Abstract
Background
Circular RNA of vimentin (circ-VIM) is a predictor for poor prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia, but we had little information on its function in esophageal cancer (EC). Here we examined the effects of circ-VIM together with sevoflurane on immune escape and multiple oncogenic activities of EC.
Methods
Bioinformatic tools, luciferase assay, and RNA immunoprecipitation were used to examine regulations between circ-VIM, miR-124-3p (miR-124), and PD-L1. CCK-8, wound healing, and Transwell assays were used to measure cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, respectively. The impacts of EC cells on cytotoxicity, proliferation, and apoptosis of CD8+ T cells were examined using LDH assay, CFSE staining, and Annexin V/PI staining, respectively. The in vivo tumorigenesis and lung metastases were assessed using xenograft model and tail vein injection of EC cells.
Results
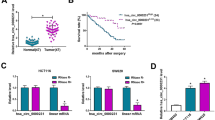
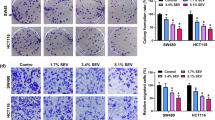
Significant upregulation of circ-VIM and PD-L1 and downregulation of miR-124 were detected in EC tissues or cells. Circ-VIM sponged miR-124 and released its suppression on the downstream target PD-L1. Sevoflurane, independent of circ-VIM, also upregulated miR-124 to lower PD-L1 expression. By modulating miR-124/PD-L1 axis, silencing circ-VIM and applying sevoflurane both inhibited immune escape and multiple oncogenic activities of EC in vitro, and suppressed xenograft growth and lung metastases in vivo. The inactivation of Ras/ERK signaling pathway was involved in suppression of malignant phenotypes by silencing circ-VIM and sevoflurane treatment.
Conclusions
Silencing circ-VIM and applying sevoflurane, by separately regulating miR-124/PD-L1 axis, presented synergistic effects in inhibiting immune escape and multiple malignant phenotypes of EC cells.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable
References
Anastasiadou E, Jacob LS, Slack FJ. Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018;18(1):5–18.
Bach DH, Lee SK, Sood AK. Circular RNAs in cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;16:118–29.
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424.
Chen W, He Y, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zeng H, Zou X, et al. Esophageal cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2009. J Thorac Dis. 2013;5(1):19–26.
Cheng Y, Li Y, Nian Y, Liu D, Dai F, Zhang J. STAT3 is involved in miR-124-mediated suppressive effects on esophageal cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:306.
Cheng Y, Sun H, Wang H, Jiang W, Tang W, Lu C, et al. Star circular RNAs in human cancer: progress and perspectives. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:8249–61.
Crowley LC, Christensen ME, Waterhouse NJ. Measuring survival of adherent cells with the colony-forming assay. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2016;2016(8):721–24.
Enlund M, Berglund A, Andreasson K, Cicek C, Enlund A, Bergkvist L. The choice of anaesthetic--sevoflurane or propofol--and outcome from cancer surgery: a retrospective analysis. Ups J Med Sci. 2014;119(3):251–61.
Enlund M, Berglund A, Ahlstrand R, Wallden J, Lundberg J, Warnberg F, et al. Survival after primary breast cancer surgery following propofol or sevoflurane general anesthesia-a retrospective, multicenter, database analysis of 6305 Swedish patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2020;64(8):1048–54.
Fan L, Wu Y, Wang J, He J, Han X. Sevoflurane inhibits the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through regulating ERK/MMP-9 pathway by up-regulating miR-203. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;850:43–52.
Farhood B, Najafi M, Mortezaee K. CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes in cancer immunotherapy: a review. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(6):8509–21.
Gao C, Shen J, Meng ZX, He XF. Sevoflurane inhibits glioma cells proliferation and metastasis through miRNA-124-3p/ROCK1 Axis. Pathol Oncol Res. 2019.
Huang H, Benzonana LL, Zhao H, Watts HR, Perry NJ, Bevan C, et al. Prostate cancer cell malignancy via modulation of HIF-1alpha pathway with isoflurane and propofol alone and in combination. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(7):1338–49.
Hurmath FK, Mittal M, Ramaswamy P, Umamaheswara Rao GS, Dalavaikodihalli NN. Sevoflurane and thiopental preconditioning attenuates the migration and activity of MMP-2 in U87MG glioma cells. Neurochem Int. 2016;94:32–8.
Ito M, Yajima S, Suzuki T, Oshima Y, Nanami T, Sumazaki M, et al. High serum PD-L1 level is a poor prognostic biomarker in surgically treated esophageal cancer. Cancer Med. 2020;9(4):1321–7.
Jiang X, Wang J, Deng X, Xiong F, Ge J, Xiang B, et al. Role of the tumor microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):10.
Jun IJ, Jo JY, Kim JI, Chin JH, Kim WJ, Kim HR, et al. Impact of anesthetic agents on overall and recurrence-free survival in patients undergoing esophageal cancer surgery: a retrospective observational study. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):14020.
Kang K, Wang Y. Sevoflurane inhibits proliferation and invasion of human ovarian cancer cells by regulating JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:4451–60.
Kim R. Effects of surgery and anesthetic choice on immunosuppression and cancer recurrence. J Transl Med. 2018;16(1):8.
Kudo T, Hamamoto Y, Kato K, Ura T, Kojima T, Tsushima T, et al. Nivolumab treatment for oesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma: an open-label, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(5):631–9.
Lai RC, Shan WR, Zhou D, Zeng XQ, Zuo K, Pan DF, et al. Sevoflurane promotes migration, invasion, and colony-forming ability of human glioblastoma cells possibly via increasing the expression of cell surface protein 44. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019;40(11):1424–35.
Li S, Han L. Circular RNAs as promising biomarkers in cancer: detection, function, and beyond. Genome Med. 2019;11(1):15.
Li X, Fan Q, Li J, Song J, Gu Y. MiR-124 down-regulation is critical for cancer associated fibroblasts-enhanced tumor growth of oral carcinoma. Exp Cell Res. 2017;351(1):100–8.
Li R, Huang Y, Lin J. Distinct effects of general anesthetics on lung metastasis mediated by IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway in mouse models. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):642.
Liang H, Gu M, Yang C, Wang H, Wen X, Zhou Q. Sevoflurane inhibits invasion and migration of lung cancer cells by inactivating the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. J Anesth. 2012;26(3):381–92.
Liang YJ, Wang QY, Zhou CX, Yin QQ, He M, Yu XT, et al. MiR-124 targets Slug to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34(3):713–22.
Lin EW, Karakasheva TA, Hicks PD, Bass AJ, Rustgi AK. The tumor microenvironment in esophageal cancer. Oncogene. 2016;35(41):5337–49.
Liu J, Yang L, Guo X, Jin G, Wang Q, Lv D, et al. Sevoflurane suppresses proliferation by upregulating microRNA-203 in breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(1):455–60.
Liu J, Li D, Luo H, Zhu X. Circular RNAs: The star molecules in cancer. Mol Asp Med. 2019.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8.
Lu N, Piao MH, Feng CS, Yuan Y. Isoflurane promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of bladder cancer cells through HIF-1alpha-beta-catenin/Notch1 pathways. Life Sci. 2020;258:118154.
Ohigashi Y, Sho M, Yamada Y, Tsurui Y, Hamada K, Ikeda N, et al. Clinical significance of programmed death-1 ligand-1 and programmed death-1 ligand-2 expression in human esophageal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(8):2947–53.
Qiu XY, Hu DX, Chen WQ, Chen RQ, Qian SR, Li CY, et al. PD-L1 confers glioblastoma multiforme malignancy via Ras binding and Ras/Erk/EMT activation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis. 2018;1864(5 Pt A):1754–69.
Quah BJ, Parish CR. The use of carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (CFSE) to monitor lymphocyte proliferation. J Vis Exp. 2010;(44).
Raufi AG, Almhanna K. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for esophageal cancer: are we moving in the right direction? Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(Suppl 3):S102.
Satelli A, Li S. Vimentin in cancer and its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(18):3033–46.
Saxena NK, Sharma D, Ding X, Lin S, Marra F, Merlin D, et al. Concomitant activation of the JAK/STAT, PI3K/AKT, and ERK signaling is involved in leptin-mediated promotion of invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67(6):2497–507.
Sumi C, Matsuo Y, Kusunoki M, Shoji T, Uba T, Iwai T, et al. Cancerous phenotypes associated with hypoxia-inducible factors are not influenced by the volatile anesthetic isoflurane in renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 2019;14(4):e0215072.
Sun Y, Zhao X, Zhou Y, Hu Y. miR-124, miR-137 and miR-340 regulate colorectal cancer growth via inhibition of the Warburg effect. Oncol Rep. 2012;28(4):1346–52.
Sun SQ, Ren LJ, Liu J, Wang P, Shan SM. Sevoflurane inhibits migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by regulating microRNA-34a/ADAM10 axis. Neoplasma. 2019;66(6):887–95.
Wakita A, Motoyama S, Nanjo H, Sato Y, Yoshino K, Sasaki T, et al. PD-L1 expression is a prognostic factor in patients with thoracic esophageal cancer treated without adjuvant chemotherapy. Anticancer Res. 2017;37(3):1433–41.
Wang P, Chen L, Zhang J, Chen H, Fan J, Wang K, et al. Methylation-mediated silencing of the miR-124 genes facilitates pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis by targeting Rac1. Oncogene. 2014;33(4):514–24.
Wang M, Meng B, Liu Y, Yu J, Chen Q, Liu Y. MiR-124 inhibits growth and enhances radiation-induced apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting STAT3. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(5):2017–28.
Wei J, Wang F, Kong LY, Xu S, Doucette T, Ferguson SD, et al. miR-124 inhibits STAT3 signaling to enhance T cell-mediated immune clearance of glioma. Cancer Res. 2013;73(13):3913–26.
Wilting SM, van Boerdonk RA, Henken FE, Meijer CJ, Diosdado B, Meijer GA, et al. Methylation-mediated silencing and tumour suppressive function of hsa-miR-124 in cervical cancer. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:167.
Wu DH, Liang H, Lu SN, Wang H, Su ZL, Zhang L, et al. miR-124 suppresses pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma growth by regulating monocarboxylate transporter 1-mediated cancer lactate metabolism. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(3):924–35.
Yagi T, Baba Y, Ishimoto T, Iwatsuki M, Miyamoto Y, Yoshida N, et al. PD-L1 expression, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, and clinical outcome in patients with surgically resected esophageal cancer. Ann Surg. 2019;269(3):471–8.
Yang Y, Hu R, Yan J, Chen Z, Lu Y, Jiang J, et al. Sevoflurane inhibits the malignant potential of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via activating the hypoxiainducible factor-1alpha signaling pathway in vitro. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(2):995–1002.
Yi W, Li D, Guo Y, Zhang Y, Huang B, Li X. Sevoflurane inhibits the migration and invasion of glioma cells by upregulating microRNA-637. Int J Mol Med. 2016;38(6):1857–63.
Yi YY, Yi J, Zhu X, Zhang J, Zhou J, Tang X, et al. Circular RNA of vimentin expression as a valuable predictor for acute myeloid leukemia development and prognosis. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(4):3711–9.
Zeng H, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zuo T, Xia C, Zou X, et al. Esophageal cancer statistics in China, 2011: Estimates based on 177 cancer registries. Thorac Cancer. 2016;7(2):232–7.
Zhang C, Wang B, Wang X, Sheng X, Cui Y. Sevoflurane inhibits the progression of ovarian cancer through down-regulating stanniocalcin 1 (STC1). Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:339.
Zhu G, Zhang L, Dan J, Zhu Q. Differential effects and mechanisms of local anesthetics on esophageal carcinoma cell migration, growth, survival and chemosensitivity. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020;20(1):126.
Funding
This work was supported by the Youth Talent Science and Technology Project of Changzhou Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (no. QN201924, no. QN202017), the Applied Basic Science Research Projects of Changzhou Science and Technology Bureau (no. CJ20200048), Changzhou High-Level Medical Talents Training Project (no. 2016CZBJ043) and Funding from Young Talent Development Plan of Changzhou Health Commission (2020-233) (no. CZQM2020029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor of integrity of the entire study: Cao Gao, Liang Zheng
Study concepts: Yan-Jie Xu, Cao Gao
Study design: Cao Gao, Liang Zheng
Definition of intellectual content: Lei Qi, Liang Zheng
Literature research: Lei Zhang, Liang Zheng
Clinical studies: Ya-fei Bao, Liang Zheng
Experimental studies: Cao Gao
Data acquisition: Ya-fei Bao
Data analysis: Ya-fei Bao
Statistical analysis: Cao Gao
Manuscript preparation: Cao Gao
Manuscript editing: Liang Zheng
Manuscript review: Liang Zheng
All the authors approved for the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the third affiliated hospital of Soochow University (Changzhou, Jiangsu, China) and all participants provided written consents.
Consent for publication
The informed consent obtained from study participants.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Graphical headlights
1. Silencing circ-VIM suppressed immune escape and multiple oncogenic activities of esophageal cancer by upregulating miR-124.
2. MiR-124 inhibited immune escape and multiple oncogenic activities of esophageal cancer by directly targeting PD-L1.
3. Sevoflurane suppressed immune escape and multiple oncogenic activities of esophageal cancer by upregulating miR-124.
4. Circ-VIM silence synergized with sevoflurane on targeting immune escape and multiple oncogenic activities of esophageal cancer.
Supplementary information
Supplemental Figure 1.
Sevoflurane regulated miR-124/PD-L1 axis to inhibit multiple oncogenic activities of EC. (A) Cell viability was examined using CCK-8 assay. (B-C) Clone formation assay was used to evaluate long-term proliferation in indicated treatments. (D-E) Migration ability of indicated cells was assessed by wound healing experiment. (F-G) Transwell assay was performed to measure the invasion ability in indicated cells. KYSE-150 or Eca-109 cells were treated with indicated concentrations of sevoflurane. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. (PNG 10188 kb)
Supplemental Figure 2.
Sevoflurane suppressed multiple oncogenic activities of EC by upregulating miR-124. (A) Cell viability was examined using CCK-8 assay. (B-C) Clone formation assay was used to evaluate long-term proliferation in indicated treatments. (D-E) Migration ability of indicated cells was assessed by wound healing experiment. (F-G) Transwell assay was performed to measure the invasion ability in indicated cells. KYSE-150 or Eca-109 cells were transfected with inhibitor NC or miR-124 inhibitor and treated with 4% sevoflurane. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. (PNG 10456 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, C., Xu, YJ., Qi, L. et al. CircRNA VIM silence synergizes with sevoflurane to inhibit immune escape and multiple oncogenic activities of esophageal cancer by simultaneously regulating miR-124/PD-L1 axis. Cell Biol Toxicol 38, 825–845 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09613-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09613-0