Abstract
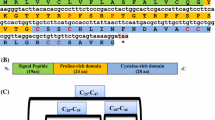
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are an important element of the innate immune system of all living organisms and serve as a barrier that safeguards the organisms against a wide range of pathogens. Fishes are proven to be a prospective source of AMPs, and β-defensins form an important family of AMPs with potent antimicrobial, chemotactic and immunomodulatory activities. The present study reports a β-defensin AMP sequence (Lc-BD) from the Asian sea bass, Lates calcarifer, a commercially important fish species in tropical and subtropical regions of Asia and the Pacific. A 202-bp cDNA fragment with an open reading frame encoding 63 amino acids (aa) was obtained from the mRNA of gill tissue by RT-PCR. The deduced aa sequence of Lc-BD possessed a signal and a mature peptide region with 20 and 43 aa residues, respectively. Lc-BD was characterized at the molecular level, and a molecular weight of 5.24 kDa and a net charge of +4.5 was predicted for the mature peptide. The molecular characterization of Lc-BD revealed the presence of three intramolecular disulphide bonds involving the six conserved cysteine residues in the sequence, and the phylogenetic analysis of Lc-BD showed a close relationship with β-defensins from fishes like Siniperca chuatsi, Argyrosomus regius, Trachinotus ovatus and Oplegnathus fasciatus.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Pushpanathan M, Gunasekaran P, Rajendhran J (2013) Antimicrobial peptides: versatile biological properties. Int J Pept 2013:675391. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/675391
Giuliani A, Pirri G, Nicoletto S (2007) Antimicrobial peptides: an overview of a promising class of therapeutics. Open Life Sci 2:1–33. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11535-007-0010-5
Bahar A, Ren D (2013) Antimicrobial peptides. Pharmaceuticals 6:1543–1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph6121543
Bechinger B, Gorr SU (2017) Antimicrobial peptides: mechanisms of action and resistance. J Dent Res 96:254–260. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034516679973
Rajanbabu V, Chen JY (2011) Applications of antimicrobial peptides from fish and perspectives for the future. Peptides 32:415–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2010.11.005
Mahlapuu M, Håkansson J, Ringstad L, Björn C (2016) Antimicrobial peptides: an emerging category of therapeutic agents. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 6:194. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2016.00194
Neshani A, Zare H, Eidgahi MRA, Khaledi A, Ghazvini K (2019) Epinecidin-1, a highly potent marine antimicrobial peptide with anticancer and immunomodulatory activities. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 20:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40360-019-0309-7
Haney EF, Mansour SC, Hancock RE (2017) Antimicrobial peptides: an introduction. In: Hansen P. (ed) Antimicrobial Peptides. Methods Mol Biol 1548. Humana Press, New York, pp 3-22. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6737-7_1
Chaturvedi P, Dhanik M, Pande A (2015) Molecular characterization and in silico analysis of defensin from Tor putitora (Hamilton). Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 7:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-015-9197-3
Seo MD, Won HS, Kim JH, Mishig-Ochir T, Lee BJ (2012) Antimicrobial peptides for therapeutic applications: a review. Molecules 17:12276–12286. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171012276
Shabir U, Ali S, Magray AR, Ganai BA, Firdous P, Hassan T, Nazir R (2018) Fish antimicrobial peptides (AMP’s) as essential and promising molecular therapeutic agents: a review. Microb Pathog 114:50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2017.11.039
Valero Y, Chaves-Pozo E, Meseguer J, Esteban MA, Cuesta A (2013) Biological role of fish antimicrobial peptides. In: Hak YI (ed) Seong MD. Antimicrobial Peptides, Nova Science Publishers, pp 31–60
Ganz T (2011) Hepcidin and iron regulation, 10 years later. Blood 117:4425–4433. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-01-258467
Lauth X, Shike H, Burns JC, Westerman ME, Ostland VE, Carlberg JM, Van Olst JC, Nizet V, Taylor SW, Shimizu C, Bulet P (2002) Discovery and characterization of two isoforms of moronecidin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from hybrid striped bass. J Biol Chem 277:5030–5039. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109173200
Jiang H, Hu Y, Wei X, Xiao X, Jakovlić I, Liu X, Su J, Yuan G (2018) Chemotactic effect of β-defensin 1 on macrophages in Megalobrama amblycephala. Fish Shellfish Immunol 74:35–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.12.016
Zhou Y, Lei Y, Cao Z, Chen X, Sun Y, Xu Y, Guo W, Wang S, Liu C (2019) A β-defensin gene of Trachinotus ovatus might be involved in the antimicrobial and antiviral immune response. Dev Comp Immunol 92:105–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2018.11.011
Cuesta A, Meseguer J, Esteban MÁ (2011) Molecular and functional characterization of the gilthead seabream β-defensin demonstrate its chemotactic and antimicrobial activity. Mol Immunol 48:1432–1438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2011.03.022
Seebah S, Suresh A, Zhuo S, Choong YH, Chua H, Chuon D, Beuerman R, Verma C (2007) Defensins knowledgebase: a manually curated database and information source focused on the defensins family of antimicrobial peptides. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D265–D268. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl866
Wu Q, Patočka J, Kuča K (2018) Insect antimicrobial peptides, a mini-review. Toxins 10:461. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10110461
Zou J, Mercier C, Koussounadis A, Secombes C (2007) Discovery of multiple beta-defensin-like homologues in teleost fish. Mol Immunol 44:638–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2006.01.012
Zhu S (2008) Discovery of six families of fungal defensin-like peptides provides insights into origin and evolution of the CSαβ defensins. Mol Immunol 45:828–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2007.06.354
Diaz GA (2010) Defensins and cystein rich peptides: two types of antimicrobial peptides in marine molluscs. Invert Surviv J 7:157–164
Schneider JJ, Unholzer A, Schaller M, Schäfer-Korting M, Korting HC (2005) Human defensins. J Mol Med 83:587–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-005-0657-1
Falco A, Chico V, Marroqui L, Perez L, Coll JM, Estepa A (2008) Expression and antiviral activity of a β-defensin-like peptide identified in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) EST sequences. Mol Immunol 45:757–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2007.06.358
Jin JY, Zhou L, Wang Y, Li Z, Zhao JG, Zhang QY, Gui JF (2010) Antibacterial and antiviral roles of a fish β-defensin expressed both in pituitary and testis. PLoS One 5:e12883. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0012883
Casadei E, Wang T, Zou J, Vecino JLG, Wadsworth S, Secombes CJ (2009) Characterization of three novel β-defensin antimicrobial peptides in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Mol Immunol 46:3358–3366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2009.07.018
Zhao JG, Zhou L, Jin JY, Zhao Z, Lan J, Zhang YB, Zhang QY, Gui JF (2009) Antimicrobial activity-specific to Gram-negative bacteria and immune modulation-mediated NF-κB and Sp1 of a medaka β-defensin. Dev Comp Immunol 33:624–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2008.11.006
Nam BH, Moon JY, Kim YO, Kong HJ, Kim WJ, Lee SJ, Kim KK (2010) Multiple β-defensin isoforms identified in early developmental stages of the teleost Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 28:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2009.11.004
Wang G, Li J, Zou P, Xie H, Huang B, Nie P, Chang M (2012) Expression pattern, promoter activity and bactericidal property of β-defensin from the mandarin fish Siniperca chuatsi. Fish Shellfish Immunol 33:522–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2012.06.003
van der Marel M, Adamek M, Gonzalez SF, Frost P, Rombout JH, Wiegertjes GF, Savelkoul HF, Steinhagen D (2012) Molecular cloning and expression of two β-defensin and two mucin genes in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) and their up-regulation after β-glucan feeding. Fish Shellfish Immunol 32:494–501. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2014.885830
Ruangsri J, Kitani Y, Kiron V, Lokesh J, Brinchmann MF, Karlsen BO, Fernandes JM (2013) A novel beta-defensin antimicrobial peptide in Atlantic cod with stimulatory effect on phagocytic activity. PLoS One 8:e62302. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0062302
Chen Y, Zhao H, Zhang X, Luo H, Xue X, Li Z, Yao B (2013) Identification, expression and bioactivity of Paramisgurnus dabryanus β-defensin that might be involved in immune defense against bacterial infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol 35:399–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2013.04.049
Liang T, Wang DD, Zhang GR, Wei KJ, Wang WM, Zou GW (2013) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of two β-defensin genes in the blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 166:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpb.2013.07.006
Dong JJ, Wu F, Ye X, Sun CF, Tian YY, Lu MX, Chen ZH (2015) β-Defensin in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): sequence, tissue expression, and anti-bacterial activity of synthetic peptides. Gene 566:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.04.025
Zhu J, Wang H, Wang J, Wang X, Peng S, Geng Y, Wang K, Ouyang P, Li Z, Huang X, Chen D (2017) Identification and characterization of a β-defensin gene involved in the immune defense response of channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus. Mol Immunol 85:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2017.03.009
Yang K, Hou B, Ren F, Zhou H, Zhao T (2019) Characterization of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) beta-defensin 1: implications for its role in inflammation control. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 83:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2018.1519386
Ganz T, Lehrer RI (1994) Defensins. Curr Opin Immunol 6:584–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/0952-7915(94)90145-7
Anooja VV, Anju MV, Athira PP, Archana K, Radhakrishnan CK, Philip R (2020) Structural, functional and phylogenetic analysis of a beta defensin gene from the Whipfin silverbiddy, Gerres filamentosus (Cuvier, 1829). Gene Reports 21:100805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genrep.2020.100805
Barnes AC, Trewin B, Snape N, Kvennefors ECE, Baiano JC (2011) Two hepcidin-like antimicrobial peptides in Barramundi Lates calcarifer exhibit differing tissue tropism and are induced in response to lipopolysaccharide. Fish Shellfish Immunol 31:350–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2011.05.027
Taheri B, Mohammadi M, Nabipour I, Momenzadeh N, Roozbehani M (2018) Identification of novel antimicrobial peptide from Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer) by in silico and activity characterization. PloS One 13:e0206578. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0206578
Katzenback B (2015) Antimicrobial peptides as mediators of innate immunity in teleosts. Biology 4:607–639. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4040607
Ganz T (2004) Hepcidin in iron metabolism. Curr Opin Hematol 11:251–254. https://doi.org/10.1097/00062752-200407000-00004
Peng K, Wang JH, Sheng JQ, Zeng LG, Hong YJ (2012) Molecular characterization and immune analysis of a defensin from freshwater pearl mussel, Hyriopsis schlegelii. Aquaculture 334:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2011.12.039
Bauer F, Schweimer K, Klüver E, Conejo-Garcia JR, Forssmann WG, Rösch P, Andermann K, Sticht H (2001) Structure determination of human and murine β-defensins reveals structural conservation in the absence of significant sequence similarity. Protein Sci 10:2470–2479. https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.24401
Islam MM, Kobayashi K, Kidokoro SI, Kuroda Y (2019) Hydrophobic surface residues can stabilize a protein through improved water–protein interactions. FEBS J 286:4122–4134. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14941
Chen Y, Guarnieri MT, Vasil AI, Vasil ML, Mant CT, Hodges RS (2007) Role of peptide hydrophobicity in the mechanism of action of α-helical antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:1398–1406. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00925-06
Wang G, Mishra B (2012) The importance of amino acid composition in natural AMPs: an evolutional, structural, and functional perspective. Front Immunol 3:221. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00221
Ventura S (2005) Sequence determinants of protein aggregation: tools to increase protein solubility. Microb Cell Fact 4:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/2F1475-2859-4-11
Conchillo-Solé O, de Groot NS, Avilés FX, Vendrell J, Daura X, Ventura S (2007) AGGRESCAN: a server for the prediction and evaluation of “hot spots” of aggregation in polypeptides. BMC Bioinf 8:65. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-8-65
Torrent M, Andreu D, Nogués VM, Boix E (2011) Connecting peptide physicochemical and antimicrobial properties by a rational prediction model. PLoS One 6:e16968. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016968
Semple F, Dorin JR (2012) β-Defensins: multifunctional modulators of infection, inflammation and more? J Innate Immun 4:337–348. https://doi.org/10.1159/000336619
Hanaoka Y, Yamaguchi Y, Yamamoto H, Ishii M et al (2016) In vitro and In vivo anticancer activity of human β-defensin-3 and its mouse homolog. Anticancer Res 36:5999–6004. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.11188
Guo M, Wei J, Huang X, Huang Y, Qin Q (2012) Antiviral effects of β-defensin derived from orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Fish Shellfish Immunol 32:828–838. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2012.02.005
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Cochin University of Science and Technology for the research grant (No. PL.(UGC)1/SPG/SMNRI/2017-18) and facilities provided and all the persons for their assistance and valuable contributions.
Funding
The study was funded by the Cochin University of Science and Technology (Research Grant No.PL.(UGC)1/SPG/SMNRI/2017-18).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Athira Raveendran: Investigation, writing the original draft. Dhanya Lenin K. L.: Investigation, writing. Anju M.V, Neelima S., Anooja V.V, Athira P. P., Archana K.: Investigation. Rosamma Philip and Swapna P. Antony: Supervision, review, and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Research Involving Human and Animal Participants
The care and treatment of animals used in this study were in accordance with the guidelines of the CPCSEA [(Committee for the Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals), Ministry of Environment and Forests (Animal Welfare Division), Govt of India] on care and use of animals in scientific research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raveendran, A., L., D.L.K., M.V., A. et al. β-Defensin from the Asian Sea Bass, Lates calcarifer: Molecular Prediction and Phylogenetic Analysis. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 13, 1798–1807 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09804-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09804-5