Abstract
Objective
To establish a temperature-induced chitosanase bacterial cell-surface display system to produce chitooligosaccharides (COSs) efficiently for industrial applications.
Results
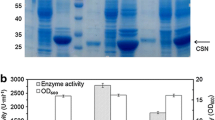
Temperature-inducible chitosanase CSN46A bacterial surface display systems containing one or two copies of ice nucleation protein (InaQ-N) as anchoring motifs were successfully constructed on the basis of Escherichia coli and named as InaQ-N-CSN46A (1 copy) and 2InaQ-N-CSN46A (2 copies). The specific enzyme activity of 2InaQ-N-CSN46A reached 761.34 ± 0.78 U/g cell dry weight, which was 45.6% higher than that of InaQ-N-CSN46A. However, few proteins were detected in the 2InaQ-N-CSN46A hydrolysis system. Therefore, 2InaQ-N-CSN46A had higher hydrolysis efficiency and stability than InaQ-N-CSN46A. Gel permeation chromatography revealed that under the optimum enzymatic hydrolysis temperature, the final products were mainly chitobiose and chitotriose. Chitopentaose accumulated (77.62%) when the hydrolysis temperature reached 60 °C. FTIR and NMR analysis demonstrated that the structures of the two hydrolysis products were consistent with those of COSs.
Conclusions
In this study, chitosanase was expressed on the surfaces of E. coli by increasing the induction temperature, and chitosan was hydrolysed directly without enzyme purification steps. This study provides a novel strategy for industrial COS production.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Doan CT, Tran TN, Nguyen VB, Tran TD, Nguyen AD, Wang SL (2020) Bioprocessing of squid pens waste into chitosanase by Paenibacillus sp. TKU047 and its application in low-molecular weight chitosan oligosaccharides production. Polymers (Basel) 12:1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12051163
Dong H, Wang Y, Zhao L, Zhou J, Xia Q, Qiu Y (2015) Key technologies of enzymatic preparation for DP 6–8 chitooligosaccharides. J Food Process Eng 38:336–344. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.12159
Dubeau MP, Poulin-Laprade D, Ghinet MG, Brzezinski R (2011) Properties of CsnR, the transcriptional repressor of the chitosanase gene, csnA, of Streptomyces lividans. J Bacteriol 193:2441–2450. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01476-10
Fukamizo T, Amano S, Yamaguchi K, Yoshikawa T, Katsumi T, Ji S, Suzuki M, Miki K, Nagata Y, Ando A (2005) Bacillus circulans MH-K1 chitosanase: amino acid residues responsible for substrate binding. J Biochem 138:563–569. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvi156
Fukuda T, Isogawa D, Takagi M, Kato-Murai M, Kimoto H, Kusaoke H, Ueda M, Suye SI (2007) Yeast cell-surface expression of chitosanase from Paenibacillus fukuinensis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:2845–2847. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.70315
Guo N, Sun J, Wang W, Gao L, Liu J, Liu Z, Xue C, Mao X (2019) Cloning, expression and characterization of a novel chitosanase from Streptomyces albolongus ATCC 27414. Food Chem 286:696–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.02.056
Han Y, Guan F, Sun J, Wu N, Tian J (2020) Identification of a chitosanase from the marine metagenome and its molecular improvement based on evolution data. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:6647–6657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10715-8
Jung HC, Lebeault JM, Pan JG (1998) Surface display of Zymomonas mobilis levansucrase by using the ice-nucleation protein of Pseudomonas syringae. Nat Biotechnol 16:576–580. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0698-576
Kang LX, Chen XM, Fu L, Ma LX (2012) Recombinant expression of chitosanase from Bacillus subtilis HD145 in Pichia pastoris. Carbohydr Res 352:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2012.01.025
Kunanusornchai W, Witoonpanich B, Tawonsawatruk T, Pichyangkura R, Chatsudthipong V, Muanprasat C (2016) Chitosan oligosaccharide suppresses synovial inflammation via AMPK activation: an in vitro and in vivo study. Pharmacol Res 113:458–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.09.016
Kuroiwa T, Izuta H, Nabetani H, Nakajima M, Sato S, Mukataka S, Ichikawa S (2009) Selective and stable production of physiologically active chitosan oligosaccharides using an enzymatic membrane bioreactor. Process Biochem 44:283–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2008.10.020
Li L, Kang DG, Cha HJ (2004) Functional display of foreign protein on surface of Escherichia coli using N-terminal domain of ice nucleation protein. Biotechnol Bioeng 85:214–221. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.10892
Li P, Linhardt RJ, Cao Z (2016) Structural characterization of oligochitosan elicitor from Fusarium sambucinum and its elicitation of defensive responses in Zanthoxylum bungeanum. Int J Mol Sci 17:2076. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17122076
Li Q, Ni H, Meng S, He Y, Yu Z, Li L (2011) Suppressing Erwinia carotovora pathogenicity by projecting N-acyl homoserine lactonase onto the surface of Pseudomonas putida cells. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:1330–1335. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1107.07011
Li Q, Yu Z, Shao X, He J, Li L (2009) Improved phosphate biosorption by bacterial surface display of phosphate-binding protein utilizing ice nucleation protein. FEMS Microbiol Lett 299:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01724.x
Liu X, Xia W, Jiang Q, Xu Y, Yu P (2014) Synthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial activity of kojic acid grafted chitosan oligosaccharide. J Agric Food Chem 62:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf404026f
Liu Y, Li Y, Tong S, Yuan M, Wang X, Wang J, Fan Y (2020) Expression of a Beauveria bassiana chitosanase (BbCSN-1) in Pichia pastoris and enzymatic analysis of the recombinant protein. Protein Expr Purif 166:105519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2019.105519
Luo S, Qin Z, Chen Q, Fan L, Jiang L, Zhao L (2020) High level production of a Bacillus amlyoliquefaciens chitosanase in Pichia pastoris suitable for chitooligosaccharides preparation. Int J Biol Macromol 149:1034–1041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.001
Ma C, Li X, Yang K, Li S (2020) Characterization of a new chitosanase from a Marine Bacillus sp. and the anti-oxidant activity of its hydrolysate. Mar Drugs 18:126. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18020126
Muanprasat C, Chatsudthipong V (2017) Chitosan oligosaccharide: biological activities and potential therapeutic applications. Pharmacol Ther 170:80–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.10.013
Muley AB, Chaudhari SA, Mulchandani KH, Singhal RS (2018) Extraction and characterization of chitosan from prawn shell waste and its conjugation with cutinase for enhanced thermo-stability. Int J Biol Macromol 111:1047–1058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.115
Nguyen HM, Mathiesen G, Stelzer EM, Pham ML et al (2016) Display of a β-mannanase and a chitosanase on the cell surface of Lactobacillus plantarum towards the development of whole-cell biocatalysts. Microb Cell Fact 15:169. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0570-z
Shi L, Fang B, Yong Y, Li X et al (2019) Chitosan oligosaccharide-mediated attenuation of LPS-induced inflammation in IPEC-J2 cells is related to the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Carbohydr Polym 219:269–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.05.036
Sinha S, Chand S, Tripathi P (2016) Recent progress in chitosanase production of monomer-free chitooligosaccharides: bioprocess strategies and future applications. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 180:883–899. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2140-6
Sun Y, Zhang J, Wang S (2015) Heterologous expression and efficient secretion of chitosanase from Microbacterium sp. in Escherichia coli. Indian J Microbiol 55:194–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-014-0505-5
Wen C, Gan R, Zhu S (2003) Construction of secretory expression system suitable to express glucagon under the control of PL promoter. Curr Microbiol 47:180–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-002-3988-y
Yang G, Sun H, Cao R, Liu Q, Mao X (2020) Characterization of a novel glycoside hydrolase family 46 chitosanase, Csn-BAC, from Bacillus sp. MD-5. Int J Biol Macromol 146:518–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.031
Yang Y, Zheng Z, Xiao Y, Zhang J, Zhou Y, Li X, Li S, Yu H (2019) Cloning and characterization of a cold-adapted chitosanase from marine bacterium Bacillus sp. BY01. Molecules 24:3915. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213915
Zhang J, Sun X, Chen Y, Mi Y, Tan W, Miao Q, Li Q, Dong F, Guo Z (2020) Preparation of 2,6-diurea-chitosan oligosaccharide derivatives for efficient antifungal and antioxidant activities. Carbohydr Polym 234:115903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115903
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grant No. 17441905400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Wang, T., Ye, Y. et al. A temperature-induced chitosanase bacterial cell-surface display system for the efficient production of chitooligosaccharides. Biotechnol Lett 43, 1625–1635 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03139-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03139-5