Abstract
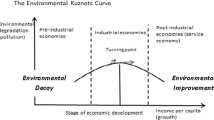
Developing economies are suffering to fulfill the sustainable environment’s commitments in fiscal imbalance. This study attempted to highlight the core issue of fiscal imbalance in developing economies and its impact on a sustainable environment. For this purpose, the study utilized generalized least squares (GLS) and quantile autoregressive distributive lag (QARDL) on a 19-year dataset (2000–2018) of the South Asian region. The results of GLS indicate that fiscal imbalance contributing positively to South Asia’s environmental degradation process. Here, energy consumption (due to dirty sources of energy) and energy intensity (due to inefficient energy conversion technology) are also sources of environmental degradation in this region. The results of QARDL confirm that economic and political fluctuations can be the long-run source of fiscal imbalance in this region, which ultimately slows down the process of the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) theory and contributes positively to environmental degradation. Based on the empirical analysis, this study provides a comprehensive set of policy guidance for developing and developed economies for the smooth transition of sustainable environmental conditions in South Asia.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahmed Z, Wang Z, Mahmood F, Hafeez M, Ali N (2019) Does globalization increase the ecological footprint? Empirical evidence from Malaysia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:18565–18582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05224-9
Ali S, Anwar S, Nasreen S (2017) Renewable and non-renewable energy and its impact on environmental quality in South Asian Countries. Forman J Econ Stud. https://doi.org/10.32368/fjes.20170009
Carratù M, Chiarini B, D’Agostino A, Marzano E, Regoli A (2019) Air pollution and public finance: evidence for European countries. J Econ Stud 46:1398–1417. https://doi.org/10.1108/JES-03-2019-0116
Chaudhary S, McGregor A, Houston D, Chettri N (2015) The evolution of ecosystem services: a time series and discourse-centered analysis. Environ Sci Policy 54:25–34
Cho JS, Kim TH, Shin Y (2015) Quantile cointegration in the autoregressive distributed-lag modeling framework. J Econ 188:281–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconom.2015.05.003
Desbordes R, Wei SJ (2017) The effects of financial development on foreign direct investment. J Dev Econ 127:153–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdeveco.2017.02.008
Dulal HB, Dulal R, Yadav PK (2015) Delivering green economy in Asia: the role of fiscal instruments. Futures. 73:61–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.futures.2015.08.002
Gerlagh R, van den Bijgaart I, Nijland H, Michielsen T (2018) Fiscal Policy and CO 2 Emissions of new passenger cars in the EU. Environ Resour Econ 69:103–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10640-016-0067-6
Harris RDF, Tzavalis E (1999) Inference for unit roots in dynamic panels where the time dimension is fixed. J Econ 91:201–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4076(98)00076-1
Jebali E, Essid H, Khraief N (2017) The analysis of energy efficiency of the Mediterranean countries: a two-stage double bootstrap DEA approach. Energy. 134:991–1000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.06.063
Katircioglu S, Katircioglu S (2018) Testing the role of fiscal policy in the environmental degradation: the case of Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:5616–5630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0906-1
Kim TI, Shin YH, White-Traut RC (2003) Multisensory intervention improves physical growth and illness rates in Korean orphaned newborn infants. Res Nurs Health 26:424–433. https://doi.org/10.1002/nur.10105
Kmenta J (2016) Elements of Econometrics, Elements of Econometrics. https://doi.org/10.3998/mpub.15701
Kumar R, Alex D (2011) Large asian economies and the united states: is rebalancing feasible?: Asia and policymaking for the global economy, ISBN 9780815704218
Lee CI (2016) The tax and expenditure mix in environmental public finance. J Econ Theory Econ 27:46–72
Lepitzki J, Axsen J (2018) The role of a low carbon fuel standard in achieving long-term GHG reduction targets. Energy Policy 119:423–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.03.067
Liu Y, Han L, Yin Z, Luo K (2017) A competitive carbon emissions scheme with hybrid fiscal incentives: the evidence from a taxi industry. Energy Policy 102:414–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.12.038
Melina G, Yang SCS, Zanna LF (2016) Debt sustainability, public investment, and natural resources in developing countries: the DIGNAR model. Econ Model 52:630–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2015.10.007
Muhafidin D (2020) The role of fiscal policy and monetary policy in environmental degradation in Indonesia. Int J Energy Econ Policy. https://doi.org/10.32479/ijeep.9586
Munir K, Riaz N (2019) Fiscal policy and macroecomonic stability in South Asian countries. Hacienda Publica Esp 228:13–33. https://doi.org/10.7866/HPE-RPE.19.1.1
NCE TNCE (2018) Unlocking the inclusive growth story of the 21st century: accelerating climate action in urgent times, The New Climate Economy
Pesaran HH, Shin Y (1998) Generalized impulse response analysis in linear multivariate models. Econ Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0165-1765(97)00214-0
Rathnayake ASK (2020) Sustainability of the fiscal imbalance and public debt under fiscal policy asymmetries in Sri Lanka. J Asian Econ 66:101161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asieco.2019.101161
Rausch S (2013) Fiscal consolidation and climate policy: an overlapping generations perspective. Energy Econ 40:S134–S148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2013.09.009
Ren S, Yuan B, Ma X, Chen X (2014) The impact of international trade on China’s industrial carbon emissions since its entry into WTO. Energy Policy 69:624–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2014.02.032
Rodriguez-Gonzalez PT, Rico-Martinez R, Rico-Ramirez V (2018) An integrated stochastic economic-ecological-social model with stratified-population. Ecol Model 368:15–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2017.11.012
Rosenfeld D, Andreae MO, Asmi A, Chin M, De Leeuw G, Donovan DP, Kahn R, Kinne S, Kivekäs N, Kulmala M et al. (2014) Global observations of aerosol-cloud-precipitation-climate interactions. Rev. Geophys 52(4)750–808. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013RG000441
Singhania M, Saini N (2020) Revisiting environmental degradation and economic growth nexus using autoregressive distributed lag approach. Int J Product Perform Manag 69:1765–1796. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPPM-10-2019-0509
Street R, Opitz-Stapleton S, Nadin R et al (2015) Climate change adaptation planning to policy: critical considerations and challenges. In: Climate Risk and Resilience in China. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315744988-13
Winner H (2012) Fiscal competition and the composition of public expenditure: an empirical study. Contemp Econ 6:38–54. https://doi.org/10.5709/ce.1897-9254.49
World Bank (2010) The economics of adaptation to climate change: a synthesis report. http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/646291468171244256/Economics-of-adaptation-to-climate-change-Synthesis-report
Xiao Z (2009) Quantile cointegrating regression. J Econom. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconom.2008.12.005
Yuelan P, Akbar MW, Hafeez M, Ahmad M, Zia Z, Ullah S (2019) The nexus of fiscal policy instruments and environmental degradation in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:28919–28932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06071-4
Zhou X, Zhang J, Li J (2013) Industrial structural transformation and carbon dioxide emissions in China. Energy Policy 57:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2012.07.017
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The abovementioned authors contributed to this research paper in the following way: The conceptualization was done by Guo Wei and Qaiser Abbas; methodology was formed by Ishtiaq Ahmad; software validation and formal analysis were performed by Nabila Asghar; investigation and resources and data curation were performed by Saeed ur Rahman; writing—original draft preparation was done by Fatima Farooq; writing—review and editing, visualization, and supervision were done by Weihua Yin.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval consent to participate
We declared that we do not have human participants, human data, or human tissue.
Consent for publication
We do not have any person’s data in any form.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, G., Asghar, N., Ahmad, I. et al. Economic growth, fiscal imbalance, and environmental sustainability: What is desirable and undesirable for developing economies?. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 52283–52294 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14379-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14379-3