Abstract
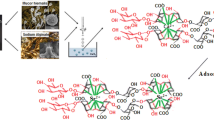
The residue derived from the alginate extraction from S. filipendula was applied for the biosorption of aluminum from aqueous medium. The adsorptive capacity of the residue (RES) was completely evaluated in batch mode. The effect of pH, contact time, initial concentration, and temperature was assessed through kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic studies. The biosorbent was characterized prior and post-Al biosorption by N2 physisorption, Hg porosimetry, He pycnometry, and thermogravimetry analyses. Equilibrium was achieved in 60 min. Kinetics obeys pseudo-second-order model at aluminum higher concentrations. Isotherms followed Freundlich model at low temperature (293.15 K) and D-R or Langmuir model at higher temperatures (303 and 313 K). Data modeling indicated the occurrence of both chemical and physical interactions in the aluminum adsorption mechanism using RES. The maximum adsorption capacity obtained was 1.431 mmol/g at 293 K. The biosorption showed a spontaneous, favorable, and exotherm character. A simplified batch design was performed, indicating that the residue is a viable biosorbent, achieving high percentages of removal using low biomass dosage.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal A, Upadhyay U, Sreedhar I, Singh SA, Patel CM (2020) A review on valorization of biomass in heavy metal removal from wastewater. J Water Process Eng 38:101602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101602
Akaike H (1998) Information theory and an extension of the maximum likelihood principle, pp 199–213
Aravindhan R, Rao JR, Nair BU (2007) Removal of basic yellow dye from aqueous solution by sorption on green alga Caulerpa scalpelliformis. J Hazard Mater 142:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.07.058
Ates N, Basak A (2021) Selective removal of aluminum, nickel and chromium ions by polymeric resins and natural zeolite from anodic plating wastewater. Int J Environ Health Res 31:102–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2019.1631263
Biswas B, Arun Kumar A, Bisht Y, Singh R, Kumar J, Bhaskar T (2017) Effects of temperature and solvent on hydrothermal liquefaction of Sargassum tenerrimum algae. Bioresour Technol 242:344–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.045
Boeris PS, Agustín M del R, Acevedo DF, Lucchesi GI (2016) Biosorption of aluminum through the use of non-viable biomass of Pseudomonas putida. J Biotechnol 236:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.07.026
Boyd GE, Adamson AW, Myers LS (1947) The exchange adsorption of ions from aqueous solutions by organic zeolites. II. Kinetics 1. J Am Chem Soc 69:2836–2848. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01203a066
Bulgariu L, Bulgariu D, Rusu C (2015) Marine algae biomass for removal of heavy metal ions. In: Hb25_Springer Handbook of Marine Biotechnology. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 611–648
Cardoso SL, Costa CSD, Nishikawa E, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2017) Biosorption of toxic metals using the alginate extraction residue from the brown algae Sargassum filipendula as a natural ion-exchanger. J Clean Prod 165:491–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.114
Cardoso SL, Costa CSD, Da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2020) Insight into zinc(II) biosorption on alginate extraction residue: kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics. J Environ Chem Eng 8:103629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103629
Cayllahua JEB, Torem ML (2010) Biosorption of aluminum ions onto Rhodococcus opacus from wastewaters. Chem Eng J 161:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.03.025
Chen JP, Wu S, Chong K-H (2003) Surface modification of a granular activated carbon by citric acid for enhancement of copper adsorption. Carbon N Y 41:1979–1986. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(03)00197-0
Chowdhury S, Mishra R, Saha P, Kushwaha P (2011) Adsorption thermodynamics, kinetics and isosteric heat of adsorption of malachite green onto chemically modified rice husk. Desalination 265:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.07.047
Coelho CM, de Andrade JR, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2020) Removal of propranolol hydrochloride by batch biosorption using remaining biomass of alginate extraction from Sargassum filipendula algae. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:16599–16611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08109-4
Costa CSD, Cardoso SL, Nishikawa E et al (2016) Characterization of the residue from double alginate extraction from Sargassum filipendula seaweed. Chem Eng Trans 52:133–138. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1652023
Costa CSD, Bertagnolli C, Boos A, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2020) Application of a dealginated seaweed derivative for the simultaneous metal ions removal from real and synthetic effluents. J Water Process Eng 37:37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101546
Costa HP d S, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2021) Biosorption of aluminum ions from aqueous solutions using non-conventional low-cost materials: a review. J Water Process Eng 40:101925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.101925
Daneshvar E, Vazirzadeh A, Niazi A, Sillanpää M, Bhatnagar A (2017) A comparative study of methylene blue biosorption using different modified brown, red and green macroalgae – effect of pretreatment. Chem Eng J 307:435–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.093
Davis TA, Volesky B, Mucci A (2003) A review of the biochemistry of heavy metal biosorption by brown algae. Water Res 37:4311–4330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00293-8
de Andrade JR, Oliveira MF, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2018) Adsorption of pharmaceuticals from water and wastewater using nonconventional low-cost materials: a review. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:3103–3127. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b05137
Dermience M, Lognay G, Mathieu F, Goyens P (2015) Effects of thirty elements on bone metabolism. J Trace Elem Med Biol 32:86–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2015.06.005
Djeribi R, Hamdaoui O (2008) Sorption of copper(II) from aqueous solutions by cedar sawdust and crushed brick. Desalination 225:95–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.04.091
Do Nascimento WJ, Landers R, Gurgel Carlos da Silva M, Vieira MGA (2021) Equilibrium and desorption studies of the competitive binary biosorption of silver(I) and copper(II) ions on brown algae waste. J Environ Chem Eng 9:104840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104840
Dubinin MM, Radushkevitch LV (1947) The equation of the characteristic curve of activated charcoal. Proc Acad Sci USSR:55
El Houda Larbi N, Merouani DR, Aguedal H et al (2019) Removal of heavy metals Cd(II) and Al(III) from aqueous solutions by an eco-friendly biosorbent. Key Eng Mater 800 KEM:181–186. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.800.181
Erbil HY (2009) Solid surfaces. In: Surface Chemistry of Solid and Liquid Interfaces. Blackwell Publishing, p 368
Farooq U, Kozinski JA, Khan MA, Athar M (2010) Biosorption of heavy metal ions using wheat based biosorbents - a review of the recent literature. Bioresour Technol 101:5043–5053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.030
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.013
Freda J (1991) The effects of aluminum and other metals on amphibians. Environ Pollut 71:305–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/0269-7491(91)90035-U
Freitas GR, Vieira MGA, Silva MGC (2017) Kinetic adsorption of copper ions by the residue of alginate extraction from the seaweed Sargassum filipendula. Chem Eng Trans 57:655–660. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1757110
Freitas GR, Vieira MGA, Da Silva MGC (2018) Batch and fixed bed biosorption of copper by acidified algae waste biomass. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:11767–11777. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b02541
Freitas GR, Vieira MGA, da Silva MGC (2019) Fixed bed biosorption of silver and investigation of functional groups on acidified biosorbent from algae biomass. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:36354–36366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06731-5
Freitas GR, Adeodato Vieira MG, Carlos da Silva MG (2020) Characterization and biosorption of silver by biomass waste from the alginate industry. J Clean Prod 271:122588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122588
Freundlich H (1907) Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Zeitschrift für Phys Chemie 57U. https://doi.org/10.1515/zpch-1907-5723
Gensemer RW, Playle RC (1999) The bioavailability and toxicity of aluminum in aquatic environments. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 29:315–450. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389991259245
Gibbs JW (1873) Graphical methods in the thermodynamics of fluids. Trans Connecticut Acad Arts Sci 2:309–342
Giles CH, MacEwan TH, Nakhwa SN, Smith D (1960) 786. Studies in adsorption. Part XI. A system of classification of solution adsorption isotherms, and its use in diagnosis of adsorption mechanisms and in measurement of specific surface areas of solids. J Chem Soc:3973. https://doi.org/10.1039/jr9600003973
Goher ME, Hassan AM, Abdel-Moniem IA, Fahmy AH, Abdo MH, el-sayed SM (2015) Removal of aluminum, iron and manganese ions from industrial wastes using granular activated carbon and Amberlite IR-120H. Egypt J Aquat Res 41:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2015.04.002
Halim AA, Ezani E, Othman MS et al (2012) Adsorption study of aluminium onto Curcuma longa. Nat Environ Pollut Technol 11:193–197
Hartzog DG, Sircar S (1995) Sensitivity of PSA process performance to input variables. Adsorption 1:133–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00705001
He J, Chen JP (2014) A comprehensive review on biosorption of heavy metals by algal biomass: materials, performances, chemistry, and modeling simulation tools. Bioresour Technol 160:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.01.068
Ho Y, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Irannajad M, Kamran Haghighi H (2021) Removal of heavy metals from polluted solutions by zeolitic adsorbents: a review. Environ Process 8:7–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-020-00476-x
Kalderis D, Bethanis S, Paraskeva P, Diamadopoulos E (2008) Production of activated carbon from bagasse and rice husk by a single-stage chemical activation method at low retention times. Bioresour Technol 99:6809–6816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.01.041
Krewski D, Yokel RA, Nieboer E, et al. (2007) KREWSKI, D. et al. Human health risk assessment for aluminium, aluminium oxide, and aluminium hydroxide. [s.l: s.n.]. v. 10Human Health Risk Assessment For Aluminium, Aluminium Oxide, and Aluminium Hydroxide
Lagergren S (1898) Zur theorie Der Sogenannten adsorption geloster stoffe, Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 24:1–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01501332
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02242a004
Lee HS, Suh JH, Kim IB, Yoon T (2004) Effect of aluminum in two-metal biosorption by an algal biosorbent. Miner Eng 17:487–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2004.01.002
Lobo-Recio MÁ, Rodrigues C, Custódio Jeremias T, Lapolli FR, Padilla I, López-Delgado A (2021) Highly efficient removal of aluminum, iron, and manganese ions using Linde type-A zeolite obtained from hazardous waste. Chemosphere 267:128919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128919
Lodeiro P, Gudiña Á, Herrero L, Herrero R, Sastre de Vicente ME (2010) Aluminium removal from wastewater by refused beach cast seaweed. Equilibrium and dynamic studies. J Hazard Mater 178:861–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.02.017
Mahdavi M, Ebrahimi A, Mahvi AH, Fatehizadeh A, Karakani F, Azarpira H (2018) Experimental data for aluminum removal from aqueous solution by raw and iron-modified granular activated carbon. Data Br 17:731–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2018.01.063
McHugh DJ (1987) FAO Fisheries Technical Paper 288. In: Chapter 2 - Prod. Prop. uses alginates. http://www.fao.org/3/x5822e04.htm#chapter
Merian E, Anke M, Ihnat M, Stoeppler M (2004) Elements and their compounds in the environment edited by related titles Joachim Nölte Bernhard Welz , Michael Sperling Handbook of Elemental Speciation Markus Stoeppler , Wayne R . Wolf , Peter J . Jenks (eds) Reference Materials for Chemical Analysis
Milonjic S (2007) A consideration of the correct calculation of thermodynamic parameters of adsorption. J Serbian Chem Soc 72:1363–1367. https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC0712363M
Moino BP, Costa CSD, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2017) Removal of nickel ions on residue of alginate extraction from Sargassum filipendula seaweed in packed bed. Can J Chem Eng 95:2120–2128. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.22859
Moino BP, Costa CSD, Carlos da Silva MG, Vieira MGA (2020) Reuse of the alginate extraction waste from Sargassum filipendula for Ni(II) biosorption. Chem Eng Commun 207:17–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2018.1564909
Naeemullah N, Tuzen M, Sari A, Mendil D (2017) Biosorption of aluminum from aqueous solutions by using macrofungus (Cortinarius armillatus): equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies and determination by GFAAS. At Spectrosc 38:149–157. https://doi.org/10.46770/as.2017.05.005
Nishikawa E, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2018) Cadmium biosorption by alginate extraction waste and process overview in life cycle assessment context. J Clean Prod 178:166–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.025
Otunola BO, Ololade OO (2020) A review on the application of clay minerals as heavy metal adsorbents for remediation purposes. Environ Technol Innov 18:100692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100692
Ozdemir G, Baysal SH (2004) Chromium and aluminum biosorption on Chryseomonas luteola TEM05. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:599–603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1479-0
Pagnanelli F (2011) Equilibrium, kinetic and dynamic modelling of biosorption processes. In: Microbial Biosorption of Metals. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 59–120
Puranik P, Modak J, Paknikar K (1999) A comparative study of the mass transfer kinetics of metal biosorption by microbial biomass. Hydrometallurgy 52:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-386X(99)00017-1
Rajamohan N, Rajasimman M, Rajeshkannan R, Saravanan V (2014) Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies on the removal of aluminum by modified Eucalyptus camaldulensis barks. Alexandria Eng J 53:409–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2014.01.007
Rosa LMT, Botero WG, Santos JCC, Cacuro TA, Waldman WR, do Carmo JB, de Oliveira LC (2018) Natural organic matter residue as a low cost adsorbent for aluminum. J Environ Manag 215:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.03.048
Ruthven DM (1984) Principles of adsorption and adsorption processes. Wiley
Saha P, Chowdhury S (2011) Insight into adsorption thermodynamics. In: Tadashi M (ed) Thermodynamics. InTech, pp 349–364
Santos NT d G, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2019) Development of novel sericin and alginate-based biosorbents for precious metal removal from wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:28455–28469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3378-z
Santos NT d G, Moraes LF, da Silva MGC, Vieira MGA (2020) Recovery of gold through adsorption onto sericin and alginate particles chemically crosslinked by proanthocyanidins. J Clean Prod 253:119925. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119925
Sari A, Tuzen M (2009) Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies on aluminum biosorption from aqueous solution by brown algae (Padina pavonica) biomass. J Hazard Mater 171:973–979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.101
Shaaban AESM, Badawy RK, Mansour HA, Abdel-Rahman ME, Aboulsoud YIE (2017) Competitive algal biosorption of Al3+, Fe3+, and Zn2+ and treatment application of some industrial effluents from Borg El-Arab region, Egypt. J Appl Phycol 29:3221–3234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-017-1185-4
Sing KSW (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl Chem 57:603–619. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac198557040603
Singh KK, Rastogi R, Hasan SH (2005) Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater using rice bran. J Colloid Interface Sci 290:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.04.011
Skibniewska E, Skibniewski M (2019) Aluminum, Al. In: Mammals and Birds as Bioindicators of Trace Element Contaminations in Terrestrial Environments. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 413–462
Soares S, Camino G, Levchik S (1995) Comparative study of the thermal decomposition of pure cellulose and pulp paper. Polym Degrad Stab 49:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-3910(95)87009-1
Soares JP, Santos JE, Chierice GO, Cavalheiro ETG (2004) Thermal behavior of alginic acid and its sodium salt. Eclética Química 29:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-46702004000200009
Sotirelis NP, Chrysikopoulos CV (2015) Interaction between graphene oxide nanoparticles and quartz sand. Environ Sci Technol 49:13413–13421. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b03496
Srivastava SK, Tyagi R, Pant N (1989) Adsorption of heavy metal ions on carbonaceous material developed from the waste slurry generated in local fertilizer plants. Water Res 23:1161–1165. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(89)90160-7
Stephens BR, Jolliff JS (2015) Aluminum and Alzheimer’s disease. Elsevier Inc.
Tassist A, Lounici H, Abdi N, Mameri N (2010) Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies on aluminum biosorption by a mycelial biomass (Streptomyces rimosus). J Hazard Mater 183:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.06.078
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark AV, Olivier JP, Rodriguez-Reinoso F, Rouquerol J, Sing KSW (2015) Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem 87:1051–1069. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
Titah HS, Purwanti IF, Tangahu BV, Kurniawan SB, Imron MF, Abdullah SRS, Ismail N‘I (2019) Kinetics of aluminium removal by locally isolated Brochothrix thermosphacta and Vibrio alginolyticus. J Environ Manag 238:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.03.011
U.S. Geological Survey (2020) Mineral commodity summaries - zeolites (natural)
Vijayaraghavan K, Gupta S, Joshi UM (2012) Comparative assessment of Al(III) and Cd(II) biosorption onto Turbinaria conoides in single and binary systems. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:2923–2931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1075-y
Wagenmakers E-J, Farrell S (2004) AIC model selection using Akaike weights. Psychon Bull Rev 11:192–196. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03206482
Walton JR (2011) Bioavailable aluminum: its metabolism and effects on the environment. In: Encyclopedia of Environmental Health. Elsevier, pp 343–352
Weber WJ, Morris CJ (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div 89:31–60
Young DM, Crowell AD (1962) Physical adsorption of gases. Butterworths, London
Yu LJ, Wang S, Jiang XM, Wang N, Zhang CQ (2008) Thermal analysis studies on combustion characteristics of seaweed. J Therm Anal Calorim 93:611–617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-007-8274-6
Yurtsever M, Nalçak M (2019) Al(III) removal from wastewater by natural clay and coconut shell. Glob Nest J 21:477–483. https://doi.org/10.30955/gnj.002566
Zhu B, Xia P, Ho W, Yu J (2015) Isoelectric point and adsorption activity of porous g-C3N4. Appl Surf Sci 344:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.03.086
Availability of data and material
Not applicable
Code availability
Not applicable.
Funding
The authors thank the Coordination Office for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), Brazilian Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) (Grant No. 308046/2019-6) and São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) (Grant No. 2017/18236-1 and 2019/11353-8) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Melissa Gurgel Adeodato Vieira
Literature search and data analysis: Heloisa Pereira de Sá Costa
Writing—original draft preparation: Heloisa Pereira de Sá Costa
Writing—review and editing: Melissa Gurgel Adeodato Vieira, Meuris Gurgel Carlos da Silva, and Heloisa Pereira de Sá Costa
Supervision: Melissa Gurgel Adeodato Vieira
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 289 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, H.P.d.S., da Silva, M.G.C. & Vieira, M.G.A. Application of alginate extraction residue for Al(III) ions biosorption: a complete batch system evaluation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 51826–51840 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14333-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14333-3