Abstract
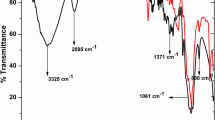
Pollution of water by leaking industrial dyes has become a major problem for aquatic organisms and human-being. Polluted water treatment methods need efficient alternatives to conventional dye removing techniques. In this study, the catalytic activity of cellulose based silver nanocomposite against the pollutant methylene blue dye was searched. Cellulose based silver nanocomposite was synthesized by using in situ green synthesis method with Laurus nobilis extract. UV–VIS, FTIR, SEM, TEM, EDS, XRD, BET analyses were used to characterization of synthesized nanocomposite. Electron microscopy results confirmed that 25 nm diameter silver nanoparticles were supporting the 25 nm width cellulose nanofibers. Elemental composition of confirmed by UV–VIS, FTIR, XRD and EDS results which including silver and cellulose specific peaks. BET results showed that nanocomposite have 11.1 nm pore size with 199,8508 m2/g specific surface area. Catalytic activity of nanocomposite was performed against methylene blue in the presence of NaBH4. Catalytic activity was traced for up to 120 min and complete removal of methylene blue dye was estimated as 1 h. Moreover, the recycled nanocomposite was found reusable without activity loss for three times. These results offer an easy, eco-friendly and reusable dye removing material for wastewaters which were polluted by industrial dyes.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors accepted data transparency statement.
References
P. I. Dolez, in P. I. Dolez (ed.), Nanoengineering: global approaches to health and safety issues, 1st ed. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2015).
K. T. Ramesh, Nanomaterials (Springer, Boston, MA, 2009).
R. G. Saratale, G. D. Saratale, H. S. Shin, J. M. Jacob, A. Pugazhendhi, M. Bhaisare, and G. Kumar (2018). New insights on the green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant and waste biomaterials: current knowledge, their agricultural and environmental applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25, 10164–10183.
L. A. Kolahalam, I. K. Viswanath, B. S. Diwakar, B. Govindh, V. Reddy, and Y. L. N. Murthy (2019). Review on nanomaterials: synthesis and applications. Mater. Today: Proc. 18, 2182–2190.
H. N. Tran, Y. Wang, S. You, and H. Chao, in T. K. Sen (ed.), Air, gas, and water pollution control using industrial and agricultural solid wastes adsorbents, 1st ed. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2017).
M. Faisal, M. A. Tariq, and M. Muneer (2007). Photocatalysed degradation of two selected dyes in UV-irradiated aqueous suspensions of titania. Dyes Pigments 72, 233–239.
K. H. Gonawala and M. J. Mehta (2014). Removal of color from different dye wastewater by using ferric oxide as an adsorbent. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 4, 102–109.
M. Goswami, D. Baruah, and A. M. Das (2018). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles supported on cellulose and their catalytic application in the scavenging of organic dyes. New J. Chem. 42, 10868–10878.
H. Deng, J. Lu, G. Li, G. Zhang, and X. Wang (2011). Adsorption of methylene blue on adsorbent materials produced from cotton stalk. Chem. Eng. J. 172, 326–334.
L. Chen, A. Ramadan, L. Lü, W. Shao, F. Luo, and J. Chen (2011). Biosorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution using lawny grass modified with citric acid. J. Chem. Eng. Data 56, 3392–3399.
V. Katheresan, J. Kansedo, and S. Y. Lau (2018). Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: a review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 6, 4676–4697.
A. Jamil, T. H. Bokhari, T. Javed, R. Mustafa, M. Sajid, S. Noreen, M. Zuber, A. Nazir, M. Iqbal, and M. I. Jilani (2020). Photocatalytic degradation of disperse dye violet-26 using TiO2 and ZnO nanomaterials and process variable optimization. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 1119–1128.
W. Ahlawat, N. Kataria, N. Dilbaghi, A. A. Hassan, S. Kumar, and K. H. Kim (2020). Carbonaceous nanomaterials as effective and efficient platforms for removal of dyes from aqueous systems. Environ. Res. 181, 108904.
T. Shahnaz, V. C. Padmanaban, and S. Narayanasamy (2020). Surface modification of nanocellulose using polypyrrole for the adsorptive removal of Congo red dye and chromium in binary mixture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 151, 322–332.
T. N. J. I. Edison, Y. R. Lee, and M. G. Sethuraman (2016). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Terminalia cuneata and its catalytic action in reduction of direct yellow-12 dye. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 161, 122–129.
C. G. Selvi Barnabas, J. Theerthagiri, and A. Santhanam (2018). Comparative photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes using silver nanoparticles synthesized from Padina tetrastromatica. Curr. Nanosci. 14, 71–75.
N. Isa and Z. Lockman (2019). Methylene blue dye removal on silver nanoparticles reduced by Kyllinga brevifolia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 26, 11482–11495.
L. David and B. Moldovan (2020). Green synthesis of biogenic silver nanoparticles for efficient catalytic removal of harmful organic dyes. Nanomaterials 10, 202.
M. Zahedifar, M. Shirani, A. Akbari, and N. Seyedi (2019). Green synthesis of Ag2S nanoparticles on cellulose/Fe3O4 nanocomposite template for catalytic degradation of organic dyes. Cellulose 26, 6797–6812.
Y. Habibi, L. A. Lucia, and O. J. Rojas (2010). Cellulose nanocrystals: chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem. Rev. 110, 3479–3500.
S. J. Eichhorn (2011). Cellulose nanowhiskers: promising materials for advanced applications. Soft Matter 7, 303–315.
B. L. Peng, N. Dhar, H. L. Liu, and K. C. Tam (2011). Chemistry and applications of nanocrystalline cellulose and its derivatives: a nanotechnology perspective. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 89, 1191–1206.
F. T. Seta, X. An, L. Liu, H. Zhang, J. Yang, W. Zhang, S. Nie, S. Yao, H. Cao, Q. Xu, Y. Bu, and H. Liu (2020). Preparation and characterization of high yield cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) derived from ball mill pretreatment and maleic acid hydrolysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 234, 115942.
S. P. Akhlaghi, R. C. Berry, and K. C. Tam (2013). Surface modification of cellulose nanocrystal with chitosan oligosaccharide for drug delivery applications. Cellulose 20, 1747–1764.
R. Batmaz, N. Mohammed, M. Zaman, G. Minhas, R. M. Berry, and K. C. Tam (2014). Cellulose nanocrystals as promising adsorbents for the removal of cationic dyes. Cellulose 21, 1655–1665.
J. Tang, Y. Song, F. Zhao, S. Spinney, B. J. da Silva, and K. C. Tam (2019). Compressible cellulose nanofibril (CNF) based aerogels produced via a bio-inspired strategy for heavy metal ion and dye removal. Carbohydr. Polym. 208, 404–412.
C. Zhijiang, X. Ping, Z. Cong, Z. Tingting, G. Jie, and Z. Kongyin (2018). Preparation and characterization of a bi-layered nano-filtration membrane from a chitosan hydrogel and bacterial cellulose nanofiber for dye removal. Cellulose 25, 5123–5137.
J. Tang, Z. Shi, R. M. Berry, and K. C. Tam (2015). Mussel-inspired green metallization of silver nanoparticles on cellulose nanocrystals and their enhanced catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol in the presence of β-cyclodextrin. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 54, 3299–3308.
M. A. Rabbi, M. M. Rahman, H. Minami, M. R. Habib, and H. Ahmad (2020). Ag impregnated sub-micrometer crystalline jute cellulose particles: catalytic and antibacterial properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 233, 115842.
Y. Zhang, L. Chen, L. Hu, and Z. Yan (2019). Characterization of cellulose/silver nanocomposites prepared by vegetable oil-based microemulsion method and their catalytic performance to 4-nitrophenol reduction. J. Polym. Environ. 27, 2943–2955.
M. Gopiraman, S. Saravanamoorthy, R. Baskar, A. Ilangovan, and C. Ill-Min (2019). Green synthesis of Ag@ Au bimetallic regenerated cellulose nanofibers for catalytic applications. New J. Chem. 43, 17090–17103.
S. W. Chook, C. H. Chia, C. H. Chan, S. X. Chin, S. Zakaria, M. S. Sajab, and N. M. Huang (2015). A porous aerogel nanocomposite of silver nanoparticles-functionalized cellulose nanofibrils for SERS detection and catalytic degradation of rhodamine B. RSC Adv. 5, 88915–88920.
S. M. Li, N. Jia, M. G. Ma, Z. Zhang, Q. H. Liu, and R. C. Sun (2011). Cellulose–silver nanocomposites: microwave-assisted synthesis, characterization, their thermal stability, and antimicrobial property. Carbohydr. Polym. 86, 441–447.
M. Goswami and A. M. Das (2019). Synthesis and characterization of a biodegradable cellulose acetate-montmorillonite composite for effective adsorption of Eosin Y. Carbohydr. Polym. 206, 863–872.
B. H. Dong and J. P. Hinestroza (2009). Metal nanoparticles on natural cellulose fibers: electrostatic assembly and in situ synthesis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 1, 797–803.
F. Deuber, S. Mousavi, L. Federer, M. Hofer, and C. Adlhart (2018). Exploration of ultralight nanofiber aerogels as particle filters: capacity and efficiency. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 9069–9076.
G. Chen, L. Yan, X. Wan, Q. Zhang, and Q. Wang (2019). In situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles on cellulose fibers using D-glucuronic acid and its antibacterial application. Materials 12, 3101.
G. H. Jiang, L. Wang, T. Chen, H. J. Yu, and J. J. Wang (2005). Preparation and characterization of dendritic silver nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. 40, 1681–1683.
H. Sehaqui, Q. Zhou, and L. A. Berglund (2011). High-porosity aerogels of high specific surface area prepared from nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC). Compos. Sci. Technol. 71, 1593–1599.
G. Yang, J. Xie, F. Hong, Z. Cao, and X. Yang (2012). Antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticle impregnated bacterial cellulose membrane: effect of fermentation carbon sources of bacterial cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 87, 839–845.
A. Ali, I. U. Haq, J. Akhtar, M. Sher, N. Ahmed, and M. Zia (2016). Synthesis of Ag-NPs impregnated cellulose composite material: its possible role in wound healing and photocatalysis. IET Nanobiotechnol. 11, 477–484.
J. T. Harris and A. J. McNeil (2020). Localized hydrogels based on cellulose nanofibers and wood pulp for rapid removal of methylene blue. J. Polym. Sci. 58, 3042–3049.
P. Vennila, D. J. Yoo, and A. R. Kim (2017). Ni-Co/Fe3O4 flower-like nanocomposite for the highly sensitive and selective enzyme free glucose sensor applications. J. Alloys Compd. 703, 633–642.
M. Pirhashemi, A. Habibi-yangjeh, and S. Rahim (2018). Journal of industrial and engineering chemistry review on the criteria anticipated for the fabrication of highly efficient ZnO-based visible-light-driven photocatalysts. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 62, 1–25.
L. Yu, J. Xi, H. T. Chan, T. Su, D. L. Phillips, and W. K. Chan (2012). The degradation mechanism of methyl orange under photo-catalysis of TiO 2. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14, 3589–3595.
C. Shi, L. Zhang, H. Bian, Z. Shi, J. Ma, and Z. Wang (2021). Construction of Ag–ZnO/cellulose nanocomposites via tunable cellulose size for improving photocatalytic performance. J. Clean Prod. 288, 125089.
K. Mallick, M. Witcomb, and M. Scurrell (2006). Silver nanoparticle catalysed redox reaction: an electron relay effect. Mater. Chem. Phys. 97, 283–287.
V. K. Vidhu and D. Philip (2014). Catalytic degradation of organic dyes using biosynthesized silver nanoparticles. Micron 56, 54–62.
V. K. Gupta, S. Agarwal, D. Pathania, N. C. Kothiyal, and G. Sharma (2013). Use of pectin–thorium (IV) tungstomolybdate nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Carbohydr. Polym. 96, 277–283.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by YK, MA, SH, and LY. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YK and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical Approval
The authors accepted ethical statement.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kucukcobanoglu, Y., Ayisigi, M., Haseki, S. et al. In situ Green Synthesis of Cellulose based Silver Nanocomposite and its Catalytic Dye Removal Potential Against Methylene Blue. J Clust Sci 33, 1623–1633 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02093-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-021-02093-6