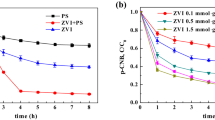
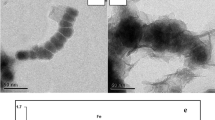
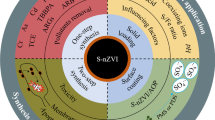
Abstract
Under the action of different activators, persulfate can produce sulfate radicals (SO4·–) with strong oxidizing ability, which can destruct many organic compounds. Meanwhile, persulfate is widely used in groundwater and soil remediation because of its fast reaction and wide application. With the high specific surface area and reactivity of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI), it can enhance the degradation efficiency of the persulfate system on organic pollutants in soil and water as a persulfate activator. However, nZVI is easy to get oxidized and has a tendency to aggregation. To solve these problems, a variety of nZVI modification methods have been put forward and put into to applications in the activation of persulfate. This article will give a systematic introduction of the background and problems of nZVI-activated persulfate in the remediation of organic pollution. In addition, the modification methods and mechanisms of nZVI are summarized, and the applications and progress of modified nZVI-activated persulfate are reviewed. The factors that affect the removal of organic compounds by the activation system are discussed as well. Worldwide, the field studies and full-scale remediation using modified nZVI in persulfate activation are yet limited. However, the already known cases reveal the good prospect of applying modified nZVI in persulfate activation to organic pollution remediation.
Graphical abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Abd El-Lateef HM, KhalafAli MM, Saleh MM (2018) Adsorption and removal of cationic and anionic surfactants using zero-valent iron nanoparticles. J Mol Liq 268:497–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.07.093
Adamek E, Baran W, Ziemianska J, Sobczak A (2012) Effect of FeCl3 on sulfonamide removal and reduction of antimicrobial activity of wastewater in a photocatalytic process with TiO2. Appl Catal B Environ 126:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.06.027
Akbari S, Ghanbari F, Moradi M (2016) Bisphenol A degradation in aqueous solutions by electrogenerated ferrous ion activated ozone, hydrogen peroxide and persulfate: Applying low current density for oxidation mechanism. Chem Eng J 294:298–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.02.106
Al-Shamsi MA, Thomson NR (2013) Treatment of Organic Compounds by Activated Persulfate Using Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:13564–13571. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie400387p
Altuntas K, Debik E, Kozal D, Yoruk II (2017) Adsorption of copper metal ion from aqueous solution by Nanoscale Zero Valent Iron (nZVI) supported on activated carbon (Article). Period Eng Nat Sci 5(1):61–64. https://doi.org/10.21533/pen.v5i1.77
Ariel NG, Hardiljeet KB, Cjestmir V, de Boer, Ahmed IAC, Chris MDK, Leanne MA, Jose H, Denis MO (2020) Fate and transport of sulfidated nano zerovalent iron (S-nZVI): A field study. Water Res 170:115319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115319
Binh N, Imsapsangworn C, Oanh N, Parkpian P, Karstensen K, Giao P, DeLaune R (2016) Sequential anaerobic–aerobic biodegradation of 2,3,7,8-TCDD contaminated soil in the presence of CMC-coated nZVI and surfactant. Environ Technol 37(3):388–398. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2015.1070918
Bouzid I, Maire J, Fatin-Rouge N (2019) Comparative assessment of a foam-based method for ISCO of coal tar contaminated unsaturated soils (Article). J Environ Chem Eng 7:2213–3437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103346
Bu L, Shi Z, Zhou S (2016) Modeling of Fe(II)-activated persulfate oxidation using atrazine as a target contaminant. Sep Purif Technol 169:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2016.05.037
Butler EC, Hayes KF (2001) Factors influencing rates and products in the transformation of trichloroethylene by iron sulfide and iron metal. Environ Sci Technol 35:3884–3891. https://doi.org/10.1021/es010620f
Cai J, Zhou M, Liu Y (2018) Indirect electrochemical oxidation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid using electrochemically-generated persulfate. Chemosphere 204:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.04.004
Cao Z, Liu X, Xu J, Zhang J, Yang Y, Zhou J, Xu X, Lowry GV (2017) Removal of Antibiotic Florfenicol by Sulfide-Modified Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron. Environ Sci Technol 51:11269–11277. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02480
Cao J, Lai L, Lai B, Yao G, Chen X, Song L (2019) Degradation of tetracycline by peroxymonosulfate activated with zero-valent iron: Performance, intermediates, toxicity and mechanism. Chem Eng J 364:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.113
Carmen S, Rodrigues D, Luis MM (2020) p-Nitrophenol degradation by activated persulfate. Environ Technol Innov 21:101265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101265
Chen J, Qian Y, Liu H, Huang T (2016) Oxidative degradation of diclofenac by thermally activated persulfate: implication for ISCO. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:3824–3833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5630-0
Chen, X., Ji, D., Wang, X., Zang, L., 2017. Review on Nano zerovalent Iron (nZVI): From Modification to Environmental Applications. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. 51,012004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/51/1/012004
Chen L, Hu X, Cai T, Yang Y, Zhao R, Liu C, Li A, Jiang C (2019) Degradation of Triclosan in soils by thermally activated persulfate under conditions representative of in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO). Chem Eng J 369:344–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.084
Chrysochoou M, Reeves K (2017) Reduction of Hexavalent Chromium by Green Tea Polyphenols and Green Tea Nano Zero-Valent Iron (GT-nZVI). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98(3):353–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1901-9
Crane RA, Scott TB (2012) Nanoscale zero-valent iron: Future prospects for an emerging water treatment technology. J Hazard Mater 211-212:112–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.11.073
Daraei H, Rafiee M, Yazdanbakhsh A, Amoozegar M, Guanglei Q (2019) A comparative study on the toxicity of nano zero valent iron (nZVI) on aerobic granular sludge and flocculent activated sludge: Reactor performance, microbial behavior, and mechanism of toxicity. Process Saf Environ Protect: Transact Inst Chem Eng B 129:238–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.07.011
De Laat J, Truong Le G, Legube B (2004) A comparative study of the effects of chloride, sulfate and nitrate ions on the rates of decomposition of H2O2 and organic compounds by Fe(II)/H2O2 and Fe(III)/H2O2. Chemosphere (Oxford) 55:715–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.11.021
Deng J, Dong H, Li L, Wang Y, Ning Q, Wang B, Zeng G (2019) Ca(OH)2 coated nanoscale zero-valent iron as a persulfate activator for the degradation of sulfamethazine in aqueous solution. Sep Purif Technol 227:115731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115731
Desalegn B, Megharaj M, Chen Z, Naidu R (2018) Green mango peel-nanozerovalent iron activated persulfate oxidation of petroleum hydrocarbons in oil sludge contaminated soil. Environ Technol Innov 11:142–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2018.05.007
Diao Z, Xu X, Jiang D, Kong L, Sun Y, Hu Y, Hao Q, Chen H (2016) Bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron/persulfate system for the simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and phenol from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 302:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.062
Dong H, He Q, Zeng G, Tang L, Zhang C, Xie Y, Zeng Y, Zhao F, Wu Y (2016) Chromate removal by surface-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron: Effect of different surface coatings and water chemistry. J Colloid Interface Sci 471:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.03.011
Dong H, Deng J, Xie Y, Zhang C, Jiang Z, Cheng Y, Hou K, Zeng G (2017) Stabilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 332:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.03.002
Dong H, Hou K, Qiao W, Cheng Y, Zhang L, Wang B, Li L, Wang Y, Ning Q, Zeng G (2019a) Insights into enhanced removal of TCE utilizing sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron activated persulfate. Chem Eng J 359:1046–1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.080
Dong H, Wang B, Li L, Wang Y, Ning Q, Tian R, Li R, Chen J, Xie Q (2019b) Activation of persulfate and hydrogen peroxide by using sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron for oxidative degradation of sulfamethazine: A comparative study. Sep Purif Technol 218:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.02.052
Dong H, Ning Q, Li L, Wang Y, Wang B, Zhang L, Tian R, Li R, Chen J, Xie Q (2020) A comparative study on the activation of persulfate by bare and surface-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron for the removal of sulfamethazine. Sep Purif Technol 230:115869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115869
Drzewicz P, Perez-Estrada L, Alpatova A, Martin JW, Gamal EM (2012) Impact of peroxydisulfate in the presence of zero valent iron on the oxidation of cyclohexanoic acid and naphthenic acids from oil sands process-affected water. Environ Sci Technol 46:8984–8991. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3011546
Du J, Bao J, Lu C, Werner D (2016) Reductive sequestration of chromate by hierarchical FeS@Fe0 particles. Water Res 102:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.06.009
Eljamal R, Eljamal O, Maamoun I, Yilmaz G, Sugihara Y (2020) Enhancing the characteristics and reactivity of nZVI: Polymers effect and mechanisms. J Mol Liq 315:0167–7322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2020.113714
Epold I, Trapido M, Dulova N (2015) Degradation of levofloxacin in aqueous solutions by Fenton, ferrous ion-activated persulfate and combined Fenton/persulfate systems. Chem Eng J 279:452–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.054
Fajardo C, Garcí, a-Cantalejo J, Botí ASP, Costa G, Nande M, Martin M (2019) New insights into the impact of nZVI on soil microbial biodiversity and functionality. J Environ Sci Health A: Toxic/Hazard Subst Environ Eng 54(3):157–167. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2018.1535159
Fan D, O Brien Johnson G, Tratnyek PG, Johnson RL (2016) Sulfidation of Nano Zerovalent Iron (nZVI) for Improved Selectivity During In-Situ Chemical Reduction (ISCR). Environ Sci Technol 50:9558–9565. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02170
Fan Z, Zhang Q, Gao B, Li M, Liu C, Qiu Y (2019) Removal of hexavalent chromium by biochar supported nZVI composite: Batch and fixed-bed column evaluations, mechanisms, and secondary contamination prevention. Chemosphere. 217:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.009
Fang G, Dionysiou DD, Al-Abed SR, Zhou D (2013a) Superoxide radical driving the activation of persulfate by magnetite nanoparticles: Implications for the degradation of PCBs. Appl Catal B Environ 129:325–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.09.042
Fang G, Gao J, Dionysiou DD, Liu C, Zhou D (2013b) Activation of Persulfate by Quinones: Free Radical Reactions and Implication for the Degradation of PCBs. Environ Sci Technol 47:4605–4611. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400262n
Farhat A, Keller J, Tait S, Radjenovic J (2015) Removal of Persistent Organic Contaminants by Electrochemically Activated Sulfate. Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b02705
Franze A (2015) Accelerated Degradation of Chlorinated Solvents byCopper-Modified Nanoscale Zero Valent Iron (Cu-nZVI) Stabilizedwith Carboxymethyl Cellulose. Wright State University
Fu X, Zhang J, Zhao H, Zhang S, Nie T, Zhang Y, Lu J (2020) Enhanced peroxymonosulfate activation by coupling zeolite-supported nano-zero-valent iron with weak magnetic field. Sep Purif Technol 230:115886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115886
Gao Y, Gao N, Wang W, Kang S, Xu J, Xiang H, Yin D (2018) Ultrasound-assisted heterogeneous activation of persulfate by nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) for the propranolol degradation in water. Ultrason Sonochem 49:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.07.001
Gao J, Han D, Xu Y, Liu Y, Shang J (2020a) Persulfate activation by sulfide-modified nanoscale iron supported by biochar (S-nZVI/BC) for degradation of ciprofloxacin. Sep Purif Technol 235:116202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.116202
Gao Y, Zhang J, Zhou J, Li C, Gao N, Yin D (2020b) Persulfate activation by nano zero-valent iron for the degradation of metoprolol in water: influencing factors, degradation pathways and toxicity analysis. RSC Adv 35(10):20991–20999
Gopal G, Sankar H, Natarajan C, Mukherjee A (2020) Tetracycline removal using green synthesized bimetallic nZVI-Cu and bentonite supported green nZVI-Cu nanocomposite: A comparative study (Article). J Environ Manag 254:109812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109812
Greenlee LF, Torrey JD, Amaro RL, Shaw JM (2012) Kinetics of Zero Valent Iron Nanoparticle Oxidation in Oxygenated Water. Environ Sci Technol 46:12913–12920. https://doi.org/10.1021/es303037k
Gu Y, Wang B, He F, Bradley MJ, Tratnyek PG (2017) Mechanochemically Sulfidated Microscale Zero Valent Iron: Pathways, Kinetics, Mechanism, and Efficiency of Trichloroethylene Dechlorination. Environ Sci Technol 51:12653–12662. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b03604
Gu M, Farooq U, Lu S, Zhang X, Qiu Z, Sui Q (2018) Degradation of trichloroethylene in aqueous solution by rGO supported nZVI catalyst under several oxic environments. J Hazard Mater 349:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.01.037
Guo W, Zhao Q, Du J, Wang H, Li X, Ren N (2020) Enhanced removal of sulfadiazine by sulfidated ZVI activated persulfate process: Performance, mechanisms and degradation pathways. Chem Eng J 388:124303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124303
Habish A, Lazarević S, Janković-Častvan I, Jokić B, Rogan J, Janaćković Đ, Petrović R, Kovač J (2017) Nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI) supported by natural and acid-activated sepiolites: the effect of the nZVI/support ratio on the composite properties and Cd adsorption. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(1):628–643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7802-y
Hamid S, Abudanash D, Han S, Kim JR, Lee W (2019) Strategies to enhance the stability of nanoscale zero-valent iron (NZVI) in continuous BrO3− reduction. J Environ Manag 231:714–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.026
He F, Zhao D, Paul C (2010) Field assessment of carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized iron nanoparticles for in situ destruction of chlorinated solvents in source zones. Water Res 44:2360–2370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.12.041
Helman WP, Ross AB (1990) Bibliographies on radiation chemistry: XII. Rate constants for reactions of nonmetallic inorganic radicals in aqueous solution. J Radiat Appl Instrument C Radiat Phys Chem 36:845–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/1359-0197(90)90188-N
Herlekar M, Barve S, Kumar R (2014) Plant-Mediated Green Synthesis of Iron Nanoparticles. J Nanopart 2014:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/140614
Hernandez R, Zappi M, Kuo C (2004) Chloride Effect on TNT Degradation by Zerovalent Iron or Zinc during Water Treatment. Environ Sci Technol 38:5157–5163. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049815o
Hoag GE, Collins JB, Holcomb JL, Hoag JR, Nadagouda MN, Varma RS (2009) Degradation of bromothymol blue by ‘greener’ nano-scale zero-valent iron synthesized using tea polyphenols. J Mater Chem 19:8671. https://doi.org/10.1039/b909148c
Hou X, Zhan G, Huang X, Wang N, Ai Z, Zhang L (2019) Persulfate activation induced by ascorbic acid for efficient organic pollutants oxidation. Chem Eng J 382:122355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122355
Hua Y, Liu J, Gu T, Wang W, Zhang W (2018) The colorful chemistry of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI). J Environ Sci 67:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.04.025
Huang L, Zhou S, Jin F, Huang J, Bao N (2014) Characterization and mechanism analysis of activated carbon fiber felt-stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 447:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.01.037
Huang L, Liu Q, Zhou S, Xue J, Liu G (2016) Laboratory investigation of a magnetic system used for enhancing the migration of nanoscale zero-valent iron (NZVI)(Article). J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 61:205–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2015.12.011
Huang J, Yi S, Zheng C, Lo I (2019) Persulfate activation by natural zeolite supported nanoscale zero-valent iron for trichloroethylene degradation in groundwater. Sci Total Environ 684:351–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.05.331
Huang X, Zhang F, Peng K, Liu J, Lu L, Li S (2020) Effect and Mechanism of Graphene Structured Palladized Zero-Valent Iron Nanocomposite (nZVI-Pd/NG) for Water Denitration. Sci Rep 10(1):9931. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66725-z
Ike IA, Foster SL, Shinn SR, Watson ST, Orbell JD, Greenlee LF, Duke MC (2017) Advanced oxidation of orange G using phosphonic acid stabilised zerovalent iron. J Environ Chem Eng 5:4014–4023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.07.069
Indra H, Elke E, Michael JP, Nazende G, Akif Emre T, Marc W, Christoph S, Martina F, Matthias G, Wacker (2020) Evaluation of potential environmental toxicity of polymeric nanomaterials and surfactants. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 76:103353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2020.103353
Jaroslav S, Natividad INP, Alena G, Petra P, Martin P, Lenka P, Tomas C (2020) In Vitro Study of the Toxicity Mechanisms of Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) and Released Iron Ions Using Earthworm Cells. Nanomaterials (Basel, Switzerland) 10(11):E2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112189
Ji Y, Dong C, Kong D, Lu J, Zhou Q (2015) Heat-activated persulfate oxidation of atrazine: Implications for remediation of groundwater contaminated by herbicides. Chem Eng J 263:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.10.097
Jiang D, Hu X, Wang R, Wang Y, Yin D (2017) The decreasing aggregation of nanoscale zero-valent iron induced by trivalent chromium. Environ Chem 14(2):99–105. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN16144
Jiang Z, Li J, Jiang D, Gao Y, Chen Y, Wang W, Cao B, Tao Y, Wang L, Zhang Y (2020) Removal of atrazine by biochar-supported zero-valent iron catalyzed persulfate oxidation: Reactivity, radical production and transformation pathway. Environ Res 184:109260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109260
Kang J, Wu W, Liu W, Li J, Dong C (2019) Zero-valent iron (ZVI) Activation of Persulfate (PS) for Degradation of Para-Chloronitrobenzene in Soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 103(1):140–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2511-5
Kim E, Kim J, Chang Y, Turcio-Ortega D, Tratnyek PG (2014) Effects of Metal Ions on the Reactivity and Corrosion Electrochemistry of Fe/FeS Nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 48:4002–4011. https://doi.org/10.1021/es405622d
Kim C, Ahn J, Kim T, Shin W, Hwang I (2018) Activation of Persulfate by Nanosized Zero-Valent Iron (NZVI): Mechanisms and Transformation Products of NZVI. Environ Sci Technol 52(6):3625–3633. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b05847
Kocur CM, Chowdhury A, Sakulchaicharoen N, Boparai HK, Weber K, Prabhakar S, Krol MM, Austrins L, Peace C, Sleep B, O'Carroll D (2014) Characterization of nZVI Mobility in a Field Scale Test. Environ Sci Technol 48(5):2862–2869. https://doi.org/10.1021/es4044209
Kustov LM, Finashina ED, Shuvalova EV, Tkachenko OP, Kirichenko OA (2011) Pd-Fe nanoparticles stabilized by chitosan derivatives for perchloroethene dechlorination. Environ Int 37:1044–1052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2011.05.003
Lefevre E, Bossa N, Wiesner MR, Gunsch CK (2016) A review of the environmental implications of in situ remediation by nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI): behavior, transport and impacts on microbial communities. Sci Total Environ 565:889–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.003
Li H, Wan J, Ma Y, Huang M, Wang Y, Chen Y (2014a) New insights into the role of zero-valent iron surface oxidation layers in persulfate oxidation of dibutyl phthalate solutions. Chem Eng J 250:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.092
Li H, Wan J, Ma Y, Wang Y, Huang M (2014b) Influence of particle size of zero-valent iron and dissolved silica on the reactivity of activated persulfate for degradation of acid orange 7. Chem Eng J 237:487–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.10.035
Li R, Jin X, Megharaj M, Naidu R, Chen Z (2015) Heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of 2,4-dichlorophenol using iron-based nanoparticles and persulfate system. Chem Eng J 264:587–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.128
Li J, Zhang X, Sun Y, Liang L, Pan B, Zhang W, Guan X (2017a) Advances in Sulfidation of Zerovalent Iron for Water Decontamination. Environ Sci Technol 51:13533–13544. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b02695
Li X, Zhou M, Pan Y, Xu L (2017b) Pre-magnetized Fe0/persulfate for notably enhanced degradation anddechlorination of 2,4-dichlorophenol. Chem Eng J 307:1092–1104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.140
Li A, Wu Z, Wang T, Hou S, Huang B, Kong X, Li X, Guan Y, Qiu R, Fang J (2018a) Kinetics and mechanisms of the degradation of PPCPs by zero-valent iron (Fe degrees) activated peroxydisulfate (PDS) system in groundwater. J Hazard Mater 357:207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.06.008
Li M, Pei J, Tang X, Guo X (2018b) Effects of surfactants on the combined toxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles and cadmium to Escherichia coli. J Environ Sci 74(12):126–133
Li Y, Zhao X, Yan Y, Yan J, Pan Y, Zhang Y, Lai B (2019) Enhanced sulfamethoxazole degradation by peroxymonosulfate activation with sulfide-modified microscale zero-valent iron (S-mFe(0)): Performance, mechanisms, and the role of sulfur species. Chem Eng J 376:121302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.178
Li J, Fan M, Li M, Liu X (2020a) Cr(VI) removal from groundwater using double surfactant-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI): Effects of materials in different status. Sci Total Environ 717:137112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137112
Li S, Tang J, Liu Q, Liu X, Gao B (2020b) A novel stabilized carbon-coated nZVI as heterogeneous persulfate catalyst for enhanced degradation of 4-chlorophenol. Environ Int 138:0160–4120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105639
Liang C, Lai M (2008) Trichloroethylene Degradation by Zero Valent Iron Activated Persulfate Oxidation. Environ Eng Sci 25:1071–1078. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2007.0174
Liu H, Thomas AB, Li W, Jean V, Carsten P, Fiona MD, David LS (2016a) Oxidation of Benzene by Persulfate in the Presence of Fe(III)- and Mn(IV)-Containing Oxides: Stoichiometric Efficiency and Transformation Products. Environ Sci Technol 50(2):890–898. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b04815
Liu J, Liu A, Zhang W (2016b) The influence of polyelectrolyte modification on nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI): Aggregation, sedimentation, and reactivity with Ni(II) in water. Chem Eng J 303:268–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.132
Liu Z, Zhang F, Hoekman SK, Liu T, Gai C, Peng N (2016c) Homogeneously Dispersed Zerovalent Iron Nanoparticles Supported on Hydrochar-Derived Porous Carbon: Simple, in Situ Synthesis and Use for Dechlorination of PCBs. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:3261–3267. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00306
Liu A, Liu J, Han J, Zhang W (2017) Evolution of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in water: Microscopic and spectroscopic evidence on the formation of nano- and micro-structured iron oxides. J Hazard Mater 322:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.12.070
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Lan S, Hou S (2019) Migration experiment and numerical simulation of modified nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) in porous media. J Hydrol 579:124193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124193
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Wang B, Wang S, Liu M, Wu Y, Lu L, Ren H, Li H, Dong W, Qadeer A (2020) Degradation of ibuprofen in soil systems by persulfate activated with pyrophosphate chelated Fe(II). Chem Eng J 379:1385–8947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122145
Liu J, Liu A, Guo J, Zhou T, Zhang W (2021) Enhanced aggregation and sedimentation of nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with polyacrylamide modification. Chemosphere. 263:125875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.12787
Machado S, Pinto SL, Grosso JP, Nouws HPA, Albergaria JT, Delerue-Matos C (2013a) Green production of zero-valent iron nanoparticles using tree leaf extracts. Sci Total Environ 445-446:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.033
Machado S, Stawiński W, Slonina P, Pinto AR, Grosso JP, Nouws HPA, Albergaria JT, Delerue-Matos C (2013b) Application of green zero-valent iron nanoparticles to the remediation of soils contaminated with ibuprofen. Sci Total Environ 461-462:323–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.05.016
Manz KE, Adams TJ, Carter KE (2018) Furfural degradation through heat-activated persulfate: Impacts of simulated brine and elevated pressures. Chem Eng J 353:727–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.142
Marie C, Nhung HAN, Jan N, Katrin M, Christopher B, Jonathan L, Tamas L, Roman S, Miroslav C, Alena S (2020) In situ pilot application of nZVI embedded in activated carbon for remediation of chlorinated ethene-contaminated groundwater: effect on microbial communities. Environ Sci Eur 32(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-020-00434-2
Matzek LW, Carter KE (2016) Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: A review. Chemosphere (Oxford) 151:178–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.055
Mendes GP, Magalhães VMA, Soares LCR, Aranha RM, Nascimento CAO, Vianna MMGR, Chiavone-Filho O (2020) Treatability studies of naphthalene in soil, water and air with persulfate activated by iron (II). J Environ Sci 90:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.11.015
Meng F, Zhu Y, Li H, Zhang W, Wu S, Zhang G, Li M (2017) Effects of the remediation of Cr(VI) in soil by nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI) with modified biochar(Article). Acta Sci Circumst 37(12):4715–4723. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2017.0240
Mystrioti C, Xanthopoulou TD, Tsakiridis P, Papassiopi N, Xenidis A (2016) Comparative evaluation of five plant extracts and juices for nanoiron synthesis and application for hexavalent chromium reduction. Sci Total Environ 539:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.091
Nie M, Yan C, Li M, Wang X, Bi W, Dong W (2015) Degradation of chloramphenicol by persulfate activated by Fe2+ and zerovalent iron. Chem Eng J 279:507–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.05.055
Nimita F, Subramanian S, Fulvia C, Yendaluru R (2020) Remediation of Lead and Nickel Contaminated Soil Using Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (nZVI) Particles Synthesized Using Green Leaves: First Results. Processes. 8:1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8111453
Olga L, Sunho Y, Sungjun B, Woojin L (2021) The enhanced reduction of bromate by highly reactive and dispersive green nano-zerovalent iron (G-NZVI) synthesized with onion peel extract. RSC Adv 11(9):5008–5018. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA09897C
Pardo F, Rosas JM, Santos A, Romero A (2015) Remediation of a Biodiesel Blend-Contaminated Soil with Activated Persulfate by Different Sources of Iron. Water Air Soil Pollut 226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-014-2267-4
Pate, MF (2015) Coating of NZVI particles with modified starch: Collodial stability and nitrate reduction studies. North Dakota State University
Peluffo M, Pardo F, Santos A, Romero A (2016) Use of different kinds of persulfate activation with iron for the remediation of a PAH-contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 563-564:649–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.034
Peng Y, Chen T, Wu C, Chang Y, Chen K (2019) Dispersant-modified iron nanoparticles for mobility enhancement and TCE degradation: a comparison study. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(33):34157–34166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3739-7
Pérez De La Luz A, Iuga C, Vivier-Bunge A (2020) An effective force field to reproduce the solubility of MTBE in water. Fuel. 264:116761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116761
Petala E, Dimos K, Douvalis A, Bakas T, Tucek J, Zboril R, Karakassides MA (2013) Nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on mesoporous silica: characterization and reactivity for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 261:295–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.046
Qi C, Yu G, Huang J, Wang B, Wang Y, Deng S (2018) Activation of persulfate by modified drinking water treatment residuals for sulfamethoxazole degradation. Chem Eng J 353:490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.056
Rajajayavel SR, Ghoshal S (2015) Enhanced reductive dechlorination of trichloroethylene by sulfidated nanoscale zerovalent iron. Water Res 78:144–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.04.009
Ranc B, Faure P, Croze V, Lorgeoux C, Simonnot M-O (2017) Comparison of the effectiveness of soil heating prior or during in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) of aged PAH-contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:11265–11278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8731-0
Saha AK, Sinha A, Pasupuleti S Modification, Characterization and Investigations of Key Factors Controlling the Transport of Modified Nano Zero Valent Iron (nZVI) in Porous Media. Environ Technol:1–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1426637
Sandip M, Shengyan P, Lixiang S, Shibin L, Hui M, Sangeeta A, Deyi H (2020) Synergistic construction of green tea biochar supported nZVI for immobilization of lead in soil: A mechanistic investigation. Environ Int 135:105374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105374
Shan A, Farooq U, Lyu S, Zaman W, Abbas Z, Ali M, Idrees A, Tang P, Li M, Sun Y, Sui Q (2020) Efficient removal of trichloroethylene in surfactant amended solution by nano Fe0-Nickel bimetallic composite activated sodium persulfate process. Chem Eng J 386:123995. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123995
Shao Y, Hatzinger PB, Streger S, Rezes RT, Chu K-H (2019) Evaluation of methanotrophic bacterial communities capable of biodegrading trichloroethene (TCE) in acidic aquifers. Biodegradation. 30:173–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-019-09875-w
Shi L, Zhang X, Chen Z (2011) Removal of Chromium (VI) from wastewater using bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Water Res 45:886–892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.09.025
Shi J, Long C, Li A (2016) Selective reduction of nitrate into nitrogen using Fe–Pd bimetallic nanoparticle supported on chelating resin at near-neutral pH. Chem Eng J 286:408–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.10.054
Siedlecka EM, Więckowska A, Stepnowski P (2007) Influence of inorganic ions on MTBE degradation by Fenton's reagent. J Hazard Mater 147:497–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.01.044
Silveira JE, Barreto-Rodrigues M, Cardoso TO, Pliego G, Munoz M, Zazo JA, Casas JA (2017) Nanoscale Fe/Ag particles activated persulfate: optimization using response surface methodology. Water Sci Technol 75:2216–2224. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2017.063
Song H, Yan L, Jiang J, Ma J, Pang S, Zhai X, Zhang W, Li D (2018) Enhanced degradation of antibiotic sulfamethoxazole by electrochemical activation of PDS using carbon anodes. Chem Eng J 344:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.03.050
Song Y, Fang G, Zhu C, Zhu F, Wu S, Chen N, Wu T, Wang Y, Gao J, Zhou D (2019) Zero-valent iron activated persulfate remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-contaminated soils: An in situ pilot-scale study. Chem Eng J 355:65–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.126
Sra KS, Thomson NR, Barker JF (2010) Persistence of Persulfate in Uncontaminated Aquifer Materials. Environ Sci Technol 44:3098–3104. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903480k
Su Y, Jassby D, Song S, Zhou X, Zhao H, Filip J, Petala E, Zhang Y (2018) Enhanced Oxidative and Adsorptive Removal of Diclofenac in Heterogeneous Fenton-like Reaction with Sulfide Modified Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron. Environ Sci Technol 52:6466–6475. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b00231
Sukul P, Lamshoeft M, Zuehlke S, Spiteller M (2008) Photolysis of C-14-sulfadiazine in water and manure. Chemosphere (Oxford) 71:717–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.10.045
Tang J, Tang L, Feng H, Zeng G, Dong H, Zhang C, Huang B, Deng Y, Wang J, Zhou Y (2016) pH-dependent degradation of p-nitrophenol by sulfidated nanoscale zerovalent iron under aerobic or anoxic conditions. J Hazard Mater 320:581–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.07.042
Tian H, Liang Y, Yang D, Sun Y (2020) Characteristics of PVP-stabilised NZVI and application to dechlorination of soil-sorbed TCE with ionic surfactant. Chemosphere. 239:124807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124807
Vicente F, Santos A, Romero A, Rodriguez S (2011) Kinetic study of diuron oxidation and mineralization by persulphate: Effects of temperature, oxidant concentration and iron dosage method. Chem Eng J 170:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.03.042
Vilardi G (2019) Mathematical modelling of simultaneous nitrate and dissolved oxygen reduction by Cu-nZVI using a bi-component shrinking core model (Article). Powder Technol 343:613–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2018.11.082
Vilardi G, Parisi M, Verdone N (2019) Simultaneous aggregation and oxidation of nZVI in Rushton equipped agitated vessel: Experimental and modelling. Powder Technol 353:238–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.05.033
Wacławek S, Lutze HV, Grübel K, Padil VVT, Černík M, Dionysiou DD (2017) Chemistry of persulfates in water and wastewater treatment: A review. Chem Eng J 330:44–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.132
Wan J, Li Y, He J, Zhao N, Liu Z, Lin Y, Yang C, Liang W (2019) Effect of mesoporous silica molecular sieve coating on nZVI for 2,4-DCP degradation: Morphology and mechanism during the reaction. Chem Eng Process 135:68–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2018.11.011
Wang Z, Choi F, Acosta E (2017) Effect of Surfactants on Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles (NZVI) Reactivity (Article). J Surfactant Deterg 20(3):577–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-017-19410
Wang B, Li Y, Wang L (2019a) Metal-free activation of persulfates by corn stalk biochar for the degradation of antibiotic norfloxacin: Activation factors and degradation mechanism. Chemosphere. 237:124454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124454
Wang S, Zhao M, Zhou M, Li Y, Wang J, Gao B, Sato S, Feng K, Yin W, Igalavithana A, Oleszczuk P, Wang X, Ok Y (2019b) Biochar-supported nZVI (nZVI/BC) for contaminant removal from soil and water: A critical review. J Hazard Mater 373:820–834. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.080
Wen S, Liu H, He H, Luo L, Li X, Zeng G, Zhou Z, Lou W, Yang C (2016) Treatment of anaerobically digested swine wastewater by Rhodobacter blasticus and Rhodobacter capsulatus. Bioresour Technol 222:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.09.102
Wu Y, Luo H, Wang H (2014) Removal of para-nitrochlorobenzene from aqueous solution on surfactant-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron/graphene nanocomposites. Environ Technol 35(21):2698–2707. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2014.919032
Wu S, He H, Li X, Yang C, Zeng G, Wu B, He S, Lu L (2018) Insights into atrazine degradation by persulfate activation using composite of nanoscale zero-valent iron and graphene: Performances and mechanisms. Chem Eng J 341:126–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.136
Wu J, Wang B, Blaney L, Peng G, Chen P, Cui Y, Deng S, Wang Y, Huang J, Yu G (2019) Degradation of sulfamethazine by persulfate activated with organo-montmorillonite supported nano-zero valent iron. Chem Eng J 361:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.12.024
Xia D, Li Y, Huang G, Yin R, An T, Li G, Zhao H, Lu A, Wong PK (2017) Activation of persulfates by natural magnetic pyrrhotite for water disinfection: Efficiency, mechanisms, and stability. Water Res 112:236–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.052
Xiong Z, Zhao D, Pan G (2007) Rapid and complete destruction of perchlorate in water and ion-exchange brine using stabilized zero-valent iron nanoparticles. Water Res 41:3497–3505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.05.049
Xue J, Chen M, Wang M (2020) Potassium Hydrogen Phthalate Abatement by Activated Persulfate in ZVI-PS Systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 231(5):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04621-y
Yan W, Lien HL, Koel BE, Zhang WX (2013) Iron nanoparticles for environmental clean-up: recent developments and future outlook. Environ Sci Process Impacts 15:63–77. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2em30691c
Yan J, Han L, Gao W, Xue S, Chen M (2015) Biochar supported nanoscale zerovalent iron composite used as persulfate activator for removing trichloroethylene. Bioresour Technol 175:269–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.103
Yang L, Gao J, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Zou M, Liao Q, Shang J (2018) Removal of Methyl Orange from Water Using Sulfur_Modified nZVI Supported on Biochar Composite. Water Air Soil Pollut 229(11). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-018-3992-x
Yang J, Zhou L, Ma F, Zhao H, Deng F, Pi S, Tang A, Li A (2020) Magnetic nanocomposite microbial extracellular polymeric substances@Fe3O4 supported nZVI for Sb(V) reduction and adsorption under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Environ Res 189:109950. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109950
Yi Y, Wang X, Ma J, Ning P An efficient Egeria najas-derived biochar supported nZVI composite for Cr(VI) removal: Characterization and mechanism investigation based on visual MINTEQ model. Environ Res 189:109912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109912
Yin W, Wu J, Li P, Wang X, Zhu N, Wu P, Yang B (2012) Experimental study of zero-valent iron induced nitrobenzene reduction in groundwater: The effects of pH, iron dosage, oxygen and common dissolved anions. Chem Eng J 184:198–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.030
Yousef R, Sadegh H, Ali A, Shirin A, Mehdi F, Mehdi V (2020) A novel, eco-friendly and green synthesis of PPAC-ZnO and PPAC-nZVI nanocomposite using pomegranate peel: Cephalexin adsorption experiments, mechanisms, isotherms and kinetics. Adv Powder Technol 31(4):1612–1623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.02.001
Yu Y, Zhou S, Bu L, Shi Z, Zhu S (2016) Degradation of Diuron by Electrochemically Activated Persulfate. Water Air Soil Pollut 227(8):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2978-9
Yu P, Yu H, Sun Q, Ma B (2019) Filter paper supported nZVI for continuous treatment of simulated dyeing wastewater (Article). Sci Rep 9(1):2045–2322. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47863-5
Yuan Y, Tao H, Fan J, Ma L (2015) Degradation of p-chloroaniline by persulfate activated with ferrous sulfide ore particles. Chem Eng J 268:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.12.092
Zhang L, Shen S (2020) Adsorption and catalytic degradation of sulfamethazine by mesoporous carbon loaded nano zero valent iron. J Ind Eng Chem 83:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.11.020
Zhang Y, Li Y, Li J, Hu L, Zheng X (2011) Enhanced removal of nitrate by a novel composite: Nanoscale zero valent iron supported on pillared clay. Chem Eng J 171:526–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.04.022
Zhang W, Yu T, Han X, Ying W (2016) Removal of 2-ClBP from soil-water system using activated carbon supported nanoscale zerovalent iron. J Environ Sci 47:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2015.12.032
Zhang D, Li Y, Tong S (2018a) Biochar supported sulfide-modified nanoscale zero-valent iron for the reduction of nitrobenzene. RSC Adv 8:22161–22168
Zhang L, Ding W, Qiu J, Jin H, Ma H, Li Z, Cang D (2018b) Modeling and optimization study on sulfamethoxazole degradation by electrochemically activated persulfate process. J Clean Prod 197:297–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.05.267
Zhang W, Zhou S, Sun J, Meng X, Luo J, Zhou D, Crittenden J (2018c) Impact of Chloride Ions on UV/H2O2 and UV/Persulfate Advanced Oxidation Processes. Environ Sci Technol 52:7380–7389. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b01662
Zhao J, Yang X, Liang G, Wang Z, Li S, Wang Z, Xie X (2020) Effective removal of two fluoroquinolone antibiotics by PEG-4000 stabilized nanoscale zero-valent iron supported onto zeolite (PZ-NZVI). Sci Total Environ 710:136289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136289
Zhi D, Lin Y, Jiang L, Zhou Y, Huang A, Yang J, Luo L (2020) Remediation of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Aqueous Systems by Electrochemical Activation of Persulfates: A Review. J Environ Manag 260:110125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110125
Zhong H, Brusseau ML, Wang Y, Yan N, Quig L, Johnson GR (2015) In-situ activation of persulfate by iron filings and degradation of 1, 4-dioxane. Water Res 83:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.06.025
Zhou L, Li A, Ma F, Zhao H, Deng F, Pi S, Tang A, Yang J (2020) Combining high electron transfer efficiency and oxidation resistance in nZVI with coatings of microbial extracellular polymeric substances to enhance Sb(V) reduction and adsorption. Chem Eng J 395:1385–8947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125168
Zhou J, Cheng H, Ma J, Peng G, Kong Y, Komarneni S (2021) Persulfate activation by MnCuS nanocomposites for degradation of organic pollutants. Sep Purif Technol 261:118290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.118290
Zhu C, Fang G, Dionysiou DD, Liu C, Gao J, Qin W, Zhou D (2016) Efficient transformation of DDTs with persulfate activation by zero-valent iron nanoparticles: a mechanistic study. J Hazard Mater 316:232–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.05.040
Zhu F, Ma S, Liu T, Deng X (2018) Green Synthesis of Nano Zero-Valent Iron/Cu by Green Tea to Remove Hexavalent Chromium from Groundwater. J Cleaner Product 174:184–190
Zhu F, Wu Y, Liang Y, Li H, Wenjing L (2020) Degradation mechanism of Norfloxacin in Water using Persulfate Activated by BC@nZVI/Ni. Chem Eng J 389:124276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124276
Zhuang Y, Jin L, Luthy RG (2012) Kinetics and pathways for the debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers by bimetallic and nanoscale zerovalent iron: effects of particle properties and catalyst. Chemosphere. 89:426–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.05.078
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Bing Wang contributed to the conception of the study; Chaoxiao Deng collected data and wrote the initial paper; Wei Ma and Yubo Sun revised the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ricardo Torres-Palma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
1. The background and problems of nZVI-activated persulfate were introduced.
2. Different modification methods and modification mechanisms of nZVI were summarized.
3. Applications of modified nZVI/PS to organic pollution treatment were discussed.
4. Major factors influencing modified nZVI-activated persulfate reactions were proposed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Deng, C., Ma, W. et al. Modified nanoscale zero-valent iron in persulfate activation for organic pollution remediation: a review . Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 34229–34247 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13972-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13972-w