Abstract
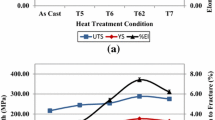
The present study was carried out to investigate the effects of Ni and Zr additions, individually or in combination, on the room-temperature tensile properties of 354 casting alloy (Al–9wt%Si–1.8wt%Cu–0.5wt%Mg) which was isothermally treated at temperatures in the range of 155–350 °C and aging times up to 1000 h. Tensile tests were carried out in the as-cast, solution heat-treated, and aged conditions using different aging times up to 1000 h. Quality charts were used as an evaluation tool for selecting the optimum conditions to achieve superior tensile properties and optimum quality in 354-type alloys. Zirconium reacts only with Ti, Si, and Al to form (Al,Si)2(Zr,Ti), (Al,Si)3(Zr,Ti), and Al3Zr phases. The beneficial effects of Zr and Ti additions appear in the refining of the α-Al grain size which reduces the size of the Al2Cu and α-Fe particles. Tensile test results at ambient temperature show a slight increase in alloys with Zr and Zr/Ni additions, particularly at aging temperatures above 240 ºC. It is suggested that the maximum obtainable quality index values by means of heat treatment are the difference between the quality index values for the as-cast and solution heat treatment conditions.
























Similar content being viewed by others

References
D.A. Porter, K.E. Easterling, Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys, 2nd edn. (Chapman and Hall, New York, 1992).
D.R. Askeland, The Science and Engineering of Materials, 3rd edn. (Chapman and Hall, Boston, MA, 1996).
D.R. Askeland, P.P. Fulay, W.J. Wright, The Science and Engineering of Materials, 6th edn. (CENGAGE Learning, Stamford, 2001), pp. 458–484
J. Hernandez-Sandoval, Improving the Performance of 354 Type Alloy, PhD. Thesis, Université du Québec à Chicoutimi, Chicoutimi, Quebec, Canada (2010).
J.L. Jorstad, W.M. Rasmussen, D.L. Zalensas, Aluminum Casting Technology, 2nd edn. (The American Foundrymen’s Society Inc, Des Plaines, 1993).
S.C. Wang, M.J. Starink, N. Gao, Precipitation hardening in Al-Cu-Mg alloys revisited. Scripta Mater. 54(2006), 287–291 (2006)
T. Gladman, Precipitation hardening in metals. Mater. Sci. Technol. 15, 30–36 (1999)
H.R. Ammar, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, E. Simielli, G.K. Sigworth, J.C. Lin, Influence of Aging Parameters on the Tensile Properties and Quality Index of Al-9 Pct Si-1.8 Pct Cu-0.5 Pct Mg 354-Type Casting Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 43A, 61–73 (2012)
R. Mahmudi, P. Sepehrband, H. Ghasemi, Improved properties of A319 aluminum casting alloy modified with Zr. Mater. Lett. 60(21), 2606–2610 (2006)
K.E. Knipling, D.C. Dunand, D.N. Seidman, Criteria for developing castable, creep-resistant aluminum-based alloys–a review. Z. Met. 97(3), 246–265 (2006)
P. Nash, M.F. Singleton, J.L. Murray, ASM Handbook, Vol. 3: Alloy-Phase Diagrams, 10th edn. (ASM, Materials Park, 1992).
J.L. Murray, Alcoa, Alcoa Center PA, Private Communication, 2005.
Z. Liu, Thermodynamics of nanoscale precipitate strengthened Fe-Cu and Al-Transition-Metal system from first principles calculations, PhD. Thesis, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL (2006).
H.M. Medrano-Prieto, C.G. Garay-Reyes, C.D. Gómez-Esparza et al., Effect of nickel addition and solution treatment time on microstructure and hardness of Al – Si – Cu aged alloys. Mater. Charact. 120, 168–174 (2016)
K.E. Knipling, Development of a nanoscale precipitation-strengthened creep-resistant aluminum alloy containing trialuminide precipitates, PhD Thesis, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, (2006).
M.H. Abdelaziz, Microstructural and mechanical characterization of transition elements-containing Al-Si-Cu-Mg Alloys for elevated-temperature applications, PhD Thesis, UQAC, Canada (2018)
T. Tanaka, T. Akasawa, Machinability of hypereutectic silicon-aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 8(4), 463–468 (1999)
M.E. Fine, Precipitation hardening of aluminum alloys. Metall. Trans. A 6(4), 625–630 (1975)
Y.W. Kim, W.M. Griffith (eds.), Dispersion Strengthened Aluminum Alloys (TMS, Warrendale, 1988), pp. 217–242
J.A. Lee, P. Chen, High strength aluminum alloy for high temperature applications, US Patent No. 6918970, 2002.
J.D. Robson, P.B. Pragnell, Modeling Al3Zr dispersoid precipitation in multicomponent aluminum alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 352, 240–250 (2003)
A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, S. Valtierra, F.H. Samuel, Defects related to incipient melting in Al-Si-Cu-Mg alloys. Mater. Des. 52, 947–956 (2013)
M. Drouzy, S. Jacob, M. Richard, Interpretation of tensile results by means of quality index and probable yield strength-application to Al-Si7-Mg foundry alloys. Int. Cast Metals J. 5(2), 43–50 (1980)
M. Tiryakioglu, J.T. Staley, J. Campbell, Evaluating structural integrity of cast Al–7%Si–Mg alloys via work hardening characteristics II A new quality index. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 368, 231–238 (2004)
C. Cáceres, A rationale for the quality index of Al-Si-Mg casting alloys. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 12(6), 385–391 (2000)
C. Cáceres, A Phenomenological approach to the quality index of Al-Si-Mg casting alloys. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 12(6), 367–375 (2000)
G.H. Garza-Elizondo, A.M. Samuel, S. Valtierra, F.H. Samuel, Effect of transition metals on the tensile properties of 354 alloy: role of precipitation hardening. Int. J. Metalcast. 11(3), 413–427 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0074-y
M.F. Ibrahim, G.H. Garza-Elizondo, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, Optimizing the heat treatment of high-strength 7075-type wrought alloys: a metallographic study. Int. J. Metalcast. 10(3), 264–275 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0038-2
M.H. Abdelaziz, A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, F.H. Samuel, Effect of extended thermal exposure and alloying elements on the morphology of eutectic Si in Al–Si cast alloys. Int. J. Metalcast. 14, 1013–1024 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00411-8
M.F. Ibrahim, A.M. Samuel, H.W. Doty, F.H. Samuel, Effect of aging conditions on precipitation hardening in Al–Si–Mg and Al–Si–Cu–Mg alloys. Int. J. Metalcast. 11(2), 274–286 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0057-z
J. Hernandez-Sandoval, A.M. Samuel, F.H. Samuel, S. Valtierra, Effect of additions of SiC and Al2O3 particulates on the microstructure and tensile properties of Al–Si–Cu–Mg cast alloys. Int. J. Metalcast. 10(3), 253–263 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0035-5
J. Gauthier, F.H. Samuel, Tensile properties and fracture behavior of solution-heat-treated 319.2 Al automotive alloy. AFS Trans. 103, 849–857 (1995)
MH Abdelaziz, A. M. Samuel, H. W. Doty, F. H. Samuel, Various aspects influencing the fracture behavior of impact tested Zr-containing Al-Si-Cu-Mg-354 type alloys, International Journal of Metalcasting, Pub Date : 2021-01-05 , DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00545-9
P. Prasad, Characterization of new, cast, high temperature aluminum alloys for diesel engine applications, Master’s Thesis, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati (2006).
S.N. Naik, S.M. Walley, The Hall-Petch and inverse Hall-Petch relations and the hardness of nanocrystalline metals. J. Mater. Sci. 55, 2661–3268 (2020)
J. Hernandez-Sandoval, G.H. Garza-Elizondo, A.M. Samuel, S. Valtierra, F.H. Samuel, The ambient and high temperature deformation behavior of Al-Si-Cu-Mg alloy with minor Ti, Zr, Ni additions. Mater. Des. 58, 89–101 (2014)
S. Zhang, L. Pan, D. Huang et al., Effect of nickel alloying and mechanical stirring on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al – 10% Si – 5% Cu alloy. Met. Sci. Heat Treat 61, 769–776 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-020-00498-0
S. Manasijević, N. Dolić, K. Raić, R. Radiša, Identification of phases formed by Cu and Ni in Al−Si piston alloys. La Metall. Ital. 3, 11–17 (2014)
C.L. Chen, R.C. Thomson, The combined use of EBSD and EDX analyses for the identification of complex intermetallic phases in multi-component Al–Si piston alloys. J. Alloy Comp 490, 293–300 (2010)
L. Zuo, B. Ye, J. Feng, X. Xu, X. Kong, H. Jiang, Effect of δ-Al3CuNi phase and thermal exposure on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Si-Cu-Ni alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 791, 1015–1024 (2019)
H. Yang, D. Watson, Y. Wang, S. Ji (2014) Effect of nickel on the microstructure and mechanical property of die-cast Al–Mg–Si–Mn alloy. J. Mater. Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-014-8551-2.
J. Jung, S. Lee, J. Lee, Y. Cho, S. Kim, W. Yoon, Improved mechanical properties of near-eutectic Al-Si piston alloy through ultrasonic melt treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 669, 187–195 (2016)
N.E. Nwankwo, V.U. Nwoke, E.E. Nnuka, Effect of Ni-additions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe-based chill-cast Al-Si alloys for production of pistons for automobile engine applications. Int. J. Sci. Res. Eng. Technol. 1, 21–27 (2015)
H. Ye, An overview of the development of Al-Si alloy based materials for engine applications. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 12, 288–297 (2003)
C.H. Caceres, T. Din, A.K.M.B. Rashid, J. Campbell, The effect of ageing on quality index of an Al-Cu casting alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 15, 711–716 (1999)
C.H. Cáceres, J.A. Taylor, Enhanced ductility in Al-Si-Cu-Mg casting alloys with high Si content, in Shape Casting: The John Campbell Symposium. ed. by M. Tiryakiouglu, P. Crepeau (TMS, California, 2005), pp. 245–254
C.T. Rios, R. Caram, C. Bolfarini, F.W.J. Botta, C.S. Kiminami, Intermetallic compounds in the Al-Si-Cu system. Acta Microscopia 12, 77–82 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernandez-Sandoval, J., Garza-Elizondo, G.H., Abdelaziz, M.H. et al. The Effect of Ni and Zr Additions on the Tensile Properties of Isothermally Aged Ai–Si–Cu–Mg Cast Alloys. Inter Metalcast 16, 435–457 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00615-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00615-6