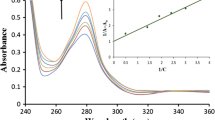
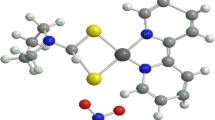
Abstract
This study was conducted to examine the binding of a newly synthesized Schiff base derived from 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde and 5-amino-2-mercaptobenzimidazole with human serum albumin (HSA) employing various biophysical techniques. The thermal-based fluorescence quenching data indicated that static quenching occurred between the ligand and HSA. The fluorescence results expose that ligand quenches the intrinsic fluorescence of HSA through a static quenching procedure. The thermodynamic parameters of the binding interaction, obtained using van't Hoff equation indicated the spontaneity of the reaction. The stability of the HSA–ligand complex resulted from hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions, which afforded a substantial binding affinity between ligand and HSA. UV–Vis and circular dichroism data indicated that ligand binding induced conformational changes in HSA. The energy transfer efficiency determined according to Fӧorster's theory. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) and Lipinski’s drug likeness of the ligand was predicted, revealing that it had auspicious physicochemical properties for oral bioavailability. Furthermore, molecular modeling was also employed to determine the location of the ligand in HSA binding sites, which revealed that the ligand interacted with polar and apolar residues of site I (subdomain IIA) of HSA, predominantly through hydrophobic and hydrogen bonding interactions.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd El-halim HF, Omar MM, Mohamed GG (2011) Synthesis, structural, thermal studies and biological activity of a tridentate Schiff base ligand and their transition metal complexes. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 78:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2010.06.003
Abdollahpour N, Soheili V, Saberi MR, Chamani J (2016) Investigation of the interaction between human serum albumin and two drugs as binary and ternary systems. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 41:705–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-015-0297-y
Afzal M, Usman M, Al-Lohedan HA, Tabassum S (2020) Synthesis and characterization of heterobimetallic SnIV–CuII/ZnII complexes: DFT studies, cleavage potential and cytotoxic activity. J Biomol Struct Dyn 38:1130–1142. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2019.1596837
Alanazi MM, Almehizia AA, Bakheit AH, Alsaif NA, Alkahtani HM, Wani TA (2019) Mechanistic interaction study of 5,6-Dichloro-2-[2-(pyridin-2-yl)ethyl]isoindoline-1,3-dione with bovine serum albumin by spectroscopic and molecular docking approaches. Saudi Pharm J 27:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2018.12.001
Al-Mehizia AA, Bakheit AH, Zargar S, Bhat MA, Asmari MM, Wani TA (2019) Evaluation of biophysical interaction between newly synthesized pyrazoline pyridazine derivative and bovine serum albumin by spectroscopic and molecular docking studies. J Spectrosc 2019:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3848670
Alsaif NA, Wani TA, Bakheit AH, Zargar S (2020) Multi-spectroscopic investigation, molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulation of competitive interactions between flavonoids (quercetin and rutin) and sorafenib for binding to human serum albumin. Int J Biol Macromol 165:2451–2461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.098
An X, Zhao J, Cui F, Qu G (2017) The investigation of interaction between Thioguanine and human serum albumin by fluorescence and modeling. Arab J Chem 10:S1781–S1787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.06.031
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Carter DC, Ho JX (1994) Structure of Serum Albumin, pp 153–203
Carter DC, Chang B, Ho JX, Keeling K, Krishnasami Z (1994) Preliminary Crystallographic Studies of Four Crystal forms of Serum Albumin. Eur J Biochem 226:1049–1052. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.01049.x
Castellan GW (1983) Physical chemistry, 3rd edn. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, California
Chadha N, Singh D, Milton MD, Mishra G, Daniel J, Mishra AK, Tiwari AK (2020) Computational prediction of interaction and pharmacokinetics profile study for polyamino-polycarboxylic ligands on binding with human serum albumin. New J Chem 44:2907–2918. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NJ05594K
Chatterjee T, Pal A, Dey S, Chatterjee BK, Chakrabarti P (2012) Interaction of virstatin with human serum albumin: spectroscopic analysis and molecular modeling. PLoS ONE 7:e37468. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037468
Chaves OA, Fernandes TVA, de Melos JLR, Netto-Ferreira JC, Echevarria A (2020) Elucidation of the interaction between human serum albumin (HSA) and 3,4-methylenedioxyde-6-iodo-benzaldehyde-thiosemicarbazone, a potential drug for Leishmania amazonensis: multiple spectroscopic and dynamics simulation approach. J Mol Liq 310:113117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113117
Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V (2017) SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci Rep 7:42717. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42717
Das A, Kumar GS (2014) Binding studies of aristololactam-β-D-glucoside and daunomycin to human serum albumin. RSC Adv 4:33082–33090. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA04327H
Dehkhodaei M, Sahihi M, Rudbari HA, Ariaeefar M, Gharaghani S, Azadbakht R, Taheri S, Kajani AA (2018) Multi experimental and computational studies for DNA and HSA interaction of new nano-scale ultrasound-assisted synthesized Pd(II) complex as a potent anticancer drug. J Mol Liq 264:386–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.05.077
Erkan S, Kaya S, Sayin K, Karakaş D (2020) Structural, spectral characterization and molecular docking analyses of mer-ruthenium(II) complexes containing the bidentate chelating ligands. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 224:117399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.117399
Eşme A, Sağdınç SG (2018) Molecular structures, spectroscopic (FT–IR, NMR, UV) studies, NBO analysis and NLO properties for tautomeric forms of 1,3-dimethyl-5-(phenylazo)-6-aminouracil by density functional method. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 188:443–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.07.034
Fani N, Bordbar AK, Ghayeb Y (2013) Spectroscopic, docking and molecular dynamics simulation studies on the interaction of two Schiff base complexes with human serum albumin. J Lumin 141:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.03.001
Friedrichs B (1997) Th. Peters. Jr.: all about albumin. biochemistry, genetics, and medical applications. XX and 432 pages, numerous figures and tables. Academic Press Inc, San Diego, California, 1996. Price: 85.00 US $. Food/Nahrung 41:382–382. https://doi.org/10.1002/food.19970410631
Geerlings P, De Proft F, Langenaeker W (2003) Conceptual density functional theory. Chem Rev 103:1793–1874. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr990029p
Guo X-J, Hao A-J, Han X-W, Kang P-L, Jiang Y-C, Zhang X-J (2011) The investigation of the interaction between ribavirin and bovine serum albumin by spectroscopic methods. Mol Biol Rep 38:4185–4192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-010-0539-7
Hu Y-J, Liu Y, Shen X-S, Fang X-Y, Qu S-S (2005) Studies on the interaction between 1-hexylcarbamoyl-5-fluorouracil and bovine serum albumin. J Mol Struct 738:143–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2004.11.062
Kala ALA, Kumara K, Harohally NV, Lokanath NK (2020) Synthesis, characterization and hydrogen bonding attributes of halogen bonded O-hydroxy Schiff bases: crystal structure, Hirshfeld surface analysis and DFT studies. J Mol Struct 1202:127238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127238
Kandagal PB, Shaikh SMT, Manjunatha DH, Seetharamappa J, Nagaralli BS (2007) Spectroscopic studies on the binding of bioactive phenothiazine compounds to human serum albumin. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 189:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2007.01.021
Kazemi Z, Rudbari HA, Sahihi M, Mirkhani V, Moghadam M, Tangestaninejad S, Mohammadpoor-Baltork I, Gharaghani S (2016) Synthesis, characterization and biological application of four novel metal-Schiff base complexes derived from allylamine and their interactions with human serum albumin: experimental, molecular docking and ONIOM computational study. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 162:448–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.07.003
Kelly SM, Jess TJ, Price NC (2005) How to study proteins by circular dichroism. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteomics 1751:119–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2005.06.005
Khosravi I, Hosseini F, Khorshidifard M, Sahihi M, Rudbari HA (2016) Synthesis, characterization, crystal structure and HSA binding of two new N, O, O-donor Schiff-base ligands derived from dihydroxybenzaldehyde and tert-butylamine. J Mol Struct 1119:373–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.04.094
Khosravi I, Sahihi M, Rudbari HA, Borhan G, Chavoshpour-Natanzi Z (2017) The Interaction of a new schiff base ligand with human serum albumin: molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation studies. J Macromol Sci Part B 56:636–643. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222348.2017.1356634
Kiyooka S, Kaneno D, Fujiyama R (2013) Parr’s index to describe both electrophilicity and nucleophilicity. Tetrahedron Lett 54:339–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2012.11.039
Kosar B, Albayrak C (2011) Spectroscopic investigations and quantum chemical computational study of (E)-4-methoxy-2-[(p-tolylimino)methyl]phenol. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 78:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2010.09.016
Krishnakumar SS, Panda D (2002) Spatial relationship between the prodan site, Trp-214, and Cys-34 residues in human serum albumin and loss of structure through incremental unfolding†. Biochemistry 41:7443–7452. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi025699v
Kumar GSS, Prabhu AAM, Bhuvanesh N (2014) Studies on the self-catalyzed Knoevenagel condensation, characterization, DPPH radical scavenging activity, cytotoxicity, and molecular properties of 5-arylidene-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4,6-diones using single crystal XRD and DFT techniques. J Mol Struct 1075:166–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.06.065
Kumar S, Vasantha Kumar BC, Chandra RHD (2019) Crystal structure, Hirshfeld analysis and HSA interaction studies of N’-[(E)-(5-bromothiophen-2-yl)methylidene]-3-hydroxynaphthalene-2-carbohydrazide. J Mol Struct 1189:343–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.03.070
Kuruvilla TK, Muthu S, Prasana JC, George J, Sevvanthi S (2019) Spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-Raman), quantum mechanical and docking studies on methyl[(3S)-3-(naphthalen-1-yloxy)-3-(thiophen-2-yl)propyl]amine. J Mol Struct 1175:163–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.07.097
Lakowicz JR (1999) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. Kluwer, New York
Lakowicz JR (2006) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy; 3rd edition, pp 282. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-46312-4
Lakowicz JR (2009) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy, 3rd edn. Springer, New York
Lakowicz JR, Weber G (1973) Quenching of fluorescence by oxygen. Probe for structural fluctuations in macromolecules. Biochemistry 12:4161–4170. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00745a020
Li Y, He W, Dong Y, Sheng F, Hu Z (2006) Human serum albumin interaction with formononetin studied using fluorescence anisotropy, FT-IR spectroscopy, and molecular modeling methods. Bioorg Med Chem 14:1431–1436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2005.09.066
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (1997) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 23:3–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(96)00423-1
Liu H, Shi X, Xu M, Li Z, Huang L, Bai D, Zeng ZZ (2011) Transition metal complexes of 2, 6-di ((phenazonyl-4-imino) methyl)-4-methylphenol: Structure and biological evaluation. Eur J Med Chem 46:1638–1647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.02.012
Liu C, Yang W, Gao Q, Du J, Luo H, Liu Y, Yang C (2018) Differential recognition and quantification of HSA and BSA based on two red-NIR fluorescent probes. J Lumin 197:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.01.021
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mrkalić EM, Jelić RM, Klisurić OR, Matović ZD (2014) Synthesis of novel palladium(II) complexes with oxalic acid diamide derivatives and their interaction with nucleosides and proteins. Structural, solution, and computational study. Dalt Trans 43:15126–15137. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3DT53384K
Nakamoto K (2006) Infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic and coordination compounds. In: Griffiths PR (ed) Handbook of vibrational spectroscopy. Wiley, Chichester
Nithya P, Helena S, Simpson J, Ilanchelian M, Muthusankar A, Govindarajan S (2016) New cobalt(II) and nickel(II) complexes of benzyl carbazate Schiff bases: syntheses, crystal structures, in vitro DNA and HSA binding studies. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 165:220–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.10.024
Parr RG, Szentpály LV, Liu S (1999) Electrophilicity Index. J Am Chem Soc 121:1922–1924. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja983494x
Parthasarathi R, Subramanian V, Roy DR, Chattaraj PK (2004) Electrophilicity index as a possible descriptor of biological activity. Bioorg Med Chem 12:5533–5543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2004.08.013
Patil SA, Unki SN, Kulkarni AD, Naik VH, Kamble U, Badami PS (2011) Spectroscopic, in vitro antibacterial, and antifungal studies of Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II) complexes with 4-chloro-3-coumarinaldehyde Schiff bases. J Coord Chem 64:323–336. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2010.541240
Pearson RG (1986) Absolute electronegativity and hardness correlated with molecular orbital theory. Proc Natl Acad Sci 83:8440–8441. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.83.22.8440
Peng S-H, Lv B-B, Ali A, Wang J-M, Ying X, Wang H, Liu J-B, Ji L-N, Liu H-Y (2016) The magnetic properties, DNA/HSA binding and nuclease activity of manganese N -confused porphyrin. J Porphyr Phthalocyanines 20:624–638. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1088424616500449
Poureshghi F, Ghandforoushan P, Safarnejad A, Soltani S (2017) Interaction of an antiepileptic drug, lamotrigine with human serum albumin (HSA): application of spectroscopic techniques and molecular modeling methods. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 166:187–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.09.046
Rastegari B, Karbalaei-Heidari HR, Yousefi R, Zeinali S, Nabavizadeh M (2016) Interaction of prodigiosin with HSA and β-Lg: spectroscopic and molecular docking studies. Bioorg Med Chem 24:1504–1512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2016.02.020
Ross PD, Subramanian S (1981) Thermodynamics of protein association reactions: forces contributing to stability. Biochemistry 20:3096–3102. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00514a017
Rudbari HA, Khorshidifard M, Askari B, Habibi N, Bruno G (2015) New asymmetric Schiff base ligand derived from allylamine and 2,3-dihydroxybenzaldehyde and its molybdenum(VI) complex: Synthesis, characterization, crystal structures, computational studies and antibacterial activity together with synergistic effect agai. Polyhedron 100:180–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2015.07.060
Sengupta B, Sengupta PK (2003) Binding of quercetin with human serum albumin: a critical spectroscopic study. Biopolymers 72:427–434. https://doi.org/10.1002/bip.10489
Shahabadi N, Khorshidi A, Moghadam NH (2013) Study on the interaction of the epilepsy drug, zonisamide with human serum albumin (HSA) by spectroscopic and molecular docking techniques. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 114:627–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2013.05.092
Shahraki S, Majd MH, Heydari A (2019) Novel tetradentate Schiff base zinc(II) complex as a potential antioxidant and cancer chemotherapeutic agent: insights from the photophysical and computational approach. J Mol Struct 1177:536–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2018.10.005
Shen G-F, Liu T-T, Wang Q, Jiang M, Shi J-H (2015) Spectroscopic and molecular docking studies of binding interaction of gefitinib, lapatinib and sunitinib with bovine serum albumin (BSA). J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 153:380–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2015.10.023
Shokrollahi S, Amiri A, Fadaei-Tirani F, Schenk-Joß K (2020) Promising anti-cancer potency of 4,5,6,7-tetrahydrobenzo[d]thiazole-based Schiff-bases. J Mol Liq 300:112262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112262
Silva D, Cortez CM, Cunha-Bastos J, Louro SR (2004) Methyl parathion interaction with human and bovine serum albumin. Toxicol Lett 147:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2003.10.014
Singh K, Kumar Y, Puri P, Kumar M, Sharma C (2012) Cobalt, nickel, copper and zinc complexes with 1,3-diphenyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxaldehyde Schiff bases: antimicrobial, spectroscopic, thermal and fluorescence studies. Eur J Med Chem 52:313–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.02.053
Song K-S, Liu L, Guo Q-X (2003) Remote substituent effects on N−X (X = H, F, Cl, CH 3, Li) bond dissociation energies in para-substituted anilines. J Org Chem 68:262–266. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo0204146
Sudlow G, Birkett DJ, Wade DN (1976) Further characterization of specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol Pharmacol 12:1052–1061
Sułkowska A, Bojko B, Równicka J, Sułkowski WW (2006) Paracetamol and cytarabine binding competition in high affinity binding sites of transporting protein. J Mol Struct 792–793:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2006.01.002
Tabassum S, Al-Asbahy WM, Afzal M, Arjmand F, Khan RH (2012a) Interaction and photo-induced cleavage studies of a copper based chemotherapeutic drug with human serum albumin: spectroscopic and molecular docking study. Mol Biosyst 8:2424. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2mb25119a
Tabassum S, Al-Asbahy WM, Afzal M, Arjmand F (2012b) Synthesis, characterization and interaction studies of copper based drug with Human Serum Albumin (HSA): spectroscopic and molecular docking investigations. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 114:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2012.05.021
Tabrizi L, McArdle P, Erxleben A, Chiniforoshan H (2015) Nickel(II) and cobalt(II) complexes of lidocaine: synthesis, structure and comparative in vitro evaluations of biological perspectives. Eur J Med Chem 103:516–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.09.018
van de Weert M, Stella L (2011) Fluorescence quenching and ligand binding: a critical discussion of a popular methodology. J Mol Struct 998:144–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2011.05.023
Veeralakshmi S, Sabapathi G, Nehru S, Venuvanalingam P, Arunachalam S (2017) Surfactant–cobalt(III) complexes: the impact of hydrophobicity on interaction with HSA and DNA—insights from experimental and theoretical approach. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 153:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.02.013
Wang Y-P, Wei Y, Dong C (2006) Study on the interaction of 3,3-bis(4-hydroxy-1-naphthyl)-phthalide with bovine serum albumin by fluorescence spectroscopy. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 177:6–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2005.04.040
Wani TA, Bakheit AH, Ansari MN, Al-Majed AA, Al-Qahtani BM, Zargar S (2018) Spectroscopic and molecular modeling studies of binding interaction between bovine serum albumin and roflumilast. Drug Des Devel Ther 12:2627–2634. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S169697
Wani TA, Bakheit AH, Zargar S, Bhat MA, Al-Majed AA (2019) Molecular docking and experimental investigation of new indole derivative cyclooxygenase inhibitor to probe its binding mechanism with bovine serum albumin. Bioorg Chem 89:103010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103010
Wani TA, Bakheit AH, Zargar S, Alanazi ZS, Al-Majed AA (2020) Evaluation of competitive binding interaction of neratinib and tamoxifen to serum albumin in multidrug therapy. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 227:117691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2019.117691
Wani TA, Alsaif N, Alanazi MM, Bakheit AH, Zargar S, Bhat MA (2021a) A potential anticancer dihydropyrimidine derivative and its protein binding mechanism by multispectroscopic, molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulation along with its in-silico toxicity and metabolic profile. Eur J Pharm Sci 158:105686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105686
Wani TA, Bakheit AH, Zargar S, Rizwana H, Al-Majed AA (2021b) Influence of antioxidant flavonoids quercetin and rutin on the in-vitro binding of neratinib to human serum albumin. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 246:118977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.118977
Yasmeen S, Riyazuddeen QFA (2017) Unraveling the thermodynamics, binding mechanism and conformational changes of HSA with chromolyn sodium: multispecroscopy, isothermal titration calorimetry and molecular docking studies. Int J Biol Macromol 105:92–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.06.122
Yasrebi SA, Takjoo R, Riazi GH (2019) HSA-interaction studies of uranyl complexes of alkyl substituted isothiosemicarbazone. J Mol Struct 1193:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.04.126
Yıldız M, Kılıç Z, Hökelek T (1998) Intramolecular hydrogen bonding and tautomerism in Schiff bases. Part I. Structure of 1,8-di[N-2-oxyphenyl-salicylidene]-3,6-dioxaoctane. J Mol Struct 441:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2860(97)00291-3
Yoosefian M, Chermahini ZJ, Raissi H, Mola A, Sadeghi M (2015) A theoretical study on the structure of 2-amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole and its 5-substituted derivatives in the gas phase, water, THF and DMSO solutions. J Mol Liq 203:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.01.002
You Z-L, Shi D-H, Xu C, Zhang Q, Zhu H-L (2008) Schiff base transition metal complexes as novel inhibitors of xanthine oxidase. Eur J Med Chem 43:862–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2007.06.015
Zhang Y-Z, Zhou B, Liu Y-X, Zhou C-X, Ding X-L (2008) Fluorescence study on the interaction of bovine serum albumin with P-aminoazobenzene. J Fluoresc 18:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-007-0247-4
Zheng D-J, Xu J, Su M-M, Sun Z-G, Jiao Q-C, Yang Y-S, Zhu H-L (2018) A small, steady, rapid and selective TICT based fluorescent HSA sensor for pre-clinical diagnosis. Sensors Actuators B Chem 271:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.05.037
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University, for funding this work through group project number RG–1440–076. The authors also thank the Deanship of Scientific Research and RSSU at King Saud University for their technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muddassir, M., Alarifi, A., Khan, A. et al. Spectroscopic and molecular docking investigation of the binding of a bioactive mercaptobenzimidazole-functionalized Schiff base to human serum albumin. Chem. Pap. 75, 3535–3550 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01585-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01585-z