Abstract
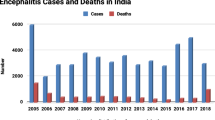
In 2019, the outbreak of Acute Encephalitis Syndrome (AES) outbreak occurred in the Bihar region of India. AES, a viral infection that affects the immune system of the human, is recognized as public health concern globally. The objective of this study is to monitor and prevent the spread of Encephalitis (ENCPH). Spatio-temporal-based Temporal-Recurrent Neural Network (T-RNN) prediction model is used to control the outbreak and generate an alarming signal to the medical caregiver in case of abnormality. T-RNN model is appended with novel Self-Organized Mapping (SOM) technique for outbreak visualization geographically. The current work presents a Tri-logical IoT-fog-cloud (TIFC) model to collect AES data for monitoring, and controlling the outbreak over the Spatio-temporal manner. Different events are correlated over the Spatio-temporal patterns in the form of a time-series granule at a different timestamps. Fuzzy C-Means (FCM) classifier is used to analyze the category of a patient based on health-related data parameters. Henceforth, for effective health-oriented decision-making and information deliverance to the user, a prediction model based on Spatio-temporal is used to manage the medical resources. For validation purposes, numerous simulations have been performed over real-data sets, and the results are compared with different state-of-the-art prediction models. Based on simulations, it can be concluded that the proposed system has outperformed other decision models in terms of statistical parameters including accuracy, f-measure, and reliability. Future research needs to focus on the security aspect for prevention and control for infectious viruses.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar R, Rajasekaran MP. An iot based patient monitoring system using raspberry pi. In 2016 International Conference on Computing Technologies and Intelligent Data Engineering (ICCTIDE’16), IEEE, 2016. p. 1–4.
Narain JP, Dhariwal A, MacIntyre CR. Acute encephalitis in india: An unfolding tragedy. Indian J Med Res. 2017;145(5):584.
Ashton K, et al. That internet of things thing. RFID journal. 2009;22(7):97–114.
Hussain M, Al-Haiqi A, Zaidan AA, Zaidan BB, Kiah M, Iqbal S, Iqbal S, Abdulnabi M. A security framework for mhealth apps on android platform. Comput Secur. 2018;75:191–21717.
Turtle L, Solomon T. Japanese encephalitis–the prospects for new treatments. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018;14(5):298.
Deshkar S, Thanseeh R, Menon VG. A review on iot based m-health systems for diabetes. Int J Comput Sci Telecommun. 2017;8(1):13–8.
Manocha A, Singh R, Bhatia M. Cognitive intelligence assisted fog-cloud architecture for generalized anxiety disorder (gad) prediction. J Med Syst. 2020;44(1):7.
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature. 2015;521(7553):436–44.
Vijayakumar V, Malathi D, Subramaniyaswamy V, Saravanan P, Logesh R. Fog computing-based intelligent healthcare system for the detection and prevention of mosquito-borne diseases. Comput Human Behav. 2019;100:275–85.
Kennedy PG, Quan P-L, Lipkin WI. Viral encephalitis of unknown cause: current perspective and recent advances. Viruses. 2017;9(6):138.
Vogrig A, Joubert B, André-Obadia N, Gigli GL, Rheims S, Honnorat J. Seizure specificities in patients with antibody-mediated autoimmune encephalitis. Epilepsia. 2019;60(8):1508–25.
Griffiths MJ, Turtle L, Solomon T. Japanese encephalitis virus infection. In Handbook of clinical neurology, volume 123, pages 561–576. Elsevier, 2014.
Sukhralia S, Verma M, Gopirajan S, Dhanaraj P, Lal R, Mehla N, Kant CR. From dengue to zika: The wide spread of mosquito-borne arboviruses. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019;38(1):3–14.
Kaewpoowat Q, Aurpibul L, Chaiwarith R. Challenges in the management and prevention of japanese encephalitis. In Meningitis and Encephalitis. Springer, 2018. p. 153–174.
Sood SK, Mahajan I. Wearable iot sensor based healthcare system for identifying and controlling chikungunya virus. Comput Ind. 2017;91:33–44.
Bhatia M, Sood SK. A comprehensive health assessment framework to facilitate iot-assisted smart workouts: A predictive healthcare perspective. Comput Ind. 2017;92:50–66.
Vani K, Neeralagi RR. Iot based health monitoring using fuzzy logic. Int J Comput Intell Res. 2017;13(10):2419–29.
Verma P, Sood SK. Cloud-centric iot based disease diagnosis healthcare framework. J Parallel Distrib Comput. 2018;116:27–38.
Bhatia M, Kaur S, Sood SK. Iot-inspired smart toilet system for home-based urine infection prediction. ACM Trans Comput Healthc.
Sood SK, Mahajan I. Fog-cloud based cyber-physical system for distinguishing, detecting and preventing mosquito borne diseases. Future Gener Comput Syst. 2018;88:764–75.
Sareen S, Sood SK, Gupta SK. Iot-based cloud framework to control ebola virus outbreak. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. 2018;9(3):459–76.
Tuli S, Basumatary N, Gill SS, Kahani M, Arya RC, Wander GS, Buyya R. Healthfog: An ensemble deep learning based smart healthcare system for automatic diagnosis of heart diseases in integrated iot and fog computing environments. Future Gener Comput Syst. 2020;104:187–200.
Yuan Y, Xiong Z, Wang Q. An incremental framework for video-based traffic sign detection, tracking, and recognition. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst. 2017;18(7).
Yuan Y, Lu Y, Wang Q. Tracking as a whole: Multi-target tracking by modeling group behavior with sequential detection. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst. 2017;18(12):3339–49.
Durga S, Nag R, Daniel E. Survey on machine learning and deep learning algorithms used in internet of things (iot) healthcare. In 2019 3rd International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC). IEEE, 2019. p. 1018–1022.
Ashmore P, Lindahl JF, Colón-González FJ, Sinh Nam V, Quang Tan D, Medley GF. Spatiotemporal and socioeconomic risk factors for dengue at the province level in vietnam, 2013–2015: Clustering analysis and regression model. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2020;5(2):81.
Haddawy P, Hasan AI, Kasantikul R, Lawpoolsri S, Sa-angchai P, Kaewkungwal J, Singhasivanon P. Spatiotemporal bayesian networks for malaria prediction. Artif Intell Med. 2018;84:127–38.
Atluri G, Karpatne A, Kumar V. Spatio-temporal data mining: A survey of problems and methods. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR). 2018;51(4):1–41.
Kupilik M, Witmer F. Spatio-temporal violent event prediction using gaussian process regression. J Comput Soc Sci. 2018;1(2):437–51.
Aguayo L, Barreto GA. Novelty detection in time series using self-organizing neural networks: a comprehensive evaluation. Neural Process Lett. 2018;47(2):717–44.
López Medina MÁ, Espinilla M, Paggeti C, Medina Quero J. Activity recognition for iot devices using fuzzy spatio-temporal features as environmental sensor fusion. Sensors. 2019;19(16):3512.
Abi Nader C, Ayache N, Robert P, Lorenzi M et al. Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Monotonic gaussian process for spatio-temporal disease progression modeling in brain imaging data. NeuroImage. 2020;205:116266.
Thway AM, Rotejanaprasert C, Sattabongkot J, Lawawirojwong S, Thi A, Hlaing TM, Soe TM, Kaewkungwal J. Bayesian spatiotemporal analysis of malaria infection along an international border: Hlaingbwe township in myanmar and tha-song-yang district in thailand. Malar J. 2018;17(1):428.
Zhu H, Zhao H, Ou R, Xiang H, Hu L, Jing D, Sharma M, Ye M. Epidemiological characteristics and spatiotemporal analysis of mumps from 2004 to 2018 in chongqing, china. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(17):3052.
Ma C-Y, Chen M-H, Kira Z, AlRegib G. Ts-lstm and temporal-inception: Exploiting spatiotemporal dynamics for activity recognition. Signal Process Image Commun. 2019;71:76–877.
Nalluri MR, Roy DS, et al. Hybrid disease diagnosis using multiobjective optimization with evolutionary parameter optimization. J Healthc Eng. 2017.
Salehinejad H, Sankar S, Barfett J, Colak E, Valaee S. Recent advances in recurrent neural networks. arXiv preprint 2017. arXiv:1801.01078
Asadi R, Regan A. A convolution recurrent autoencoder for spatio-temporal missing data imputation. arXiv preprint 2019. arXiv:1904.12413
Bhatia M, Sood SK. Exploring temporal analytics in fog-cloud architecture for smart office healthcare. Mob Netw Appl. 2019;24(4):1392–410.
Mutheneni SR, Mopuri R, Naish S, Gunti D, Upadhyayula SM. Spatial distribution and cluster analysis of dengue using self organizing maps in andhra pradesh, india, 2011–2013. Parasite Epidemiol Control. 2018;3(1):52–61.
Devarajan M, Subramaniyaswamy V, Vijayakumar V, Ravi L. Fog-assisted personalized healthcare-support system for remote patients with diabetes. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. 2019;10(10):3747–60.
Shang J, Li S, Huang J. A robust fuzzy local information c-means clustering algorithm with noise detection. In Ninth International Conference on Graphic and Image Processing (ICGIP 2017). International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2018. volume 10615, page 106151Z.
Manogaran G, Lopez D. A gaussian process based big data processing framework in cluster computing environment. Cluster Comput. 2018;21(1):189–204.
Usama M, Ahmad B, Wan J, Hossain MS, Alhamid MF, Hossain MA. Deep feature learning for disease risk assessment based on convolutional neural network with intra-layer recurrent connection by using hospital big data. IEEE Access. 2018;6:67927–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatia, M., Kumari, S. A Novel IoT-Fog-Cloud-based Healthcare System for Monitoring and Preventing Encephalitis. Cogn Comput 14, 1609–1626 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-021-09856-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-021-09856-3