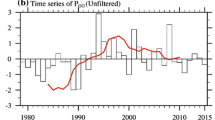
Abstract
The spatiotemporal variability of southwest China (SWC) spring (March–April–May) rainfall (SWCSR) during 1961–2017 is investigated using rainfall data from 75 meteorological stations over SWC in this study. It is found that (1) SWC can be divided into four subregions using the rotated empirical orthogonal function (REOF) method: southern Yunnan province (SY), northwestern Yunnan province (NWY), eastern Guizhou province (EG), and northeastern Sichuan province (NES). (2) All subregions show significant 2–8-year periodicity on the interannual timescale. However, only SY rainfall shows significant interdecadal periodicity. (3) The spring La Niña has a significant impact on the simultaneous rainfall over SY. The sea surface temperature anomalies (SSTAs) in the central North Pacific during late winter can be an important oceanic signal for the prediction of spring rainfall variability over NWY. The southern Indian Ocean dipole (SIOD)–like SSTA pattern during late autumn (early winter) can be an important predictor of rainfall variability over EG (NES) during the following spring. Moreover, the impact of the late autumn SIOD-like pattern on the following spring rainfall over EG is stronger than the impact of the early winter SIOD-like pattern on the NES rainfall during the following spring.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in this study are available from the China Meteorological Data Service Center http://data.cma.cn/data/cdcdetail/dataCode/SURF_CLI_CHN_MUL_MON.html and the Hadley Centre Sea Ice and Sea Surface Temperature data set https://www.metoffice.gov.uk/hadobs/hadisst.
Code availability
All analyses were performed using the NCAR Command Language (Version 6.5.0).
References
Cao J, Yao P, Wang L, Liu K (2014) Summer rainfall variability in low-latitude highlands of China and subtropical Indian Ocean dipole. J Clim 27:880–892
Chen W, Feng J, Wu R (2013) Roles of ENSO and PDO on the link of the East Asian winter monsoon to the following summer monsoon. J Clim 26:622–635
Feng J, Chen W, Tam CY, Zhou W (2011) Different impacts of El Niño and El Niño Modoki on China rainfall in the decaying phases. Int J Climatol 31:2091–2101
Hannachi A, Jolliffe I, Stephenson D (2007) Empirical orthogonal functions and related techniques in atmospheric science: a review. Int J Climatol 27(9):1119–1152
Jiang XW, Li YQ (2011) Spatio-temporal variability of winter temperature and precipitation in Southwest China. J Geogr Sci 21(2):250–262
Li XZ, Zhou W (2012) Quasi-4-yr coupling between El Niño-Southern Oscillation and water vapor transport over East Asia-WNP. J Clim 25:5879–5891
Li CY, Zhou W (2014) Interdecadal change in South China Sea tropical cyclone frequency in association with zonal sea surface temperature gradient. J Clim 27:5468–5480
Li YH, Xu HM, Liu D (2009) Features of the extremely severe drought in the east of Southwest China and anomalies of atmospheric circulation in 2006. Act Meteorol Sin 67(1):122–132 (in Chinese)
Li XZ, Zhou W, Li CY, Song J (2013) Comparison of the annual cycles of moisture supply over southwest and southeast China. J Clim 26:10139–10158
Li XZ, Zhou W, Chen DL, Li CY, Song J (2014) Water vapor transport and moisture budget over Eastern China: remote forcing from the two types of El Niño. J Clim 27:8778–8792
Li G, Chen J, Wang X, Luo X, Yang D, Zhou W, Tan Y, Yan H (2018) Remote impact of North Atlantic sea surface temperature on rainfall in southwestern China during boreal spring. Clim Dyn 50:541–553
Liu XR, Li GP, Fan GZ, Cheng BY, Li HQ (2007a) Spatial and temporal characteristics of precipitation resource in Southwest China during 1961-2000. J Nat Res 22(5):783–792 (in Chinese)
Liu Y, Zhao EX, Peng GF, Yang SQ (2007b) Severe drought in the early summer of 2005 in Yunnan and middle-high latitudes circulation. Arid Meteor 25:32–37
Liu Z, Zhou P, Zhang F, Liu X, Chen G (2013) Spatiotemporal characteristics of dryness/wetness conditions across Qinghai Province, Northwest China. Agric For Meteorol 182-183:101–108
Liu Z, Wang Y, Shao M, Jia X, Li X (2016) Spatiotemporal analysis of multiscalar drought characteristics across the Loess Plateau of China. J Hydrol 534:281–299
Ma ZF, Peng J, Gao WL, Tian H (2006) Climate variations of Southwest China during the last century. Plateau Meteor 25(4):633–642 (in Chinese)
Mao LX, Qian S, Hou YY, Li CS (2007) Study on the meteorologically-driven ecological monitoring and assessment of high temperature and drought of Sichuan-Chongqing area in summer 2006. Meteorol Monogr 33:86–88
North GR, Bell TL, Cahalan RF, Moeng FJ (1982) Sampling errors in the estimation of empirical orthogonal function. Mon Weather Rev 110(7):699–706
Qian TT, Zhao P, Zhang F, Bao X (2015) Rainy-season precipitation over the Sichuan basin and adjacent regions in southwestern China. Mon Weather Rev 143:383–394
Qin J, Ju JH, Xie ME (1997) Weather and climate in low latitudes plateau. China Meteorology Press, Beijing, p 210 (in Chinese)
Rayner NA, Parker DE, Horton EB, Folland CK, Alexander LV, Rowell DP, Kent EC, Kaplan A (2003) Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J Geophys Res 108:4407
Richman MB (1986) Review article, rotation of principal components. J Climatol 6:293–355
Ruiz-Medina MD (2012) New challenges in spatial and spatiotemporal functional statistics for high-dimensional data. Spat Stat 1:82–91
Sun XT, Li QQ, Wang LJ (2017) Characteristics of long-cycle abrupt drought-flood alternations in Southwest China and anomalies of atmospheric circulation in summer. Chin J Atmos Sci 41(6):1332–1342 (in Chinese)
Torrence C, Compo G (1998) A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 79(1):61–78
Wang X, Wang DX, Zhou W, Li CY (2012) Interdecadal modulation of the influence of La Niña events on Mei-yu rainfall over the Yangtze River Valley. Adv Atmos Sci 29:157–168
Wang WW, Zhou W, Wang X, Fong SK, Leung KC (2013) Summer high temperature extremes in southeast China associated with the East Asian jet stream and circumglobal teleconnection. J Geophys Res 118:8306–8319
Wang WW, Zhou W, Chen DL (2014) Summer high temperature extremes in southeast China: Bonding with the El Niño-Southern Oscillation and East Asian summer monsoon coupled system. J Clim 27:4122–4138
White M, Schmidt J, Topping D (2005) Application of wavelet analysis for monitoring the hydrologic effects of dam operation: Glen Canyon Dam and the Colorado River at Lees Ferry, Arizona. River Res Appl 21(5):551–565
Xia Y, Wan XL, Yan XD, Wu L, Long Y (2016) Variations of spring precipitation over southwest China and characteristic circulations for precipitation anomalies. Act Meteorol Sin 74(4):510–524 (in Chinese)
Xu HL, Li JP, Feng J, Mao JY (2012) The asymmetric relationship between the winter NAO and the precipitation in Southwest China. Act Meteorol Sin 70(6):1276–1291 (in Chinese)
Xu DF, Li DL, Wang H (2014) Autumn dry-wet conditions and main types of atmospheric circulation in anomalous years in Southwest China. Chin J Atmos Sci 38(2):373–385 (in Chinese)
Yang YL, Du Y, Chen HS, Zhang YS (2011) Influence of ENSO event on rainfall anomaly over Yunnan province and its neighboring regions during late spring-early summer. Chin J Atmos Sci 35(4):729–738 (in Chinese)
Zhang MQ, Sun JQ (2018) Enhancement of the spring East China precipitation response to tropical sea surface temperature variability. Clim Dyn 51:3009–3021
Zhang Q, Xu C, Zhang Z, Chen Y, Liu C (2009) Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation over China, 1951-2005. Theor Appl Climatol 95(1-2):53–68
Zhang WJ, Jin FF, Zhao JX, Qi L, Ren HL (2013) The possible influence of a nonconventional El Niño on the severe autumn drought of 2009 in Southwest China. J Clim 26(21):8392–8405
Zhang WL, Zhang JY, Fan GZ (2014) Dominant modes of dry- and wet-season precipitation in southwestern China. Chin J Atmos Sci 38(3):590–602 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the China Meteorological Data Service Center and the Met Office Marine Data Bank for providing datasets, and we also thank the anonymous reviewer and Dr. Hartmut Graßl for their valuable comments to improve our manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41675062, 41575097).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The participation of Gang Li and Yue Zhang includes the data collection, analyzing the results, and writing the article, and the participation of Wen Zhou and Hongming Yan includes analyzing the results.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All authors comply with the guidelines of the journal Theoretical and Applied Climatology.
Consent to participate
All authors agreed to participate in this study.
Consent for publication
All authors agreed to the publication of this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Zhou, W., Zhang, Y. et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics of spring rainfall over Southwest China and their relationships with sea surface temperature during 1961–2017. Theor Appl Climatol 145, 775–786 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03648-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-021-03648-3