No CrossRef data available.
Article contents
Most permutations power to a cycle of small prime length
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 24 May 2021
Abstract
We prove that most permutations of degree $n$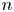 have some power which is a cycle of prime length approximately $\log n$
have some power which is a cycle of prime length approximately $\log n$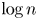 . Explicitly, we show that for $n$
. Explicitly, we show that for $n$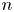 sufficiently large, the proportion of such elements is at least $1-5/\log \log n$
sufficiently large, the proportion of such elements is at least $1-5/\log \log n$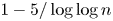 with the prime between $\log n$
with the prime between $\log n$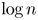 and $(\log n)^{\log \log n}$
and $(\log n)^{\log \log n}$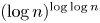 . The proportion of even permutations with this property is at least $1-7/\log \log n$
. The proportion of even permutations with this property is at least $1-7/\log \log n$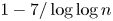 .
.
Keywords
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press on Behalf of The Edinburgh Mathematical Society
References
Bamberg, J., Glasby, S. P., Harper, S. H. and Praeger, C. E., Permutations with orders coprime to a given integer, Electronic J. Combin. 27 (2020), P1.6.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Beals, R., Leedham-Green, C. R., Niemeyer, A. C., Praeger, C. E. and Seress, Á., Permutations with restricted cycle structure and an algorithmic application, Combin. Probab. Comput. 11(5) (2002), 447–464.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Bosma, W., Cannon, J. and Playoust, C., The Magma algebra system. I. The user language, J. Symbolic Comput. 24(3–4) (1997), 235–265. Computational algebra and number theory (London, 1993).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Erdös, P. and Turán, P., On some problems of a statistical group-theory. II, Acta Math. Acad. Sci. Hungar. 18 (1967), 151–163.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Ford, K., Anatomy of integers and random permutations course lecture notes, available at https://faculty.math.illinois.edu/ford/anatomyf17.html, 25 March 2020.Google Scholar
Goh, W. M. Y. and Schmutz, E., The expected order of a random permutation, Bull. London Math. Soc. 23(1) (1991), 34–42.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Gončarov, V., On the field of combinatory analysis, Am. Math. Soc. Transl. (2) 19 (1962), 1–46.Google Scholar
Granville, A., Cycle lengths in a permutation are typically Poisson, Electron. J. Combin. 13(1) (2006), Research Paper 107, 23.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Gruder, O., Zur Theorie der Zerlegung von Permutationen in Zyklen, Ark. Mat. 2 (1952), 385–414. (German).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Havil, J., Gamma (Princeton Science Library, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, 2009). Exploring Euler's constant; Reprint of the 2003 edition.Google Scholar
Jones, G. A., Primitive permutation groups containing a cycle, Bull. Aust. Math. Soc. 89(1) (2014), 159–165.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Jordan, C., Sur la limite de transitivité des groupes non alternés, Bull. Soc. Math. France 1 (1872/73), 40–71.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Manstavičius, E., On random permutations without cycles of some lengths, Period. Math. Hungar. 42(1–2) (2001), 37–44.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Marggraff, B., Über primitive Gruppen mit transitiven Untergruppen geringeren Grades, Univ. Giessen, Giessen, circa 1890, Jbuch Volume 20, p. 141.Google Scholar
Plesken, W. and Robertz, D., The average number of cycles, Arch. Math. (Basel) 93(5) (2009), 445–449.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Rosser, J. B. and Schoenfeld, L., Approximate formulas for some functions of prime numbers, Illinois J. Math. 6 (1962), 64–94.CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Seress, Á., Permutation group algorithms, Cambridge Tracts in Mathematics, Volume 152 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2003).CrossRefGoogle Scholar
Unger, W. R., Almost all permutations power to a prime length cycle, arXiv:1905.08936 (2019).Google Scholar





