Abstract
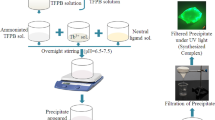
In this study, terpyridine functionalized phosphazene based metallo-supramolecular polymers were synthesized by three step reaction method. In the first step, 4′-(4-aminophenyl)-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine was synthesized with p-nitro benzaldehyde and 2-acetylpyridine. Then, the monomer containing six terpyridine (TPY) units attached to the phosphazene was prepared from 4′-(4-aminophenyl)-2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine and hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene by a condensation reaction. Finally, metallo-supramolecular phosphazene polymers were synthesised with these TPY functional phosphazenes and different transition metal ions (Cu, Co, Ni, and Zn ions). Prepared metallo-supramolecular polymers containing phosphazene unit were investigated by elemental analysis, different spectroscopic methods, energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX) and thermal analysis techniques. The stimuli-responsive, optoelectronic and spectroscopic properties of the synthesised metallo-supramolecular phosphazene polymers were investigated for external effects with UV–Vis spectroscopy and electro-analytic techniques. In addition, competitive ligand effect on these metallo-supramolecular polymers was examined with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The resulting metallo-supramolecular polymers containing phosphazene unit show very fast stimuli-responsive properties, such as 3 s. they also showed a single reversible redox structure resulting from the bonding of homometallic segments to polymer chain. In addition, they showed d-π transition (in the range of λ = 330–550 nm) depending on the metal (Co, Ni and Zn) ion forming the supramolecular structure. The addition of competing EDTA ligands caused the degradation of metallo-supramolecular polymer structures. These metallo-supramolecular phosphazene polymers are a good alternative smart material for opto-electronic, electrochromic, photochromic and intelligent material applications.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.A. Dobrzański, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 75(1–3), 133–148 (2006)
R. Pietschnig, in Smart inorganic polymers. ed. by E. Hey-Hawkins, M. Hissler (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2019), pp. 1–16
U. Jeong, Y. Yin, Adv. Funct. Mater. 30(2), 1907059 (2020)
A.J. Boydston, B. Cao, A. Nelson, R.J. Ono, A. Saha, J.J. Schwartz, C.J. Thrasher, J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 20621–20645 (2018)
S. Köytepe, M.H. Demirel, A. Gültek, T. Seçkin, Polym. Int. 63(4), 778–787 (2014)
J. Vicens, Q. Vicens, J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 65, 221–235 (2009)
J.M. Lehn, Rep. Progress Phys. 67, 249–265 (2004)
R. Dong, Y. Zhou, X. Huang, X. Zhu, Y. Lu, J. Shen, Adv. Mater. 27, 498–526 (2015)
S. Das, M. Presselt, J. Mater. Chem. C 7, 6194–6216 (2019)
H.Q. Peng, L.Y. Niu, Y.Z. Chen, L.Z. Wu, C.H. Tung, Q.Z. Yang, Chem. Rev. 115(15), 7502–7542 (2015)
A. Gugliuzza, in Smart membranes and sensors. ed. by A. Gugliuzza (John Wiley & Sons Inc, Hoboken, 2014), pp. 107–144
P.H. Dinolfo, J.T. Hupp, Chem. Mater. 13(10), 3113–3125 (2001)
A.J. Savyasachi, O. Kotova, S. Shanmugaraju, S.J. Bradberry, G.M. Ó’Máille, T. Gunnlaugsson, Chem. 3(5), 764–811 (2017)
U.S. Schubert, C. Eschbaumer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41(16), 2892–2926 (2002)
H. Hofmeier, U.S. Schubert, Chem. Soc. Rev. 33(6), 373–399 (2004)
M.R. Saboktakin, R.M. Tabatabaei, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 75, 426–436 (2015)
H.J. Yoon, W.D. Jang, J. Mater. Chem. 20, 211–222 (2010)
N.M. Sangeetha, U. Maitra, Chem. Soc. Rev. 34(10), 821–836 (2005)
A.R. Hirst, B. Escuder, J.F. Miravet, D.K. Smith, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47(42), 8002–8018 (2008)
N.M. Sangeetha, U. Maitra, Chem. Soc. Rev. 34, 821–836 (2005)
S. Chaterji, I.K. Kwon, K. Park, Progress Polym. Sci. 32(8–9), 1083–1122 (2007)
A. Noro, M. Hayashi, Y. Matsushita, Soft Matter 8, 6416–6429 (2012)
J.Y.C. Lim, Q. Lin, K. Xue, X.J. Loh, Mater. Today Adv. 3, 100021 (2019)
J.M. Knipe, N.A. Peppas, Regen. Biomater. 1(1), 57–65 (2014)
A. Zulys, D.M.A. Ovika, Mater. Sci. Eng. 188, 012036 (2017)
S. Köytepe, M.H. Demirel, T. Seçkin, J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 23(5), 1104–1112 (2013)
E.M. Hahn, N. Estrada-Ortiz, J. Han, V.F.C. Ferreira, T.G. Kapp, J.G.D. Correia, A. Casini, F.E. Kühn, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 12, 1667–1672 (2017)
N. Dhiman, P. Mohanty, New J. Chem. 43, 16670–16675 (2019)
S. Ture, R. Gurbanov, Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 193(10), 620–629 (2018)
M.H. Demirel, S. Köytepe, A. Gültek, T. Seçkin, J. Polym. Res. 21(2), 345 (2014)
B. Çoşut, S. Yeşilot, Polyhedron 35(1), 101–107 (2012)
S. Seo, J. Lee, S.Y. Choi, H. Lee, J. Mater. Chem. 22, 1868–1875 (2012)
S. Sezer, S. Köytepe, T. Seçkin, J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 28(6), 2825–2834 (2018)
M. Chiper, M.A.R. Meier, J.M. Kranenburg, U.S. Schubert, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 208, 679–689 (2007)
R. Dobrawa, F. Wurthner, J. Polym. Sci. Part A 43, 4981–4995 (2005)
J. Hoque, N. Sangaj, S. Varghese, Macromol. Biosci. 19(1), 1800259 (2018)
Acknowledgements
We gratefully to Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey, TUBITAK Research Fund (Project No: 115R023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sezer, S., Köytepe, S., Gültek, A. et al. Synthesis and Stimuli-Responsive Properties of Metallo-Supramolecular Phosphazene Polymers Based on Terpyridine Metal Complexes. J Inorg Organomet Polym 31, 3389–3405 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02008-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02008-y