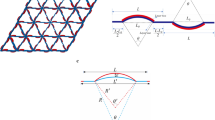
Abstract
The development of the current technology has increased the requirement for the versatility of acoustic metamaterials. In this study, the band gap (BG) tuning of the stretch-dominated thermal expansion lattice metamaterials with different configurations composed of triangular units is studied using the finite element method, and a design method for metamaterials tuned by external temperature changes in multiple frequency ranges is proposed. The results indicate that the stretch-dominated thermal expansion material can maintain the original customized thermal expansion performance while possessing the characteristics of the BG in addition to realizing different degrees of BG tunability when the temperature changes. The results provide a theoretical basis for attaining the thermal expansion/tunable BG dual-objectives design. The objective is to achieve the dual goals of tailorable coefficient of thermal expansion and tunable BG design through reasonable material selection and shape optimization.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.S. Kushwaha, P. Halevi, L. Dobrzynski, B. Djafari-Rouhani, Acoustic band structure of periodic elastic composites. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71(13), 2022–2025 (1993)
S.K. Manvir, Manvir, Classical Band Structure of Periodic Elastic Composites. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 10(09), 977–1094 (1996)
J.S. Jensen, Phononic band gaps and vibrations in one- and two-dimensional mass-spring structures. Opt. Commun. 266(5), 1053–1078 (2003)
E. Yablonovitch, Inhibited spontaneous emission in solid-state electronics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58(20), 2059–2062 (1987)
S. Ping et al., Locally resonant sonic materials. (Wave -scattering yields amplitude reduction.) (Brief Article). Phys. B-condens. Matter 4050(1–4), 201–205 (2003)
Zhao, H.G, et al., Novel Acoustic Materials--Phononic Crystals. Materials Science and Engineering, 2003.(Chinese)
W. Xu et al., Multi-objective topology optimization of two-dimensional multi-phase microstructure phononic crystals. Mater. Today Commun. 22, 100801 (2019)
Y. Huang, S. Liu, J. Zhao, Optimal design of two-dimensional band-gap materials for uni-directional wave propagation. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 48(3), 487–499 (2013)
Z. Lu et al., A tunable dielectric elastomer acoustic absorber. Acta Acust. Acust. 101(4), 863–86 (2015)
C.J. Rupp, M.L. Dunn, K. Maute, Switchable phononic wave filtering, guiding, harvesting, and actuating in polarization-patterned piezoelectric solids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96(11), 341–877 (2010)
Zi-Gui, et al., Temperature effect on the bandgaps of surface and bulk acoustic waves in two-dimensional phononic crystals Ultrasonics Ferroelectrics and Frequency Control. IEEE Trans. on 52(3), 365–370 (2005)
W.P. Yang, L.W. Chen, The tunable acoustic band gaps of two-dimensional phononic crystals with a dielectric elastomer cylindrical actuator. Smart Mater. Struct 17(1), 015011 (2008)
K.L. Jim et al., Thermal tuning of phononic bandstructure in ferroelectric ceramic/epoxy phononic crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94(19), 193501–193501 (2009)
Z. Hou, F. Wu, Y. Liu, Phononic crystals containing piezoelectric material. Solid State Commun. 130(11), 745–749 (2004)
W.F.L.Y. Yize, Tuning of band gaps for a two-dimensional piezoelectric phononic crystal with a rectangular lattice. Acta. Mech. Sin. 25(1), 65–71 (2009)
J.F. Robillard et al., Tunable magnetoelastic phononic crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95(12), 8759 (2009)
Y. Wang et al., Tuning of band gaps for a two-dimensional piezoelectric phononic crystal with a rectangular lattice. Acta Mech. Sin. 25(1), 65–71 (2009)
K. Bertoldi, M.C. Boyce, Mechanically triggered transformations of phononic band gaps in periodic elastomeric structures. Phys. Rev. B 77(5), 439–446 (2008)
J.H. Jang et al., Combining pattern instability and shape-memory hysteresis for phononic switching. Nano Lett. 9(5), 2113–2119 (2009)
J. Lehman, R. Lakes, Stiff lattices with zero thermal expansion and enhanced stiffness via rib cross section optimization. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 9(3), 213–225 (2013)
J. Lehman, R.S. Lakes, Stiff, strong, zero thermal expansion lattices via material hierarchy. Compos. Struct. 107, 654–663 (2014)
Y. Zhang et al., A new design for enhanced stiffness of dual-constituent triangular lattice metamaterial with unbounded thermal expansion. Mater. Res. Express (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aae5be
Y.C. Zhang et al., A new design of dual-constituent triangular lattice metamaterial with unbounded thermal expansion. Acta Mech. Sin. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aae5be
K. Wei et al., Planar lattices with tailorable coefficient of thermal expansion and high stiffness based on dual-material triangle unit. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 86, 173–191 (2016)
K. Wei et al., Lightweight composite lattice cylindrical shells with novel character of tailorable thermal expansion. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 137, 77–85 (2018)
K. Wei et al., Three dimensional lightweight lattice structures with large positive, zero and negative thermal expansion. Compos. Struct. 188, 287–296 (2018)
W. Kai et al., A cellular metastructure incorporating coupled negative thermal expansion and negative Poisson’s ratio. Int. J. Solids Struct. 150, 255–267 (2018)
Wei, K., et al., Additively manufactured bi-material metamaterial to program a wide range of thermal expansion. Materials & design, 2021. 198: p. 109343.
H. Xu, A. Farag, D. Pasini, Routes to program thermal expansion in three-dimensional lattice metamaterials built from tetrahedral building blocks. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 117, 54–87 (2018)
H. Xu et al., Thermally actuated hierarchical lattices with large linear and rotational expansion. J. Appl. Mech. 86(11), 111011 (2019)
M.M. Toropova, C.A. Steeves, Robust lightweight multifunctional thermally tailored lattices. Smart Mater. Struct. 29, 035011 (2019)
Liu, Y, Finite element simulation of elastic waves in 2-D artificial periodic structures[D], Harbin Institute Technology, 2019.(Chinese)
C.A. Steeves et al., Concepts for structurally robust materials that combine low thermal expansion with high stiffness. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 55(9), 1803–1822 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11502149, 11302135), Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (Nos. 2019-ZD-0229, 2019-ZD-0228 and 2019-ZD-0297), Scientific Research Fund of Liaoning Provincial Education Department (No. JYT19056). The financial contributions are gratefully acknowledged. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, S., Xu, W., Bai, L. et al. Thermal tuning of band gap properties in planar stretch-dominated lattices with tailorable coefficient of thermal expansion. Appl. Phys. A 127, 425 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04570-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04570-1