Abstract
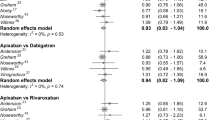
Purpose:To systematically review available evidence of indirect comparisons from RCTs and direct comparisons from observational studies regarding the comparative effectiveness and safety of DOACs in patients with AF. Methods: Electronic databases including EMBASE, MEDLINE, and PUBMED were searched up to June 5th, 2020. Primary endpoints included effectiveness (stroke or systemic embolism [SE]) and safety (major bleeding) outcomes. Bucher methods and random-effects models were conducted for indirect and direct comparisons among DOACs, respectively. Ranking probability analyses and the number needed to treat for net effect (NNTnet) were applied. Results: A total of 36 studies, involving 7 RCTs (n = 60,292 patients) and 29 observational studies (n = 1,164,821 patients), were included for analyses. Regarding the risk of stroke/SE, no significant differences were found from indirect comparisons of RCTs among the DOACs. For major bleeding, apixaban tended to be safer than rivaroxaban and dabigatran based on both direct and indirect comparisons (all p < 0.05; evidence quality: very low to moderate). Ranking probability analysis showed that apixaban had a high probability of being the best treatment in decreased risk of stroke/SE and major bleeding (80.30% and 91.30%, respectively). Likewise, apixaban was found to have the highest net clinical benefit (0.02, 95% CI: 0.014–0.029) and smallest NNTnet (48, 95% CI: 35–74). Conclusions: Apixaban appeared to have a favorable effectiveness-safety profile compared with the other DOACs in AF for stroke prevention, based on evidence from both direct and indirect comparisons. However, additional high-quality evidence is needed to support firm recommendations on clinical decision-making.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- DOACs:
-
Direct acting oral anticoagulants
- AF:
-
Atrial fibrillation
- VKAs:
-
Vitamin K antagonists
- RCTs:
-
Randomized controlled trials
- SE:
-
Systemic embolism
- SCURA:
-
Surface under the cumulative ranking
- NNTnet:
-
Number needed to treat for net effect
- ICH:
-
Intracranial hemorrhage
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- ROB:
-
Risk of bias
- ROBINS-I:
-
Bias In Non-randomized Studies of Interventions
- HRs:
-
Hazard ratios
- CIs:
-
Confidence intervals
- ARR:
-
Absolute risk reduction
- ARI:
-
Absolute risk increase
- GRADE:
-
Grading of recommendations, assessment, development, and evaluation
References
Lip GY, Freedman B, De Caterina R, Potpara TS. Stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: past, present and future. J Thrombosis Haemostasis. 2017;117:1230–9.
Lip GY, Banerjee A, Boriani G, En Chiang C, Fargo R, Freedman B, Lane DA, Ruff CT, Turakhia M, Werring D. Antithrombotic therapy for atrial fibrillation: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. J Chest. 2018;154:1121–201.
Lopez-Lopez JA, Sterne JAC, Thom HHZ, Higgins JPT, Hingorani AD, Okoli GN, Davies PA, Bodalia PN, Bryden PA, Welton NJ, Hollingworth W, Caldwell DM, Savovic J, Dias S, Salisbury C, Eaton D, Stephens-Boal A, Sofat R. Oral anticoagulants for prevention of stroke in atrial fibrillation: systematic review, network meta-analysis, and cost effectiveness analysis. BMJ. 2017;359:j5058.
Cope S, Clemens A, Hammes F, Noack H, Jansen JP. Critical appraisal of network meta-analyses evaluating the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation stroke prevention trials. Value Health. 2015;18:234–49.
Torp-Pedersen C, Goette A, Nielsen PB, Potpara T, Fauchier L, John Camm A, Arbelo E, Boriani G, Skjoeth F, Rumsfeld J. ‘Real-world’observational studies in arrhythmia research: data sources, methodology, and interpretation. A position document from European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), endorsed by Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), Asia-Pacific HRS (APHRS), and Latin America HRS (LAHRS). J EP Europace. 2020;22:831–2.
Ntaios G, Papavasileiou V, Makaritsis K, Vemmos K, Michel P, Lip GYH. Real-world setting comparison of Nonvitamin-K antagonist oral anticoagulants versus vitamin-K antagonists for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2017;48:2494–503.
Hannink G, Gooszen HG, Rovers MM. Comparison of registered and published primary outcomes in randomized clinical trials of surgical interventions. Ann Surg. 2013;257:818–23.
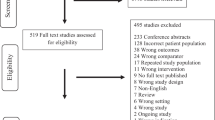
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000097.
Viera AJ, Garrett JM. Understanding interobserver agreement: the kappa statistic. Fam Med. 2005;37:360–3.
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, Henry D, Altman DG, Ansari MT, Boutron I, Carpenter JR, Chan AW, Churchill R, Deeks JJ, Hróbjartsson A, Kirkham J, Jüni P, Loke YK, Pigott TD, Ramsay CR, Regidor D, Rothstein HR, Sandhu L, Santaguida PL, Schünemann HJ, Shea B, Shrier I, Tugwell P, Turner L, Valentine JC, Waddington H, Waters E, Wells GA, Whiting PF, Higgins JP. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. 2016;355:i4919.
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JA. The Cochrane collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928.
Edwards SJ, Clarke MJ, Wordsworth S, Borrill J. Indirect comparisons of treatments based on systematic reviews of randomised controlled trials. Int J Clin Pract. 2009;63:841–54.
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1986;7:177–88.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21:1539–58.
Higgins J, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page M, Welch V. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. 2nd ed. Chichester: Wiley; 2019.
Salanti G, Ades A, Ioannidis JP. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: an overview and tutorial. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64:163–71.
Singer DE, Chang Y, Fang MC, Borowsky LH, Pomernacki NK, Udaltsova N, Go AS. The net clinical benefit of warfarin anticoagulation in atrial fibrillation. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151:297–305.
Li G, Lip GYH, Marcucci M, Thabane L, Tian J, Levine MAH. The number needed to treat for net effect (NNTnet) as a metric for measuring combined benefits and harms. J Clin Epidemiol. 2020;125:100–7.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315:629–34.
Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR, Rushton L. Comparison of two methods to detect publication bias in meta-analysis. JAMA. 2006;295:676–80.
Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, Norris S, Falck-Ytter Y, Glasziou P, De Beer H, Jaeschke R, Rind D, Meerpohl J, Dahm P, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J Clin Epidemiol. 2011;64:383–94.
Connolly SJ, Ezekowitz MD, Yusuf S, Eikelboom J, Oldgren J, Parekh A, Pogue J, Reilly PA, Themeles E, Varrone J, Wang S, Alings M, Xavier D, Zhu J, Diaz R, Lewis BS, Darius H, Diener HC, Joyner CD, Wallentin L. Committee R-LS and investigators. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1139–51.
Duraes AR, de Souza RP, de Almeida NB, Albuquerque FP, de Bulhoes FV, de Souza Fernandes AM, Aras R. Dabigatran versus warfarin after bioprosthesis valve replacement for the management of atrial fibrillation postoperatively: DAWA pilot study. Drugs R D. 2016;16:149–54.
Giugliano RP, Ruff CT, Braunwald E, Murphy SA, Wiviott SD, Halperin JL, Waldo AL, Ezekowitz MD, Weitz JI, Spinar J, Ruzyllo W, Ruda M, Koretsune Y, Betcher J, Shi M, Grip LT, Patel SP, Patel I, Hanyok JJ, Mercuri M, Antman EM, Investigators EA-T. Edoxaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:2093–104.
Granger CB, Alexander JH, McMurray JJ, Lopes RD, Hylek EM, Hanna M, Al-Khalidi HR, Ansell J, Atar D, Avezum A, Bahit MC, Diaz R, Easton JD, Ezekowitz JA, Flaker G, Garcia D, Geraldes M, Gersh BJ, Golitsyn S, Goto S, Hermosillo AG, Hohnloser SH, Horowitz J, Mohan P, Jansky P, Lewis BS, Lopez-Sendon JL, Pais P, Parkhomenko A, Verheugt FW, Zhu J, Wallentin L. Committees A and investigators. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:981–92.
Hori M, Matsumoto M, Tanahashi N, Momomura S, Uchiyama S, Goto S, Izumi T, Koretsune Y, Kajikawa M, Kato M, Ueda H, Iwamoto K. Tajiri M and investigators JRAs. Rivaroxaban vs. warfarin in Japanese patients with atrial fibrillation: the J-ROCKET AF study. Circ J. 2012;76:2104–11.
Mao L, Li C, Li T, Yuan K. Prevention of stroke and systemic embolism with rivaroxaban compared with warfarin in Chinese patients with atrial fibrillation. Vascular. 2014;22:252–8.
Patel MR, Mahaffey KW, Garg J, Pan G, Singer DE, Hacke W, Breithardt G, Halperin JL, Hankey GJ, Piccini JP, Becker RC, Nessel CC, Paolini JF, Berkowitz SD, Fox KA, Califf RM, Investigators RA. Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:883–91.
Adeboyeje G, Sylwestrzak G, Barron JJ, White J, Rosenberg A, Abarca J, Crawford G, Redberg R. Major bleeding risk during anticoagulation with warfarin, dabigatran, apixaban, or rivaroxaban in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2017;23:968–78.
Al-Khalili F, Lindstrom C, Benson L. The safety and persistence of non-vitamin-K-antagonist oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation patients treated in a well structured atrial fibrillation clinic. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016;32:779–85.
Amin A, Garcia Reeves AB, Li X, Dhamane A, Luo X, Di Fusco M, Nadkarni A, Friend K, Rosenblatt L, Mardekian J, Pan X, Yuce H, Keshishian A. Effectiveness and safety of oral anticoagulants in older adults with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and heart failure. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0213614.
Amin A, Keshishian A, Vo L, Zhang Q, Dina O, Patel C, Odell K, Trocio J. Real-world comparison of all-cause hospitalizations, hospitalizations due to stroke and major bleeding, and costs for non-valvular atrial fibrillation patients prescribed oral anticoagulants in a US health plan. J Med Econ. 2018;21:244–53.
Andersson NW, Svanstrom H, Lund M, Pasternak B, Melbye M. Comparative effectiveness and safety of apixaban, dabigatran, and rivaroxaban in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol. 2018;268:113–9.
Blin P, Dureau-Pournin C, Cottin Y, Benichou J, Mismetti P, Abouelfath A, Lassalle R, Droz C, Moore N. Comparative effectiveness and safety of standard or reduced dose dabigatran vs. rivaroxaban in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2019;105:1439–55.
Chan YH, Kuo CT, Yeh YH, Chang SH, Wu LS, Lee HF, Tu HT, See LC. Thromboembolic, bleeding, and mortality risks of rivaroxaban and dabigatran in asians with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:1389–401.
Deitelzweig S, Bruno A, Trocio J, Tate N, Gupta K, Lin J, Lingohr-Smith M. An early evaluation of bleeding-related hospital readmissions among hospitalized patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation treated with direct oral anticoagulants. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016;32:573–82.
Deitelzweig S, Luo X, Gupta K, Trocio J, Mardekian J, Curtice T, Lingohr-Smith M, Menges B, Lin J. Comparison of effectiveness and safety of treatment with apixaban vs. other oral anticoagulants among elderly nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients. Curr Med Res Opin. 2017;33:1745–54.
Gorst-Rasmussen A, Lip GY, Bjerregaard LT. Rivaroxaban versus warfarin and dabigatran in atrial fibrillation: comparative effectiveness and safety in Danish routine care. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2016;25:1236–44.
Graham DJ, Reichman ME, Wernecke M, Hsueh YH, Izem R, Southworth MR, Wei Y, Liao J, Goulding MR, Mott K, Chillarige Y, MaCurdy TE, Worrall C, Kelman JA. Stroke, bleeding, and mortality risks in elderly medicare beneficiaries treated with dabigatran or rivaroxaban for nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. JAMA Intern Med. 2016;176:1662–71.
Gupta K, Trocio J, Keshishian A, Zhang Q, Dina O, Mardekian J, Rosenblatt L, Liu X, Hede S, Nadkarni A, Shank T. Real-world comparative effectiveness, safety, and health care costs of oral anticoagulants in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients in the U.S. Department of defense population. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018;24:1116–27.
Hernandez I, Zhang Y. Comparing stroke and bleeding with rivaroxaban and dabigatran in atrial fibrillation: analysis of the US Medicare Part D Data. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2017;17:37–47.
Hernandez I, Zhang Y, Saba S. Comparison of the effectiveness and safety of apixaban, dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and warfarin in newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2017;120:1813–9.
Hsu CC, Hsu PF, Sung SH, Tu ST, Yu BH, Huang CJ, Cheng HM. Is there a preferred stroke prevention strategy for diabetic patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation? Comparing warfarin Dabigatran and Rivaroxaban. Thromb Haemost. 2018;118:72–81.
Jansson M, Sjalander S, Sjogren V, Renlund H, Norrving B, Sjalander A. Direct comparisons of effectiveness and safety of treatment with Apixaban, Dabigatran and Rivaroxaban in atrial fibrillation. Thromb Res. 2020;185:135–41.
Lai CL, Chen HM, Liao MT, Lin TT, Chan KA. Comparative effectiveness and safety of dabigatran and rivaroxaban in atrial fibrillation patients. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6:e005362.
Lee SR, Choi EK, Kwon S, Han KD, Jung JH, Cha MJ, Oh S, Lip GYH. Effectiveness and safety of contemporary oral anticoagulants among Asians with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Stroke. 2019;50:2245–9.
Li WH, Huang D, Chiang CE, Lau CP, Tse HF, Chan EW, Wong ICK, Lip GYH, Chan PH, Siu CW. Efficacy and safety of dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and warfarin for stroke prevention in Chinese patients with atrial fibrillation: the Hong Kong Atrial Fibrillation Project. Clin Cardiol. 2017;40:222–9.
Lip GY, Keshishian A, Kamble S, Pan X, Mardekian J, Horblyuk R, Hamilton M. Real-world comparison of major bleeding risk among non-valvular atrial fibrillation patients initiated on apixaban, dabigatran, rivaroxaban, or warfarin. A propensity score matched analysis. Thromb Haemost. 2016;116:975–86.
Lip GYH, Keshishian A, Li X, Hamilton M, Masseria C, Gupta K, Luo X, Mardekian J, Friend K, Nadkarni A, Pan X, Baser O, Deitelzweig S. Effectiveness and safety of oral anticoagulants among nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients. Stroke. 2018;49:2933–44.
Mueller T, Alvarez-Madrazo S, Robertson C, Wu O, Bennie M. Comparative safety and effectiveness of direct oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation in clinical practice in Scotland. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019;85:422–31.
Norby FL, Bengtson LGS, Lutsey PL, Chen LY, MacLehose RF, Chamberlain AM, Rapson I, Alonso A. Comparative effectiveness of rivaroxaban versus warfarin or dabigatran for the treatment of patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017;17:238.
Noseworthy PA, Yao X, Abraham NS, Sangaralingham LR, McBane RD, Shah ND. Direct comparison of dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban for effectiveness and safety in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Chest. 2016;150:1302–12.
Palamaner Subash Shantha G, Bhave PD, Girotra S, Hodgson Zingman D, Mazur A, Giudici M, Chrischilles E, Vaughan Sarrazin MS. Sex-specific comparative effectiveness of oral anticoagulants in elderly patients with newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2017;10:003418.
Rutherford OW, Jonasson C, Ghanima W, Soderdahl F, Halvorsen S. Comparison of dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban for effectiveness and safety in atrial fibrillation: a nationwide cohort study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2020;6:75–85.
Tepper PG, Mardekian J, Masseria C, Phatak H, Kamble S, Abdulsattar Y, Petkun W, Lip GYH. Real-world comparison of bleeding risks among non-valvular atrial fibrillation patients prescribed apixaban, dabigatran, or rivaroxaban. PLoS ONE. 2018;13:e0205989.
Villines TC, Ahmad A, Petrini M, Tang W, Evans A, Rush T, Thompson D, Oh K, Schwartzman E. Comparative safety and effectiveness of dabigatran vs rivaroxaban and apixaban in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation: a retrospective study from a large healthcare system. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2019;5:80–90.
Vinogradova Y, Coupland C, Hill T, Hippisley-Cox J. Risks and benefits of direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin in a real world setting: cohort study in primary care. BMJ. 2018;362:k2505.
Schirmer SH, Baumhakel M, Neuberger HR, Hohnloser SH, van Gelder IC, Lip GY, Bohm M. Novel anticoagulants for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: current clinical evidence and future developments. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56:2067–76.
Turpie AG. New oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2008;29:155–65.
Kubitza D, Haas S. Novel factor Xa inhibitors for prevention and treatment of thromboembolic diseases. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2006;15:843–55.
Bauer KA. New anticoagulants: anti IIa vs anti Xa—is one better? J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2006;21:67–72.
Weitz J. Factor Xa or thrombin: is thrombin a better target? J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2007;5:65–7.
Alexander JH, Singh KP. Inhibition of factor Xa: a potential target for the development of new anticoagulants. J Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2005;5:279–90.
Connolly SJ, Eikelboom J, Joyner C, Diener HC, Hart R, Golitsyn S, Flaker G, Avezum A, Hohnloser SH, Diaz R, Talajic M, Zhu J, Pais P, Budaj A, Parkhomenko A, Jansky P, Commerford P, Tan RS, Sim KH, Lewis BS, Van Mieghem W, Lip GY, Kim JH, Lanas-Zanetti F, Gonzalez-Hermosillo A, Dans AL, Munawar M, O’Donnell M, Lawrence J, Lewis G, Afzal R, Yusuf S. Apixaban in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:806–17.
De Caterina R, Husted S, Wallentin L, Andreotti F, Arnesen H, Bachmann F, Baigent C, Huber K, Jespersen J, Kristensen SD, Lip GY, Morais J, Rasmussen LH, Siegbahn A, Verheugt FW, Weitz JI, Coordinating C. New oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation and acute coronary syndromes: ESC working group on thrombosis-task force on anticoagulants in heart disease position paper. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59:1413–25.
Schneeweiss S, Gagne JJ, Patrick AR, Choudhry NK, Avorn J. Comparative efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2012;5:480–6.
Bai Y, Deng H, Shantsila A, Lip GY. Rivaroxaban versus dabigatran or warfarin in real-world studies of stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2017;48:970–6.
Amin A, Keshishian A, Trocio J, Dina O, Le H, Rosenblatt L, Liu X, Mardekian J, Zhang Q, Baser O, Nadkarni A, Vo L. A real-world observational study of hospitalization and health care costs among nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients prescribed oral anticoagulants in the U.S. Medicare population. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018;24:911–20.
Kyriacou DN, Lewis RJ. Confounding by indication in clinical research. JAMA. 2016;316:1818–9.
Ellis MH, Neuman T, Bitterman H, Dotan SG, Hammerman A, Battat E, Eikelboom JW, Ginsberg JS, Hirsh J. Bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation treated with dabigatran, rivaroxaban or warfarin: a retrospective population-based cohort study. Eur J Intern Med. 2016;33:55–9.
Jiroutek MR, Turner JR. Relative vs absolute risk and odds: understanding the difference. J Clin Hypertens. 2019;21:859–61.
Proietti M, Romanazzi I, Romiti GF, Farcomeni A, Lip GYH. Real-world use of Apixaban for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2018;49:98–106.
Li G, Lip GYH, Holbrook A, Chang Y, Larsen TB, Sun X, Tang J, Mbuagbaw L, Witt DM, Crowther M, Thabane L, Levine MAH. Direct comparative effectiveness and safety between non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants for stroke prevention in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur J Epidemiol. 2019;34:173–90.
Gomez-Outes A, Lagunar-Ruiz J, Terleira-Fernandez AI, Calvo-Rojas G, Suarez-Gea ML, Vargas-Castrillon E. Causes of death in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:2508–21.
Lip GY, Larsen TB, Skjøth F, Rasmussen LH. Indirect comparisons of new oral anticoagulant drugs for efficacy and safety when used for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:738–46.
Fahrbach K. How similar is “Similar”? A deeper dive into Bucher versus Bayesian network meta-analysis. J Interview with Head of NICE Scientific Advice; 2018:15
Acknowledgement
We acknowledge Professor Gordon H Guyatt for his help with data analyses and discussions.
Funding
This study was funded by Science Foundation of Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital (Grant recipient: Dr. Guowei Li; Grant no. :YY2018–002), Doctoral Workstation Foundation of Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital (Grant recipient: Dr. Junguo Zhang; Grant no. :2021BSGZ007) and Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province of China (Grant recipient: Dr. Guowei Li; Grant no. :A2020453).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JZ, GL, XL and GYL designed research and generated study plan; JZ, XW and GL conducted the meta-analysis and drafted the manuscript; JZ, XW, TBL, DMW, and GL analyzed the data; JZ, XW, TBL, DMW, ZY, LT, GL and GYL revised the manuscript. GL and GYL had primary responsibility for final content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10654_2021_751_MOESM2_ESM.tiff
Supplementary Figure 2 Risk of bias graph - Methodological quality summary: review authors' judgments about each methodological quality item for each included RCTs (TIFF 678 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Wang, X., Liu, X. et al. Comparative effectiveness and safety of direct acting oral anticoagulants in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation for stroke prevention: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol 36, 793–812 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-021-00751-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-021-00751-7