Abstract
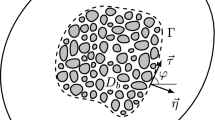
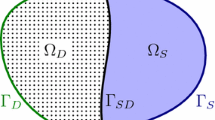
A modified formulation of the interfacial boundary condition for the coupling of the Stokes and Darcy models describing the incompressible fluid flow in the free space and porous medium domains is proposed using the dimension analysis procedure. The case is considered for the porous media formed by circular or square cylinders located in the centers of rectangular cells. The vorticity is derived as a linear combination of the tangential velocity components in the free space and porous medium. The proposed condition is potentially directly applicable for a class of 2D problems with an arbitrary shaped boundary for the boundary element method. The fluid flow problems are solved numerically using the Stokes flow model and analytically for the Stokes–Darcy flow model to determine the coefficients in the introduced linear dependence for the vorticity. As a result, the corresponding coefficients in the boundary condition are found as a porosity function for two types of the porous medium configuration. The approximate analytical estimation of the coefficients confirms the numerical dependencies. The verifications of the found coefficients were made by solving two 2D fluid flow problems. It is shown that the fluid flow calculated on the basis of the Stokes–Darcy flow model with modified boundary condition agrees well with the results of the microscopic Stokes flow model. The advantages of the proposed boundary condition are discussed.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, P.M.: Porous Media: Geometry and Transports (Butterworth-Heinemann Series in Chemical Engineering). Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/C2009-0-26183-6
Allaire, G.: One-Phase Newtonian Flow, pp. 45–76. Springer, New York (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-1920-0
Auriault, J.L.: About the Beavers and Joseph boundary condition. Transp. Porous Media 83(2), 257–266 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-009-9435-9
Barenblatt, G.I.: Scaling, Self-similarity, and Intermediate Asymptotics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1996). https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107050242
Bear, J.: Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media. Dover, New York (1988)
Beavers, G.S., Joseph, D.D.: Boundary conditions at a naturally permeable wall. J. Fluid Mech. 30, 197–207 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112067001375
Brinkman, H.C.: A calculation of the viscous force exerted by a flowing fluid on a dense swarm of particles. Appl. Sci. Res. A 1(1), 27–34 (1947)
Chandesris, M., Jamet, D.: Boundary conditions at a fluid-porous interface: an a priori estimation of the stress jump coefficients. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50(17), 3422–3436 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2007.01.053
Chandesris, M., Jamet, D.: Jump conditions and surface-excess quantities at a fluid/porous interface: a multi-scale approach. Transp. Porous Media 78, 419–438 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-008-9302-0
Chen, H., Wang, X.P.: A one-domain approach for modeling and simulation of free fluid over a porous medium. J. Comput. Phys. 259(C), 650–671 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2013.12.008
Chen, J.T., Hsiao, C.C., Leu, S.Y.: A new method for Stokes problems with circular boundaries using degenerate kernel and Fourier series. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 74(13), 1955–1987 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.2240
Cieszko, M., Kubik, J.: Derivation of matching conditions at the contact surface between fluid-saturated porous solid and bulk fluid. Transp. Porous Media 34, 319–336 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006590215455
Dullien, F.: Porous Media: Fluid Transport and Pore Structure. Academic Press, Cambridge (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/C2009-0-26184-8
Dunnett, S., Clement, C.: A numerical model of fibrous filters containing deposit. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 33(5), 601–610 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2008.10.010
Dunnett, S., Clement, C.: Numerical investigation into the loading behaviour of filters operating in the diffusional and interception deposition regimes. J. Aerosol Sci. 53, 85–99 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2012.06.008
Forchheimer, P.: Wasserbewegung durch boden. Zeitschrift des Vereins deutscher Ingenieure 45, 1782–1788 (1901)
Happel, J., Brenner, H.: Low Reynolds Number Hydrodynamics: With Special Applications to Particulate Media. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1965)
Hou, Y., Qin, Y.: On the solution of coupled Stokes/Darcy model with Beavers–Joseph interface condition. Comput. Math. Appl. 77(1), 50–65 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.camwa.2018.09.011
Jäger, W., Mikelić, A.: Modeling effective interface laws for transport phenomena between an unconfined fluid and a porous medium using homogenization. Transp. Porous Media 78, 489–508 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-009-9354-9
James, D.F., Davis, A.M.J.: Flow at the interface of a model fibrous porous medium. J. Fluid Mech. 426, 47–72 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112000002160
Kuwabara, S.: The forces experienced by randomly distributed parallel circular cylinders or spheres in a viscous flow at small Reynolds numbers. J. Phys. Soc. Japan 14(4), 527–532 (1959)
Layton, W., Schieweck, F., Yotov, I.: Coupling fluid flow with porous media flow. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 40(6), 2195–2218 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1137/S0036142901392766
Mardanov, R., Dunnett, S., Zaripov, S.: Modeling of fluid flow in periodic cell with porous cylinder using a boundary element method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 68, 54–62 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2016.03.015
Mardanov, R., Zaripov, S., Maklakov, D.: Two-dimensional Stokes flows in porous medium composed of a large number of circular inclusions. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 113, 204–218 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2019.12.010
Mosina, E.V., Chernyshev, I.V.: Slip condition on the surface of a model fibrous porous medium. Tech. Phys. Lett. 35(3), 245–248 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063785009030158
Neale, G., Nader, W.: Practical significance of Brinkman’s extension of Darcy’s law: coupled parallel flows within a channel and a bounding porous medium. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 52(4), 475–478 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.5450520407
Nield, D., Bejan, A.: One-Phase Newtonian Flow, 3rd edn. Springer, New York (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-33431-9
Nield, D.A.: The Beavers–Joseph boundary condition and related matters: a historical and critical note. Transp. Porous Media 78(3), 537 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-009-9344-y
Ochoa-Tapia, J., Whitaker, S.: Momentum transfer at the boundary between a porous medium and a homogeneous fluid—I. Theoretical development. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 38(14), 2635–2646 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0017-9310(94)00346-W
Ochoa-Tapia, J., Whitaker, S.: Momentum transfer at the boundary between a porous medium and a homogeneous fluid—II. Comparison with experiment. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 38(14), 2647–2655 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1016/0017-9310(94)00347-X
Prakash, J., Raja Sekhar, G.P., Kohr, M.: Stokes flow of an assemblage of porous particles: stress jump condition. Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik 62, 1027–1046 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00033-011-0123-6
Saffman, P.G.: On the boundary condition at the surface of a porous medium. Stud. Appl. Math. 50(2), 93–101 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1002/sapm197150293
Sokolnikoff, I.S.: Tensor Analysis, Theory and Applications to Geometry and Mechanics of Continua, p. 361. Wiley, New York (1964)
Vafai, K.: Handbook of Porous Media. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2015)
Vainshtein, P., Shapiro, M., Gutfinger, C.: Creeping flow past and within a permeable spheroid. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 28(12), 1945–1963 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-9322(02)00106-4
Valdes-Parada, F.J., Aguilar-Madera, C.G., Ochoa-Tapia, J.A., Goyeau, B.: Velocity and stress jump conditions between a porous medium and a fluid. Adv. Water Resour. 62, 327–339 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2013.08.008
Whitaker, S.: Flow in porous media I: a theoretical derivation of Darcy’s law. Transp. Porous Media 1(1), 3–25 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01036523
Zaripov, S., Mardanov, R., Sharafutdinov, V.: Determination of Brinkman model parameters using Stokes flow model. Transp. Porous Media 130(2), 529–557 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-019-01324-9
Acknowledgements
The work of Mardanov and Sharafutdinov was carried out as part of the implementation of the development program for the Scientific and Educational Mathematical Center of the Volga Federal District, Project Number 075-02-2020-1478. The work by Zaripov was performed in the frameworks of the Russian Government Program of Competitive Growth at Kazan Federal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Patrick Jenny.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mardanov, R.F., Sharafutdinov, V.F. & Zaripov, S.K. Modified formulation of the interfacial boundary condition for the coupled Stokes–Darcy problem. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 35, 449–476 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00162-021-00568-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00162-021-00568-w