Abstract
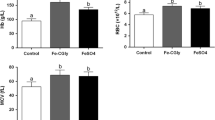
The objective of the present study was to investigate the impact of iron deficiency and iron replenishment on serum iron (Fe), copper (Cu), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn) speciation and tissue accumulation in a deferrioxamine-induced model of iron deficiency. A total of 26 male Wistar rats were divided into three groups: control; Fe-deficient; Fe-replenished (with iron (II) gluconate). Serum ferritin and transferrin levels were assessed using immunoturbudimetric method. Liver, spleen, and serum metal levels were assessed using ICP-MS. Speciation analysis was performed using a hyphenated HPLC-ICP-MS technique. Desferrioxamine injections resulted in a significant decrease in tissue iron content that was reversed by Fe supplementation. Iron speciation revealed a significant increase in serum transferrin-bound iron and reduced ferritin-bound Fe levels. Serum but not tissue Cu levels were characterized by a significant decrease in hypoferremic rats, whereas ceruloplasmin-bound fraction tended to increase. At the same time, Zn levels were found to be higher in liver, spleen, and serum of Fe-deficient rats with a predominant increase in low molecular weight fraction.Both iron-deficient and iron-replenished rats were characteirzed by increased transferrin-bound Mn levels and reduced low-molecular weight fraction. Hypothetically, these differences may be associated with impaired Fe metabolism under Fe-deficient conditions predisposing to impairment of essential metal handling. However, further studies aimed at assessment of the impact on Fe deficiency on metal metabolism are highly required.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiken SP, Horn NM, Saunders NR (1992) Effects of amino acids on zinc transport in rat erythrocytes. Journal Physiol 445:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018912
Ajsuvakova OP, Tinkov AA, Aschner M et al (2020a) Sulfhydryl groups as targets of mercury toxicity. Coord Chem Rev 417:213343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213343
Ajsuvakova OP, Tinkov AA, Willkommen D et al (2020b) Assessment of copper, iron, zinc and manganese status and speciation in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a pilot study. J Trace Elem Med Biol 59:126423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2019.126423
Alker W, Schwerdtle T, Schomburg L, Haase H (2019) A zinpyr-1-based fluorimetricmicroassay for free zinc in human serum. Int J Mol Sci 20:4006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20164006
Alleyne M, Horne MK, Miller JL (2008) Individualized treatment for iron-deficiency anemia in adults. Am J Med 121:943–948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.07.012
Angelova MG, Petkova-Marinova TV, Pogorielov MV, Loboda AN, Nedkova-Kolarova VN, Bozhinova AN (2014) Trace element status (iron, zinc, copper, chromium, cobalt, and nickel) in iron-deficiency anaemia of children under 3 years. Anemia. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/718089
Beaumier DL, Caldwell MA, Holbein BE (1984) Inflammation triggers hypoferremia and de novo synthesis of serum transferrin and ceruloplasmin in mice. Infect Immun 46:489–494
Bjørklund G, Aaseth J, Skalny AV, Suliburska J, Skalnaya MG, Nikonorov AA, Tinkov AA (2017) Interactions of iron with manganese, zinc, chromium, and selenium as related to prophylaxis and treatment of iron deficiency. J Trace Elem Med Biol 41:41–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.02.005
Chakrabarti M, Cockrell AL, Park J, McCormick SP, Lindahl LS, Lindahl PA (2015) Speciation of iron in mouse liver during development, iron deficiency, IRP2 deletion and inflammatory hepatitis. Metallomics 7:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4MT00215F
Collins JF, Prohaska JR, Knutson MD (2010) Metabolic crossroads of iron and copper. Nutr Rev 68:133–147. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2010.00271.x
Cottin SC, Roussel G, Gambling L, Hayes HE, Currie VJ, McArdle HJ (2019) The effect of maternal iron deficiency on zinc and copper levels and on genes of zinc and copper metabolism during pregnancy in the rat. Br J Nutr 121:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114518003069
Eid C, Hémadi M, Ha-Duong NT, Chahine JMEH (2014) Iron uptake and transfer from ceruloplasmin to transferrin. BiochimBiophys Acta 1840:1771–1781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.01.011
Erikson KM, Pinero DJ, Connor JR, Beard JL (1997) Regional brain iron, ferritin and transferrin concentrations during iron deficiency and iron repletion in developing rats. J Nutr 127:2030–2038. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/127.10.2030
Filippini T, Michalke B, Grill P et al (2017) Determinants of serum manganese levels in an Italian population. Mol Med Rep 15:3340–3349. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6379
Fitsanakis VA, Zhang N, Garcia S, Aschner M (2010) Manganese (Mn) and iron (Fe): interdependency of transport and regulation. Neurotox Res 18:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9130-1
Garrick MD, Singleton ST, Vargas F et al (2006) DMT1: which metals does it transport? Biol Res 39:79–85. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0716-97602006000100009
Graham RD, Knez M, Welch RM (2012) How much nutritional iron deficiency in humans globally is due to an underlying zinc deficiency? In: Sparks DL (ed) Advances in agronomy, vol 115. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 1–40
Gropper SS, Bader-Crowe DM, McAnulty LS, White BD, Keith RE (2002) Non-anemic iron depletion, oral iron supplementation and indices of copper status in college-aged females. J Am Coll Nutr 21:545–552. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2002.10719253
Gunter TE, Gerstner B, Gunter KK et al (2013) Manganese transport via the transferrin mechanism. Neurotoxicology 34:118–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2012.10.018
Gürgöze MK, Ölçücü A, Aygün AD, Taşkin E, Kiliç M (2006) Serum and hair levels of zinc, selenium, iron, and copper in children with iron-deficiency anemia. Biol Trace Elem Res 111:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1385/BTER:111:1:23
Keshav S, Stevens R (2017) New concepts in iron deficiency anaemia. Brit J Genl Pract 67:10–11. https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgp17X688465
Knez M, Graham RD, Welch RM, Stangoulis JC (2017) New perspectives on the regulation of iron absorption via cellular zinc concentrations in humans. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 57:2128–2143. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2015.1050483
Kondaiah P, Yaduvanshi PS, Sharp PA, Pullakhandam R (2019) Iron and zinc homeostasis and interactions: does enteric zinc excretion cross-talk with intestinal iron absorption? Nutrients 11:1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081885
Lee SH, Choi SC, Chae BJ, Lee JK, Acda SP (2001) Evaluation of metal-amino acid chelates and complexes at various levels of copper and zinc in weanling pigs and broiler chicks. Asian Austral J Anim 14:1734–1740. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.2001.1734
Lenartowicz M, Kennedy C, Hayes H, McArdle HJ (2015) Transcriptional regulation of copper metabolism genes in the liver of fetal and neonatal control and iron-deficient rats. Biometals 28:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-014-9802-z
Lopez A, Cacoub P, Macdougall IC, Peyrin-Biroulet L (2016) Iron deficiency anaemia. Lancet 387:907–916. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60865-0
Maret W (2015) Analyzing free zinc (II) ion concentrations in cell biology with fluorescent chelating molecules. Metallomics 7:202–211. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4MT00230J
Michalke B, Aslanoglou L, Ochsenkühn-Petropoulou M et al (2015) An approach for manganese biomonitoring using a manganese carrier switch in serum from transferrin to citrate at slightly elevated manganese concentration. J Trace Elem Med Biol 32:145–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2015.07.006
Michalke B, Halbach S, Berthele A, Mistritiotis P, Ochsenkühn-Petropoulou M (2007) Size characterization of manganese species from human serum and cerebrospinal fluid using size exclusion chromatography coupled to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Anal AtSpectrom 22:267–272. https://doi.org/10.1039/B610639K
Mobarra N, Shanaki M, Ehteram H et al (2016) A review on iron chelators in treatment of iron overload syndromes. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res 10:239
Mukhopadhyay CK, Mazumder B, Fox PL (2000) Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in transcriptional activation of ceruloplasmin by iron deficiency. J Biol Chem 275:21048–21054. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M000636200
Nam H, Knutson MD (2012) Effect of dietary iron deficiency and overload on the expression of ZIP metal-ion transporters in rat liver. Biometals 25:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9487-5
Neth K, Lucio M, Walker A et al (2015) Diverse serum manganese species affect brain metabolites depending on exposure conditions. Chem Res Toxicol 28:1434–1442. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00104
Neth K, Lucio M, Walker A et al (2015) Changes in Brain Metallome/Metabolome Pattern due to a Single i. V. Injection of Manganese in Rats. PLoS ONE 10:e0138270. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0138270
Nischwitz V, Berthele A, Michalke B (2008) Speciation analysis of selected metals and determination of their total contents in paired serum and cerebrospinal fluid samples: an approach to investigate the permeability of the human blood-cerebrospinal fluid-barrier. Anal Chim Acta 627:258–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2008.08.018
Oladiji TA (2003) Tissue levels of iron, copper, zinc and magnesium in iron deficient rats. Biokemistri 14:75–81
Papanikolaou G, Gkouvatsos K, Pantopoulos K (2018) Transferrin. In: Choi S (ed) Encyclopedia of signaling molecules. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-67199-4
Prasad AS, Oberleas D (1970) Binding of zinc to amino acids and serum proteins in vitro. J Lab Clin Med 76:416–425. https://doi.org/10.5555/uri:pii:0022214370900508
Ranganathan PN, Lu Y, Jiang L, Kim C, Collins JF (2011) Serum ceruloplasmin protein expression and activity increases in iron-deficient rats and is further enhanced by higher dietary copper intake. Blood 118:3146–3153. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-05-352112
Reeves PG, Chaney RL (2004) Marginal nutritional status of zinc, iron, and calcium increases cadmium retention in the duodenum and other organs of rats fed rice-based diets. Environ Res 96:311–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2004.02.013
Sarpong-Kumankomah S, Gailer J (2019) Identification of a haptoglobin-hemoglobin complex in human blood plasma. J Inorg Biochem 201:110802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.110802
Seo YA, Li Y, Wessling-Resnick M (2013) Iron depletion increases manganese uptake and potentiates apoptosis through ER stress. Neurotoxicology 38:67–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2013.06.002
Shukla A, Agarwal KN, Shukla GS (1990) Effect of latent iron deficiency on the levels of iron, calcium, zinc, copper, manganese, cadmium and lead in liver, kidney and spleen of growing rats. Experientia 46:751–752. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01939956
Smith EA, Newland P, Bestwick KG, Ahmed N (2013) Increased whole blood manganese concentrations observed in children with iron deficiency anaemia. J Trace Elem Med Biol 27:65–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2012.07.002
Stelle I, Kalea AZ, Pereira DI (2019) Iron deficiency anaemia: experiences and challenges. Proc Nutr Soc 78:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665118000460
Stoltzfus RJ (2003) Iron deficiency: global prevalence and consequences. Food Nutr Bull 24:S99–S103. https://doi.org/10.1177/15648265030244S106
Tai YK, Chew KC, Tan BW, Lim KL, Soong TW (2016) Iron mitigates DMT1-mediated manganese cytotoxicity via the ASK1-JNK signaling axis: implications of iron supplementation for manganese toxicity. Sci Rep 6:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21113
Tong X, Kawabata H, Koeffler HP (2002) Iron deficiency can upregulate expression of transferrin receptor at both the mRNA and protein level. Br J Haematol 116:458–464. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2141.2002.03289.x
Vincent JB, Love S (2012) The binding and transport of alternative metals by transferrin. BiochimBiophys Acta 1820:362–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2011.07.003
Wang W, Knovich MA, Coffman LG, Torti FM, Torti SV (2010) Serum ferritin: past, present and future. BiochimBiophys Acta 1800:760–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2010.03.011
Willkommen D, Lucio M, Schmitt-Kopplin P et al (2018) Species fractionation in a case-control study concerning Parkinson’s disease: Cu-amino acids discriminate CSF of PD from controls. J Trace Elem Med Biol 49:164–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2018.01.005
Ye Q, Park JE, Gugnani K, Betharia S, Pino-Figueroa A, Kim J (2017) Influence of iron metabolism on manganese transport and toxicity. Metallomics 9:1028–1046. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00079K
Yokoi T, Hattori S, Ishii K (2019) Encapsulation of zinc phthalocyanine into bovine serum albumin aggregates. J Coord Chem 72:707–715. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2019.1566538
Zhang N, Fitsanakis VA, Erikson KM, Aschner M, Avison MJ, Gore JC (2009) A model for the analysis of competitive relaxation effects of manganese and iron in vivo. NMR Biomed 22:391–404. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1348
Zhdanov VV, Udut EV, Sotnikova LS et al (2016) Pathogenetic evaluation of dysfunction in the erythron system of experimental animals during modeling of iron deficiency anemia in the gestation period. Bull Exp Biol Med 160:417–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3185-9
Acknowledgements
The manuscript prepared with support of The Foundation for Assistance to Small Innovative Enterprises within the Project No. 379GRNTIS5/42620 from 23.08.2018 (0042620) Application No. NTI-48849.
Funding
The study was funded by Foundation for Assistance to Small Innovative Enterprises in Science and Technology (Grant No. 379GRNTIS5/42620).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10534_2021_318_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Figure S1. SEC-ICP-MS chromatograms of used standards: A - SEC-ICP-MS chromatograms of the iron blood serum species (red curve) and calibration standards (black curve – ferritin; blue curve – transferrin; green curve – iron (III) citrate, yellow - albumine). Preparation of metal complexes with chosen ligands was performed according to section ‘2.4. Speciation analysis of Fe, Zn, Cu, Mn in blood serum’. The peak corresponding to albumin is lower, because the complex of multimetal standard with albumin gave a pronounced signal in the case of copper, but not in the iron case. To our opinion this fact can be explained the high binding affinity of Cu and the low binding affinity of Fe. B – SEC-ICP-MS chromatograms for an albumin standard containing Cu and Fe at the same concentrations. The plot was obtained as a result of overlaying of the individual chromatograms. Supplementary file 1 (TIF 287 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ajsuvakova, O.P., Skalnaya, M.G., Michalke, B. et al. Alteration of iron (Fe), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), and manganese (Mn) tissue levels and speciation in rats with desferioxamine-induced iron deficiency. Biometals 34, 923–936 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-021-00318-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-021-00318-9