., Bentley, K., Brakebusch, C., Betsholtz, C., and Gaengel, K. (2018). Defective endothelial cell migration in the absence of Cdc42 leads to capillary-venous malformations. Development 145
Sabbagh MF, Heng JS, Luo C, Castanon RG, Nery JR, Rattner A, Goff LA, Ecker JR, Nathans J (2018) Transcriptional and epigenomic landscapes of CNS and non-CNS vascular endothelial cells. Elife 7:e36187
Gordon WR, Zimmerman B, He L, Miles LJ, Huang J, Tiyanont K, McArthur DG, Aster JC, Perrimon N, Loparo JJ et al (2015) Mechanical allostery: evidence for a force requirement in the proteolytic activation of Notch. Dev Cell 33:729–736
Mack JJ, Mosqueiro TS, Archer BJ, Jones WM, Sunshine H, Faas GC, Briot A, Aragon RL, Su T, Romay MC et al (2017) NOTCH1 is a mechanosensor in adult arteries. Nat Commun 8:1620
Fang JS, Coon BG, Gillis N, Chen Z, Qiu J, Chittenden TW, Burt JM, Schwartz MA, Hirschi KK (2017) Shear-induced Notch-Cx37-p27 axis arrests endothelial cell cycle to enable arterial specification. Nat Commun 8:2149
Gerhardt H, Golding M, Fruttiger M, Ruhrberg C, Lundkvist A, Abramsson A, Jeltsch M, Mitchell C, Alitalo K, Shima D et al (2003) VEGF guides angiogenic sprouting utilizing endothelial tip cell filopodia. J Cell Biol 161:1163–1177
Lohela M, Bry M, Tammela T, Alitalo K (2009) VEGFs and receptors involved in angiogenesis versus lymphangiogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:154–165
Phng LK, Gerhardt H (2009) Angiogenesis: a team effort coordinated by notch. Dev Cell 16:196–208
Eilken HM, Adams RH (2010) Dynamics of endothelial cell behavior in sprouting angiogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22:617–625
Potente M, Carmeliet P (2017) The link between angiogenesis and endothelial metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol 79:43–66
Pitulescu ME, Schmidt I, Benedito R, Adams RH (2010) Inducible gene targeting in the neonatal vasculature and analysis of retinal angiogenesis in mice. Nat Protoc 5:1518–1534
Benedito R, Hellström M (2013) Notch as a hub for signaling in angiogenesis. Exp Cell Res 319(9):1281–1288
Tammela T, Zarkada G, Nurmi H, Jakobsson L, Heinolainen K, Tvorogov D, Zheng W, Franco CA, Murtomaki A, Aranda E et al (2011) VEGFR-3 controls tip to stalk conversion at vessel fusion sites by reinforcing Notch signalling. Nat Cell Biol 13:1202–1213
Siekmann AF, Lawson ND (2007) Notch signalling limits angiogenic cell behaviour in developing zebrafish arteries. Nature 445:781–784
Shin M, Beane TJ, Quillien A, Male I, Zhu LJ, Lawson ND (2016) Vegfa signals through ERK to promote angiogenesis, but not artery differentiation. Development 143:3796–3805
del Toro R, Prahst C, Mathivet T, Siegfried G, Kaminker JS, Larrivee B, Breant C, Duarte A, Takakura N, Fukamizu A et al (2010) Identification and functional analysis. Blood 116:4025–4033
Ehling M, Adams S, Benedito R, Adams RH (2013) Notch controls retinal blood vessel maturation and quiescence. Development 140:3051–3061
Lim R, Sugino T, Nolte H, Andrade J, Zimmermann B, Shi C, Doddaballapur A, Ong YT, Wilhelm K, Fasse J, Ernst A, Kaulich M, Husnjak K, Boettger T, Guenther S, Braun T, Krüger M, Benedito R, Dikic I, Potente M (2019) Deubiquitinase USP10 regulates Notch signaling in the endothelium. Science 364(6436):188–193
Arima S, Nishiyama K, Ko T, Arima Y, Hakozaki Y, Sugihara K, Koseki H, Uchijima Y, Kurihara Y, Kurihara H (2011) Angiogenic morphogenesis driven by dynamic and heterogeneous collective endothelial cell movement. Development 138:4763–4776
Jakobsson L, Franco CA, Bentley K, Collins RT, Ponsioen B, Aspalter IM, Rosewell I, Busse M, Thurston G, Medvinsky A et al (2010) Endothelial cells dynamically compete for the tip cell position during angiogenic sprouting. Nat Cell Biol 12:943–953
Kageyama R, Niwa Y, Shimojo H, Kobayashi T, Ohtsuka T (2010) Ultradian oscillations in Notch signaling regulate dynamic biological events. Notch signaling. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 311–331
Aspalter IM, Gordon E, Dubrac A, Ragab A, Narloch J, Vizan P, Geudens I, Collins RT, Franco CA, Abrahams CL et al (2015) Alk1 and Alk5 inhibition by Nrp1 controls vascular sprouting downstream of Notch. Nat Commun 6:7264
Mouillesseaux KP, Wiley DS, Saunders LM, Wylie LA, Kushner EJ, Chong DC, Citrin KM, Barber AT, Park Y, Kim JD et al (2016) Notch regulates BMP responsiveness and lateral branching in vessel networks via SMAD6. Nat Commun 7:13247
Moya IM, Umans L, Maas E, Pereira PN, Beets K, Francis A, Sents W, Robertson EJ, Mummery CL, Huylebroeck D, Zwijsen A (2012) Stalk cell phenotype depends on integration of Notch and Smad1/5 signaling cascades. Dev cell 22(3):501–514
Bentley K, Franco CA, Philippides A, Blanco R, Dierkes M, Gebala V, Stanchi F, Jones M, Aspalter IM, Cagna G et al (2014) The role of differential VE-cadherin dynamics in cell rearrangement during angiogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 16:309–321
Franco CA, Jones ML, Bernabeu MO, Geudens I, Mathivet T, Rosa A, Lopes FM, Lima AP, Ragab A, Collins RT et al (2015) Dynamic endothelial cell rearrangements drive developmental vessel regression. PLoS Biol 13:e1002125
Panin VM, Papayannopoulos V, Wilson R, Irvine KD (1997) Fringe modulates Notch-ligand interactions. Nature 387(6636):908–912
Yang LT, Nichols JT, Yao C, Manilay JO, Robey EA, Weinmaster G (2005) Fringe glycosyltransferases differentially modulate Notch1 proteolysis induced by Delta1 and Jagged1. Mol Biol Cell 16:927–942
Williams CK, Li JL, Murga M, Harris AL, Tosato G (2006) Up-regulation of the Notch ligand Delta-like 4 inhibits VEGF-induced endothelial cell function. Blood 107(3):931–939
Harrington LS, Sainson RC, Williams CK, Taylor JM, Shi W, Li JL, Harris AL (2008) Regulation of multiple angiogenic pathways by Dll4 and Notch in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Microvasc Res 75(2):144–154
Hogan BM, Herpers R, Witte M, Helotera H, Alitalo K, Duckers HJ, Schulte-Merker S (2009) Vegfc/Flt4 signalling is suppressed by Dll4 in developing zebrafish intersegmental arteries. Development 136:4001–4009
Sanganalmath SK, Bolli R (2013) Cell therapy for heart failure: a comprehensive overview of experimental and clinical studies, current challenges, and future directions. Circ Res 113:810–834
Taimeh Z, Loughran J, Birks EJ, Bolli R (2013) Vascular endothelial growth factor in heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol 10:519–530
Potente M, Mäkinen T (2017) Vascular heterogeneity and specialization in development and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 18(8):477–494
Armulik A, Abramsson A, Betsholtz C (2005) Endothelial/pericyte interactions. Circ Res 97:512–523
Gaengel K, Genove G, Armulik A, Betsholtz C (2009) Endothelial-mural cell signaling in vascular development and angiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 29:630–638
Cuervo H, Nielsen CM, Simonetto DA, Ferrell L, Shah VH, Wang RA (2016) Endothelial notch signaling is essential to prevent hepatic vascular malformations in mice. Hepatology 64:1302–1316
Dill MT, Rothweiler S, Djonov V, Hlushchuk R, Tornillo L, Terracciano L, Meili-Butz S, Radtke F, Heim MH, Semela D (2012) Disruption of Notch1 induces vascular remodeling, intussusceptive angiogenesis, and angiosarcomas in livers of mice. Gastroenterology 142:967–977
Dou GR, Wang YC, Hu XB, Hou LH, Wang CM, Xu JF, Wang YS, Liang YM, Yao LB, Yang AG et al (2008) RBP-J, the transcription factor downstream of Notch receptors, is essential for the maintenance of vascular homeostasis in adult mice. FASEB J 22:1606–1617
Yan M, Callahan CA, Beyer JC, Allamneni KP, Zhang G, Ridgway JB, Niessen K, Plowman GD (2010) Chronic DLL4 blockade induces vascular neoplasms. Nature 463:E6-7
Couch JA, Zhang G, Beyer JC, de Zafra CL, Gupta P, Kamath AV, Lewin-Koh N, Tarrant J, Allamneni KP, Cain G et al (2016) Balancing efficacy and safety of an anti-DLL4 antibody through pharmacokinetic modulation. Clin Cancer Res 22:1469–1479
Noseda M, Chang L, McLean G, Grim JE, Clurman BE, Smith LL, Karsan A (2004) Notch activation induces endothelial cell cycle arrest and participates in contact inhibition: role of p21Cip1 repression. Mol Cell Biol 24:8813–8822
Rostama B, Turner JE, Seavey GT, Norton CR, Gridley T, Vary CP, Liaw L (2015) DLL4/Notch1 and BMP9 interdependent signaling induces human endothelial cell quiescence via P27KIP1 and thrombospondin-1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 35:2626–2637
Serra H, Chivite I, Angulo-Urarte A, Soler A, Sutherland JD, Arruabarrena-Aristorena A, Ragab A, Lim R, Malumbres M, Fruttiger M et al (2015) PTEN mediates Notch-dependent stalk cell arrest in angiogenesis. Nat Commun 6:7935
Sundlisaeter E, Edelmann RJ, Hol J, Sponheim J, Kuchler AM, Weiss M, Udalova IA, Midwood KS, Kasprzycka M, Haraldsen G (2012) The alarmin IL-33 is a notch target in quiescent endothelial cells. Am J Pathol 181:1099–1111
Polacheck WJ, Kutys ML, Yang J, Eyckmans J, Wu Y, Vasavada H, Hirschi KK, Chen CS (2017) A non-canonical Notch complex regulates adherens junctions and vascular barrier function. Nature 552(7684):258–262
Limbourg A, Ploom M, Elligsen D, Sörensen I, Ziegelhoeffer T, Gossler A, Drexler H, Limbourg FP (2007) Notch ligand Delta-like 1 is essential for postnatal arteriogenesis. Circ Res 100(3):363–371
Takeshita K, Satoh M, Ii M, Silver M, Limbourg FP, Mukai Y, Rikitake Y, Radtke F, Gridley T, Losordo DW, Liao JK (2007) Critical role of endothelial Notch1 signaling in postnatal angiogenesis. Circ Res 100(1):70–78
Cristofaro B, Shi Y, Faria M, Suchting S, Leroyer AS, Trindade A, Duarte A, Zovein AC, Iruela-Arispe ML, Nih LR et al (2013) Dll4-Notch signaling determines the formation of native arterial collateral networks and arterial function in mouse ischemia models. Development 140:1720–1729
Nus M, Martinez-Poveda B, MacGrogan D, Chevre R, D’Amato G, Sbroggio M, Rodriguez C, Martinez-Gonzalez J, Andres V, Hidalgo A et al (2016) Endothelial Jag1-RBPJ signalling promotes inflammatory leucocyte recruitment and atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res 112:568–580
Rafii S, Butler JM, Ding BS (2016) Angiocrine functions of organ-specific endothelial cells. Nature 529:316–325
Crivellato E, Nico B, Ribatti D (2007) Contribution of endothelial cells to organogenesis: a modern reappraisal of an old Aristotelian concept. J Anat 211(4):415–427
Matsumoto K, Yoshitomi H, Rossant J, Zaret KS (2001) Liver organogenesis promoted by endothelial cells prior to vascular function. Science 294(5542):559–563
Guo P, Poulos MG, Palikuqi B, Badwe CR, Lis R, Kunar B, Ding BS, Rabbany SY, Shido K, Butler JM, Rafii S (2017) Endothelial Jagged-2 sustains hematopoietic stem and progenitor reconstitution after myelosuppression. J Clin Investig 127(12):4242–4256
Poulos MG, Guo P, Kofler NM, Pinho S, Gutkin MC, Tikhonova A, Aifantis I, Frenette PS, Kitajewski J, Rafii S, Butler JM (2013) Endothelial Jagged-1 is necessary for homeostatic and regenerative hematopoiesis. Cell Rep 4(5):1022–1034
Gamrekelashvili J, Giagnorio R, Jussofie J, Soehnlein O, Duchene J, Briseño CG, Ramasamy SK, Krishnasamy K, Limbourg A, Kapanadze T, Ishifune C, Hinkel R, Radtke F, Strobl LJ, Zimber-Strobl U, Napp LC, Bauersachs J, Haller H, Yasutomo K, Kupatt C, Limbourg FP (2016) Regulation of monocyte cell fate by blood vessels mediated by Notch signalling. Nat Commun 7:12597
Krishnasamy K, Limbourg A, Kapanadze T, Gamrekelashvili J, Beger C, Häger C, Lozanovski VJ, Falk CS, Napp LC, Bauersachs J, Mack M, Haller H, Weber C, Adams RH, Limbourg FP (2017) Blood vessel control of macrophage maturation promotes arteriogenesis in ischemia. Nat Commun 8(1):952
Ramasamy SK, Kusumbe AP, Wang L, Adams RH (2014) Endothelial Notch activity promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone. Nature 507(7492):376–380
Duan JL, Ruan B, Yan XC, Liang L, Song P, Yang ZY, Liu Y, Dou KF, Han H, Wang L (2018) Endothelial Notch activation reshapes the angiocrine of sinusoidal endothelia to aggravate liver fibrosis and blunt regeneration in mice. Hepatology 68:677–690
Hilscher MB, Sehrawat T, Arab JP, Zeng Z, Gao J, Liu M, Kostallari E, Gao Y, Simonetto DA, Yaqoob U, Cao S, Revzin A, Beyder A, Wang RA, Kamath PS, Kubes P, Shah VH (2019) Mechanical stretch increases expression of CXCL1 in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells to recruit neutrophils, generate sinusoidal microthombi, and promote portal hypertension. Gastroenterology 157(1):193-209.e9
Kivelä R, Hemanthakumar KA, Vaparanta K, Robciuc M, Izumiya Y, Kidoya H, Takakura N, Peng X, Sawyer DB, Elenius K, Walsh K, Alitalo K (2019) Endothelial cells regulate physiological cardiomyocyte growth via VEGFR2-mediated paracrine signaling. Circulation 139(22):2570–2584
Cao Z, Lis R, Ginsberg M, Chavez D, Shido K, Rabbany SY, Fong GH, Sakmar TP, Rafii S, Ding BS (2016) Targeting of the pulmonary capillary vascular niche promotes lung alveolar repair and ameliorates fibrosis. Nat Med 22(2):154–162
Dobie R, Wilson-Kanamori JR, Henderson BEP, Smith JR, Matchett KP, Portman JR, Wallenborg K, Picelli S, Zagorska A, Pendem SV et al (2019) Single-cell transcriptomics uncovers zonation of function in the mesenchyme during liver fibrosis. Cell Rep 29:1832–2184
Goveia J, Rohlenova K, Taverna F, Treps L, Conradi LC, Pircher A, Geldhof V, de Rooij L, Kalucka J, Sokol L et al (2020) An integrated gene expression landscape profiling approach to identify lung tumor endothelial cell heterogeneity and angiogenic candidates. Cancer Cell 37:21–36
Guo M, Du Y, Gokey JJ, Ray S, Bell SM, Adam M, Sudha P, Perl AK, Deshmukh H, Potter SS et al (2019) Single cell RNA analysis identifies cellular heterogeneity and adaptive responses of the lung at birth. Nat Commun 10:37
Kalucka J, de Rooij L, Goveia J, Rohlenova K, Dumas SJ, Meta E, Conchinha NV, Taverna F, Teuwen LA, Veys K et al (2020) Single-cell transcriptome atlas of murine endothelial cells. Cell 180:764–779
Karaiskos N, Rahmatollahi M, Boltengagen A, Liu H, Hoehne M, Rinschen M, Schermer B, Benzing T, Rajewsky N, Kocks C et al (2018) A Single-cell transcriptome atlas of the mouse glomerulus. J Am Soc Nephrol 29:2060–2068
Khan S, Taverna F, Rohlenova K, Treps L, Geldhof V, de Rooij L, Sokol L, Pircher A, Conradi LC, Kalucka J et al (2019) EndoDB: a database of endothelial cell transcriptomics data. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D736–D744
Menon R, Otto EA, Hoover P, Eddy S, Mariani L, Godfrey B, Berthier CC, Eichinger F, Subramanian L, Harder J et al (2020) Single cell transcriptomics identifies focal segmental glomerulosclerosis remission endothelial biomarker. JCI Insight. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.133267
Ramachandran P, Dobie R, Wilson-Kanamori JR, Dora EF, Henderson BEP, Luu NT, Portman JR, Matchett KP, Brice M, Marwick JA et al (2019) Resolving the fibrotic niche of human liver cirrhosis at single-cell level. Nature 575:512–518
Tikhonova AN, Dolgalev I, Hu H, Sivaraj KK, Hoxha E, Cuesta-Dominguez A, Pinho S, Akhmetzyanova I, Gao J, Witkowski M et al (2019) The bone marrow microenvironment at single-cell resolution. Nature 569:222–228
Vanlandewijck M, He L, Mae MA, Andrae J, Ando K, Del Gaudio F, Nahar K, Lebouvier T, Lavina B, Gouveia L et al (2018) A molecular atlas of cell types and zonation in the brain vasculature. Nature 554:475–480
Halpern KB, Shenhav R, Matcovitch-Natan O, Toth B, Lemze D, Golan M, Massasa EE, Baydatch S, Landen S, Moor AE et al (2017) Single-cell spatial reconstruction reveals global division of labour in the mammalian liver. Nature 542:352–356
Acknowledgments
Work in Rui Benedito laboratory was supported by the Ministerio de Ciencia y Innovación (SAF2017-89299-P) and European Research Council (ERC-2020-COG n° 101001814). Macarena Fernandez-Chacon was supported by a PhD fellowship from Fundación La Caixa (CX_E-2015-01), Irene Garcia-Gonzalez was supported by La Caixa Severo Ochoa (CX-SO-16-1) and Severin Mühleder was funded by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) project J4358. The CNIC is currently supported by MCIN and the Pro CNIC Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MF-C, SM, IG-G and RB performed literature search and gave critical input. MF-C designed the figures. MF-C and RB wrote most of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández-Chacón, M., García-González, I., Mühleder, S. et al. Role of Notch in endothelial biology. Angiogenesis 24, 237–250 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-021-09793-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-021-09793-7