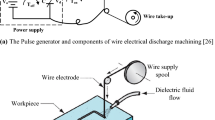
Abstract
Wire electrical discharge machining (wire-EDM) is an energy-intensive process, and its success relies on a correct selection of cutting parameters. It is vital to optimize energy consumption, along with productivity and quality. This experimental study optimized three parameters in wire-EDM: pulse-on time, servo voltage, and voltage concerning machining time, electric power, total energy consumption, surface roughness, and material removal rate. Two different plate thicknesses (15.88 mm and 25.4 mm) were machined. An orthogonal array, signal-to-noise ratio, and means graphs, and an analysis of variance (ANOVA), determine the effects and contribution of cutting parameters on responses. Pulse-on time is the most significant factor for almost all variables, with a percentage of contribution higher than 50%. Multi-objective optimization is conducted to accomplish a concurrent decrease in all variables. A case study is proposed to compute carbon dioxide (CO2) tons and electricity cost in wire-EDM, using cutting parameters from multi-objective optimization and starting values commonly employed to cut that tool steel. A sustainable manufacturing approach reduced 5.91% of the electricity cost and CO2 tons when machining the thin plate, and these responses were diminished by 14.09% for the thicker plate. Therefore, it is possible to enhance the sustainability of the process without decreasing its productivity and quality.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Devarajaiah D, Muthumari C (2018) Evaluation of power consumption and MRR in WEDM of Ti-6Al-4V alloy and its simultaneous optimization for sustainable production. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 40:400–417
Garg A, Lam JSL (2016) Modeling multiple-response environmental and manufacturing characteristics of EDM process. J Clean Prod 137:1588–1601
Zhang Z, Yu H, Zhang Y et al (2018) Analysis and optimization of process energy consumption and environmental impact in electrical discharge machining of titanium superalloys. J Clean Prod 198:833–846
Salahi N, Jafari MA (2016) Energy-performance as a driver for optimal production planning. Appl Energy 174:88–100
U.S. Energy Information Administration (2011) Annual energy review 2011
Sharma S, Kumar VU, Bansal A (2020) Parametric optimization in wire EDM of D2 tool steel using Taguchi method. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.802
Zhang G, Li W, Zhang Y et al (2020) Analysis and reduction of process energy consumption and thermal deformation in a micro-structure wire electrode electric discharge machining thin-wall component. J Clean Prod 244:118763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118763
Baroi BK, Debnath T, Jagadish Patowari PK (2020) Machinability assessment of titanium grade 2 alloy using deionized water in EDM. Mater Today Proc 26:2221–2225
Gowthaman PS, Gowthaman J, Nagasundaram N (2020) A study of machining characteristics of AISI 4340 alloy steel by wire electrical discharge machining process. Mater Today Proc. 27:565–570
Camposeco-Negrete C (2019) Prediction and optimization of machining time and surface roughness of AISI O1 tool steel in wire-cut EDM using robust design and desirability approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 103:2411–2422
Pramanik A, Basak AK (2018) Sustainability in wire electrical discharge machining of titanium alloy: understanding wire rupture. J Clean Prod 198:472–479
Majumder H, Maity K (2018) Prediction and optimization of surface roughness and micro-hardness using grnn and MOORA-fuzzy—a MCDM approach for nitinol in WEDM. Measurement 118:1–13
Sonawane SA, Kulkarni ML (2018) Optimization of machining parameters of WEDM for Nimonic-75 alloy using principal component analysis integrated with Taguchi method. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci 30:250–258
Ramanan G, Dhas JER (2018) Multi objective optimization of wire EDM machining parameters for AA7075-PAC composite using grey: fuzzy technique. Mater Today Proc 5:8280–8289
Mouralova K, Kovar J, Klakurkova L et al (2018) Analysis of surface morphology and topography of pure aluminium machined using WEDM. Meas J Int Meas Confed 114:169–176
Udaya PJ, Jebarose JS, Pallavi P et al (2018) Optimization of wire EDM process parameters for machining hybrid composites (356/B4C/Fly Ash) using Taguchi technique. Mater Today Proc 5:7275–7283
Choudhuri B, Sen R, Kumar GS et al (2018) Modelling of surface roughness and tool consumption of WEDM and optimization of process parameters based on fuzzy-PSO. Mater Today Proc 5:7505–7514
Sen R, Choudhuri B, Barma JD et al (2018) Optimization of wire EDM parameters using teaching learning based algorithm during machining of maraging steel 300. Mater Today Proc 5:7541–7551
Sreenivasa RM, Venkata NBA, Venkaiah N (2018) Modified flower pollination algorithm to optimize WEDM parameters while machining Inconel-690 alloy. Mater Today Proc 5:7864–7872
Ishfaq K, Mufti NA, Mughal MP et al (2018) Investigation of wire electric discharge machining of stainless-clad steel for optimization of cutting speed. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 96:1429–1443
Kumar A, Soota T, Kumar J (2018) Optimization of wire-cut EDM process parameter by grey-based response surface methodology. J Ind Eng Int 14:821–829
Gamage JR, DeSilva AKM, Chantzis D et al (2017) Sustainable machining: process energy optimisation of wire electrodischarge machining of Inconel and titanium superalloys. J Clean Prod 164:642–651
Tejas AB, Mayur VP, Rajyalakshmi G (2017) WEDM machining on aerospace materials for improving material properties. Mater Today Proc 4:9107–9116
Singh V, Bhandari R, Yadav VK (2017) An experimental investigation on machining parameters of AISI D2 steel using WEDM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 93:203–214
Manjaiah M, Laubscher RF, Kumar A et al (2016) Parametric optimization of MRR and surface roughness in wire electro discharge machining (WEDM) of D2 steel using Taguchi-based utility approach. Int J Mech Mater Eng 11:7–15
Maher I, Sarhan AAD, Barzani MM et al (2015) Increasing the productivity of the wire-cut electrical discharge machine associated with sustainable production. J Clean Prod 108:247–255
Shivade AS, Shinde VD (2014) Multi-objective optimization in WEDM of D3 tool steel using integrated approach of Taguchi method & grey relational analysis. J Ind Eng Int 10:149–162
Ming W, Shen F, Zhang G et al (2021) Green machining: a framework for optimization of cutting parameters to minimize energy consumption and exhaust emissions during electrical discharge machining of Al 6061 and SKD 11. J Clean Prod 285:124889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124889
Jagadish RA (2016) Optimization of process parameters of green electrical discharge machining using principal component analysis (PCA). Int J Adv Manuf Technol 87:1299–1311
Wang X, Chen L, Dan B et al (2018) Evaluation of EDM process for green manufacturing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94:633–641
Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhang G et al (2020) Reduction of energy consumption and thermal deformation in WEDM by magnetic field assisted technology. Int J Precis Eng Manuf Green Technol 7:391–404
Gao M, Wang Q, Li L et al (2019) Comprehensive energy-saving method for sheet metal forming. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 104:2273–2285
Bourithis L, Papadimitriou GD, Sideris J (2006) Comparison of wear properties of tool steels AISI D2 and O1 with the same hardness. Tribol Int 39:479–489
Kumar S, Maity SR, Patnaik L (2020) Effect of heat treatment and TiN coating on AISI O1 cold work tool steel. Mater Today Proc 26:685–688
Zheng J, Zheng W, Chen A et al (2020) Sustainability of unconventional machining industry considering impact factors and reduction methods of energy consumption: a review and analysis. Sci Total Environ 722:137897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137897
Sodick Inc (2012) Wire EDM machine operation training for LN1W/LN2W control. http://fab.cba.mit.edu/content/tools/sodick_edm/sodick_user_manual_small.pdf. Accessed 31 Oct 2019
Edem IF, Mativenga PT (2017) Modelling of energy demand from computer numerical control (CNC) toolpaths. J Clean Prod 157:310–321
Fluke-Direct.com Fluke 43B/003 Power quality analyzer. In: Fluke 43B/003 Power Qual. Anal.
Misra JP, Danish M, Prateek et al (2018) Effect of wire related parameters and servo feed on process performance characteristics during WEDM of combustor material. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/402/1/012165
Ekici E, Motorcu AR, Kuş A (2016) Evaluation of surface roughness and material removal rate in the wire electrical discharge machining of Al/B4C composites via the Taguchi method. J Compos Mater 50:2575–2586
Fard RK, Afza RA, Teimouri R (2013) Experimental investigation, intelligent modeling and multi-characteristics optimization of dry WEDM process of Al-SiC metal matrix composite. J Manuf Process 15:483–494
Kumar R, Choudhury SK (2011) Prevention of wire breakage in wire EDM. Int J Mach Mach Mater 9:86–102
Kumar H, Manna A, Kumar R (2018) Modeling of process parameters for surface roughness and analysis of machined surface in WEDM of Al/SiC-MMC. Trans Indian Inst Met 71:231–244
Sen R, Choudhuri B, Barma JD et al (2018) Study the impact of process parameters and electrode material on wire electric discharge machining performances. Mater Today Proc 5:7552–7560
Yan H, Bakadiasa KD, Yan Z et al (2020) Sustainable production of high-uniformity workpiece surface quality in wire electrical discharge machining by fabricating surface microstructure on wire electrode. J Clean Prod 259:120881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120881
United States Bureau of Labor Statistics (2019) Machinists and tool and die makers. In: Occup. Outlook Handb
United States Environmental Protection Agency (2018) Greenhouse gases equivalencies calculator: calculations and references
United States Energy Information Administration (2020) Average price of electricity to ultimate customers by end-use sector. https://www.eia.gov/electricity/monthly/epm_table_grapher.php?t=epmt_5_6_a. Accessed 5 Jan 2021
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Tecnologico de Monterrey Campus Toluca, and students of the class tooling engineering, for providing financial and human resources for conducting the experiments described in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Camposeco-Negrete, C. Analysis and optimization of sustainable machining of AISI O1 tool steel by the wire-EDM process. Adv. Manuf. 9, 304–317 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-021-00353-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40436-021-00353-2