Abstract
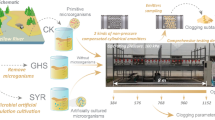
Multiple substances in the reclaimed water would be easily coupled with the effective components of fertilizers applied in the drip irrigation system when reusing it in the farmland, making the drip irrigation emitters extremely easy to be clogged, and the mechanism becoming more complex. However, the effects of different fertilizer types on emitters clogging using the reclaimed water and the influential mechanism were not clear yet. Based on these, this paper systematically studied how would different types of fertilizers affect the biofilm growth within drip irrigation emitters through the indoor controllable simulation experiment. Three kinds of reclaimed water sources were applied as replications. The results showed that biofilm components (solid particles, SP; phospholipid fatty acid, PLFAs; extracellular polymeric substance, EPS) in different fertilizer treatments gradually increased during the 80 days operation. They grew relatively slowly for the first 40 days and much more rapidly in the following 40 days. Taking the most commonly used ammonium bicarbonate fertilizer (AB) as the controlled treatment (CK), merely the SP, PLFAs and EPS contents of the ammonium sulfate (AS) treatments increased by 2.94%, 10.8% and 1.34%, respectively. And the biofilm components in all other fertilizer treatments mentioned above were reduced, although the decreasing extents of potassium sulfate (PS) and calcium superphosphate (CS) treatments were not as significant as those of the urea phosphate (UP) and monopotassium phosphate (MP) treatments. This was closely related to the acidic solution conditions, which resulted in weaker adhesion abilities of the latter two fertilizers. Compared to SP, PLFAs and EPS contents in the AB fertilizer treatment, MP treatment reduced by 14.9%, 16.1% and 21.8%, respectively. Despite their differences, significant linear correlations of biofilm components were all observed among six fertilizer treatments (R2 > 0.98, p < 0.05). From the perspective of effective control in biofilms’ accumulation, UP and MP were more suitable for drip irrigation system using the reclaimed water. The results obtained in this study could offer reliable guidance for appropriate fertilizer selection when reusing the reclaimed water in the drip irrigation systems.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiyer KS, Vijayakumar BS (2019) An improvised microtiter dish biofilm assay for non-invasive biofilm detection on microbial fuel cell anodes and studying biofilm growth conditions. Braz J Microbiol 50(3):769–775
Becerra-Castro C, Lopes AR, Vaz-Moreira I et al (2015) Wastewater reuse in irrigation: a microbiological perspective on implications in soil fertility and human and environmental health. Environ Int 75:117–135
Duran-Ros M, Puig-Bargues J, Arbat G et al (2009) Effect of filter, emitter and location on clogging when using effluents. Agric Water Manag 96(1):67–79
Guan YH, Niu WQ, Liu L et al (2018) Effect of potassium sulfate on clogging of dripper with muddy water. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition) 46(10):137–146+154 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Han YP, Liu JX, Guo XS et al (2012) Micro-environment characteristics and microbial communities in activated sludge flocs of different particle size. Biores Technol 124:252–258
Hansen SK, Rainey PB, Haagensen JAJ, Molin S (2007) Evolution of species interactions in a biofilm community. Nature 445:533–536
Hao FZ, Li JS, Wang Z et al (2017) Effect of ions on clogging and biofilm formation in drip emitters applying secondary sewage effluent. Irrig Drain 66(5):687–698
Hao FZ, Li JS, Wang Z et al (2018) Effect of chlorination and acidification on clogging and biofilm formation in drip emitters applying secondary sewage effluent. Trans ASABE 61(4):1351–1363
Laspidou CS, Rittmann BE (2004) Modeling the development of biofilm density including active bacteria, inert biomass, and extracellular polymeric substances. Water Res 38(14–15):3349–3361
Lequette K, Nassim AM, Wéry N (2020) Hydrodynamic effect on biofouling of milli-labyrinth channel and bacterial communities in drip irrigation systems fed with reclaimed wastewater. Sci Total Environ 738:139778
Lequette K, Nassim AM, Adam N et al (2021) Effects of the chlorination and pressure flushing of drippers fed by reclaimed wastewater on biofouling. Sci Total Environ 758:143598
Li YK, Wang TZ, Feng J et al (2014) Biofilms cultivation system for drip irrigation and its application method. Chinese patent: CN 103881898A, 2014-06-25.
Liu Y, Liu Z, Wang F, Chen Y et al (2014) Regulation of aerobic granular sludge reformulation after granular sludge broken: effect of poly aluminum chloride (PAC). Biores Technol 158:201–208
Liu L, Niu WQ, Wu ZG et al (2017) Risk and inducing mechanism of acceleration emitter clogging with fertigation through drip irrigation systems. Trans Chin Soci Agric Mach 48(1):228–236 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu ZY, Xiao Y, Li YK et al (2019) Influence of operating pressure on emitter anti-clogging performance of drip irrigation system with high-sediment water. Agric Water Manag 213:174–184
Liu Y, Ao C, Zeng WZ et al (2021) Simulating water and salt transport in subsurface pipe drainage systems with HYDRUS-2D. J Hydrol 592:125823
Ma CJ, Xiao Y, Puig-Bargues J et al (2020) Using phosphate fertilizer to reduce emitter clogging of drip fertigation systems with high salinity water. J Environ Manag 263:110366
Mridula RM, Manissery JK, Keshavanath P et al (2003) Water quality, biofilm production and growth of fringe-lipped carp (Labeo fimbriatus) in tanks provided with two solid substrates. Bioresour Technol 87(3):263–267
Muhammad T, Zhou B, Liu ZY et al (2021) Effects of phosphorus-fertigation on emitter clogging in drip irrigation system with saline water. Agric Water Manag 243:106392
Salama Y, Chennaoui M, Sylla A et al (2016) Characterization, structure, and function of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial biofilm in biological wastewater treatment systems: a review. Desalin Water Treat 57(35):16220–16237
Sharma VK, Burnett CR, O’Connor DB et al (2002) Iron(VI) and iron(V) oxidation of thiocyanate. Environ Sci Technol 36(19):4182–4416
Solé-Torres C, Puig-Bargués J, Duran-Ros M et al (2019) Effect of underdrain design, media height and filtration velocity on the performance of microirrigation sand filters using reclaimed effluents. Biosyst Eng 187:292–304
Wang J, Chen R, Yang T, Wei T, Wang XK (2021) A computationally-efficient finite element method for the hydraulic analysis and design of subsurface drip irrigation subunits. J Hydrol 595:125990
Watnick P, Kolter R (2000) Biofilm, city of microbes. J Bacteriol 182(10):2675–2679
Xiao J, Koo H (2010) Structural organization and dynamics of exopolysaccharide matrix and microcolonies formation by Streptococcus mutans in biofilms. J Appl Microbiol 108(6):2103–2113
Yi L, Jiao W, Chen X et al (2011) An overview of reclaimed water reuse in China. J Environ Sci 23(10):1585–1593
Zhou B, Li YK, Song P et al (2016) A kinetic model for biofilm growth inside non-PC emitters under reclaimed water drip irrigation. Agric Water Manag 168:23–34
Zhou B, Li YK, Song P et al (2017) Anti-clogging evaluation for drip irrigation emitters using reclaimed water. Irrig Sci 35:181–192
Zhou B, Wang D, Wang TZ et al (2018) Chemical clogging behavior in drip irrigation systems using reclaimed water. Trans ASABE 61(5):1667–1675
Zhou B, Li YK, Liu YZ et al (2019a) Critical controlling threshold of internal water shear force of anti-clogging drip irrigation emitters using reclaimed water. Irrig Sci 37(4):469–481
Zhou HX, Li YK, Wang Y et al (2019b) Composite fouling of drip emitters applying surface water with high sand concentration: dynamic variation and formation mechanism. Agric Water Manag 215:25–43
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the financial support from the Science and Technology Project of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps of China (2020DB004) and National Natural Science Fundation of China (51621061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Zhou, B., Zhang, J. et al. Effects of fertilizer types on biofilm growth in the drip irrigation system using the reclaimed water. Irrig Sci 39, 725–734 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-021-00738-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-021-00738-y